Introduction
The role of iron in human health
Iron-rich foods
Iron content of selected foods
Health benefits of iron
Recommended intake and deficiency risks
Safety and excess intake
Conclusions
References
Further reading
Iron-rich meals, paired with vitamin C and sensible supplementation, can forestall iron deficiency anemia whereas supporting power metabolism, mind perform, and immunity throughout the lifespan. Balanced consumption issues: too little impairs cognition and efficiency, whereas extra raises oxidative stress and organ threat.
 Picture Credit score: Corona Borealis Studio / Shutterstock.com
Picture Credit score: Corona Borealis Studio / Shutterstock.com
Introduction
Iron deficiency stays one of the vital widespread dietary challenges, affecting roughly 1.6 billion individuals, or practically one-third of the worldwide inhabitants, who’re anemic, mostly attributable to iron deficiency. Ladies of reproductive age, pregnant moms, and younger youngsters are notably weak to iron deficiency.1,2
Iron supplementation and fortification can assist handle deficiencies; nevertheless, these approaches can also trigger negative effects or have restricted long-term advantages. Incorporating iron-rich meals into on a regular basis meals stays the simplest, sensible, and financial technique to forestall deficiency, improve power, help blood well being, and improve mind perform.3,7
The function of iron in human well being
Roughly 65% of whole iron is current in hemoglobin, the protein in purple blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues. A smaller fraction of iron is certain to myoglobin for storing oxygen in muscle tissues, together with these concerned in mind and coronary heart features.9
Hemoglobin ensures optimum oxygen supply to all organs, whereas myoglobin offers oxygen throughout muscle contraction and metabolic load. Insufficient iron ranges impair hemoglobin manufacturing, which reduces oxygen supply and results in iron-deficiency anemia (IDA).3,4
Inside the mitochondria, iron is crucial for the electron transport chain (ETC), a course of that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Iron–sulfur (Fe-S) clusters and heme teams inside these pathways facilitate environment friendly respiration. Nevertheless, iron deficiency disrupts this technique to trigger fatigue and impaired mobile metabolism, whereas extra iron can contribute to oxidative stress induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS).2,4
Throughout early growth, iron helps neuronal proliferation, myelination, and neurotransmitter synthesis, performing as a cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), monoamine oxidase (MAO), and tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH). Deficiency in the course of the preliminary 1,000 days of life may cause long-term deficits in cognitive, attentional, and social-emotional functioning.4 Low mind iron content material may worsen cognitive efficiency in wholesome younger people.5
Conversely, dysregulated mind iron accumulation in growing older can lead to neurodegenerative issues, together with Alzheimer’s illness (AD) and Parkinson’s illness (PD). Thus, balanced iron homeostasis is important for sustaining progress, metabolic effectivity, and cognitive integrity all through the lifespan.4
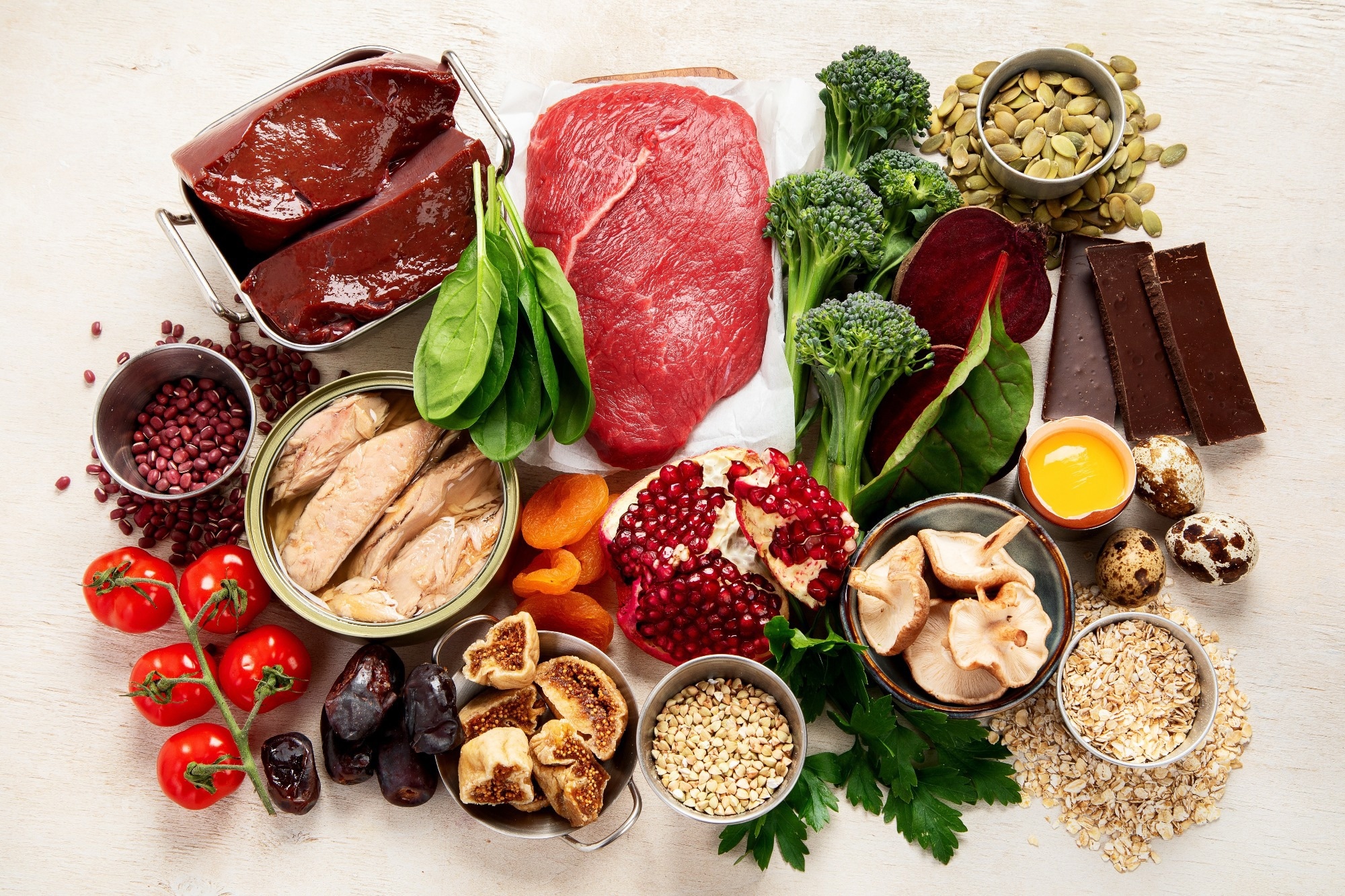
Iron-rich meals
Dietary iron exists in two kinds: heme and non-heme iron. Heme iron, which is current in animal-based meals like purple meat, poultry, fish, shellfish, and organ meats, is very bioavailable, as it’s absorbed instantly within the ferrous kind.9
Cooking preserves the heme iron content material, with beef retaining the very best ranges, starting from 1.1 to 2.6 mg/100 g, adopted by pork, fish, and hen at 0.3–0.6 mg/100 g, 0.5 mg/100 g, and 0.2–0.5 mg/100 g, respectively. Greater consumption of heme iron is related to a decreased threat of anemia.3
Non-heme iron in plant-based meals considerably contributes to dietary consumption; nevertheless, it’s much less effectively absorbed and should be decreased from ferric to ferrous kinds. Wealthy plant-based sources of iron embrace lentils (6.6 mg), tofu (3.5 mg), spinach (6.4 mg), kidney beans (5.2 mg), soybeans (4.5 mg), fortified cereals and breads, quinoa (2.8 mg), and peas (2.5 mg).3,6,9 Millets (e.g., pearl and finger millet) usually present ~2–8 mg iron per 100 g and have been proven in human interventions to enhance hemoglobin and ferritin ranges.10
Consuming iron alongside meals wealthy in ascorbic acid, equivalent to citrus fruits, peppers, or strawberries, can improve absorption. Ascorbic acid improves solubility, reduces ferric to ferrous kinds, and chelates iron. These processes reduce iron binding to phytates in grains and legumes, tannins in tea and occasional, and calcium, which inhibit non-heme iron absorption by forming insoluble complexes.3,7,9
 Picture Credit score: Tatjana Baibakova / Shutterstock.com
Picture Credit score: Tatjana Baibakova / Shutterstock.com
Iron content material of chosen meals
| Meals | Milligrams (mg) per serving | P.c Each day Worth |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast cereals, fortified with 100% of the DV for iron, 1 serving | 18 | 100 |
| Oysters, jap, cooked with moist warmth, 3 ounces | 8 | 44 |
| White beans, canned, 1 cup | 8 | 44 |
| Beef liver, pan fried, 3 ounces | 5 | 28 |
| Lentils, boiled and drained, ½ cup | 3 | 17 |
| Spinach, boiled and drained, ½ cup | 3 | 17 |
| Tofu, agency, ½ cup | 3 | 17 |
| Chocolate, darkish, 45%–69% cacao solids, 1 ounce | 2 | 11 |
| Kidney beans, canned, ½ cup | 2 | 11 |
| Sardines, Atlantic, canned in oil, drained solids with bone, 3 ounces | 2 | 11 |
| Chickpeas, boiled and drained, ½ cup | 2 | 11 |
| Tomatoes, canned, stewed, ½ cup | 2 | 11 |
| Beef, braised backside spherical, with fats trimmed, 3 ounces | 2 | 11 |
| Potato, baked, flesh and pores and skin, 1 medium potato | 2 | 11 |
| Cashew nuts, oil roasted, 1 ounce (18 nuts) | 2 | 11 |
| Inexperienced peas, boiled, ½ cup | 1 | 6 |
| Hen, roasted, meat and pores and skin, 3 ounces | 1 | 6 |
| Rice, white, lengthy grain, enriched, parboiled, drained, ½ cup | 1 | 6 |
| Bread, complete wheat, 1 slice | 1 | 6 |
| Bread, white, 1 slice | 1 | 6 |
| Raisins, seedless, ¼ cup | 1 | 6 |
| Spaghetti, complete wheat, cooked, 1 cup | 1 | 6 |
| Tuna, gentle, canned in water, 3 ounces | 1 | 6 |
| Turkey, roasted, breast meat and pores and skin, 3 ounces | 1 | 6 |
| Nuts, pistachio, dry roasted, 1 ounce (49 nuts) | 1 | 6 |
| Broccoli, boiled and drained, ½ cup | 1 | 6 |
| Egg, arduous boiled, 1 giant | 1 | 6 |
| Rice, brown, lengthy or medium grain, cooked, 1 cup | 1 | 6 |
| Cheese, cheddar, 1.5 ounces | 0 | 0 |
| Cantaloupe, diced, ½ cup | 0 | 0 |
| Mushrooms, white, sliced and stir-fried, ½ cup | 0 | 0 |
| Cheese, cottage, 2% milk fats, ½ cup | 0 | 0 |
| Milk, 1 cup | 0 | 0 |
What does %DV imply? % Each day Worth (%DV) signifies the share of iron a serving of meals contributes towards the really useful each day consumption for many adults. For instance, if a meals has 20% DV iron, it offers you about one-fifth of your each day iron wants.
Well being advantages of iron
Along with the ETC, iron additionally helps the citric acid cycle as a cofactor in mitochondrial enzymes to additional improve ATP manufacturing. Insufficient iron disrupts these processes, thereby lowering power availability, which manifests as fatigue, weak spot, and impaired bodily efficiency.2
As a key part of hemoglobin and myoglobin, iron allows environment friendly oxygen transport and storage. Oxygen supply ensures wholesome purple blood cell manufacturing and performance; thus, with out ample iron, the physique can not produce sufficient hemoglobin, leading to IDA and weak spot.1
Iron may be neurotrophic, because it helps neuronal growth by rising the degrees of neurotransmitters equivalent to dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, which affect reminiscence, studying, and temper.4
Iron deficiency impairs neurodevelopment throughout early childhood and contributes to cognitive and temper disturbances amongst older adults. For instance, in a research of 162 community-dwelling older adults, decrease iron standing was related to extra depressive temper, useful fatigue, and decreased reminiscence capacity, moderated by dietary standing.8
Iron additionally regulates lymphocyte proliferation, macrophage exercise, and cytokine signaling. Due to this fact, dysregulation can impair host protection and improve susceptibility to infections and inflammatory illnesses.2
Iron displays thermoregulatory results by supporting the synthesis of thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), in addition to mitochondrial power manufacturing, each of which contribute to basal metabolic charge and warmth era. Iron additionally regulates non-shivering thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue by uncoupling proteins (UCPs), which launch power as warmth. Iron deficiency impairs these processes, resulting in chilly intolerance and altered vasomotor responses.2
Beneficial consumption and deficiency dangers
In line with the World Well being Group (WHO), pregnant ladies residing in areas with a 20% or increased prevalence of anemia amongst ladies of reproductive age ought to obtain 30–60 mg of elemental iron each day, together with 400 μg of folic acid. Menstruating ladies in these areas are additionally suggested to take 60 mg of elemental iron and a couple of,800 μg of folic acid weekly for 3 months, adopted by a three-month break earlier than repeating the cycle.1
The place anemia prevalence amongst menstruating ladies and adolescent women exceeds 40%, each day supplementation of 30–60 mg of elemental iron is really useful, with pregnant ladies requiring increased doses.1
In populations with a excessive anemia burden of over 40%, the WHO recommends that infants and toddlers obtain 10–12.5 mg of elemental iron each day for 3 consecutive months every year. Preschool youngsters between 24 and 59 months of age are suggested to devour 30 mg of iron each day, whereas school-aged youngsters between 5 and 12 years of age might require 30–60 mg each day.1
In line with america Nationwide Institutes of Well being (NIH), the really useful dietary allowance (RDA) for adults aged 19–50 years is 8.0 mg/day for males and 18 mg/day for girls. Throughout being pregnant and lactation, each day iron necessities improve to 27 mg/day and 10 mg/day, respectively.9
For adults 51 years of age and older, the RDA is 8 mg each day for each sexes. Throughout infancy, the RDA for iron is 0.27 mg/day from delivery to 6 months of age, with this dose rising to 11 mg/day by seven months of age. Between the ages of 1 and three, toddlers are suggested to devour 7 mg/day, whereas youngsters between 4 and eight years of age require 10 mg/day.9
Youngsters between the ages of 9 and 13 years are suggested to devour 8 mg/day. Comparatively, the RDA for iron throughout adolescence is 11 mg/day and 15 mg/day for men and women, respectively.9
IDA is the most typical dietary deficiency worldwide. The WHO estimates that anemia impacts roughly 37% of pregnant ladies globally, with prevalence notably excessive in low- and middle-income international locations, the place staples equivalent to wheat, rice, and maize, that are low in iron, dominate diets, and entry to bioavailable heme iron is proscribed.1,10
Signs of IDA embrace persistent fatigue, exhaustion, pallor, brittle nails, complications, impaired focus, and diminished work capability. Excessive-risk teams embrace ladies of reproductive age, pregnant ladies, infants, frequent blood donors, and vegetarians/vegans. With out ample iron consumption, the chance of impaired progress, cognitive deficits, and opposed being pregnant outcomes considerably will increase.1,6
Security and extra consumption
Hereditary hemochromatosis, a genetic dysfunction affecting one in each 200–300 people of European descent, is characterised by extreme iron absorption and progressive accumulation in organs such because the liver, coronary heart, and pancreas. If left untreated, hemochromatosis can result in cirrhosis, diabetes, cardiomyopathy, arthritis, and elevated most cancers threat.2
Secondary iron overload can also happen in transfusion-dependent circumstances equivalent to thalassemia and sickle cell illness, thereby contributing to excessive morbidity and mortality in these affected person populations.1
On the molecular stage, extra iron catalyzes ROS formation by the Fenton response to provide hydroxyl radicals that harm lipids, proteins, and DNA. This oxidative stress contributes to organ damage, neurodegenerative circumstances, cardiovascular illnesses, and most cancers.2,4
As a result of increased single doses can acutely increase hepcidin and cut back subsequent absorption, alternate-day morning dosing of ~60–120 mg elemental iron (with ascorbic acid) might optimize fractional absorption and reduce negative effects in iron-deficient ladies.7
10 Iron Wealthy Meals (Say GOODBYE to Fatigue!)
Conclusions
Iron regulates power metabolism, blood well being, and mind perform, with imbalances affecting practically each organ system. Though iron deficiency contributes to anemia, fatigue, and cognitive delays, the overload of this aspect may cause organ harm and speed up neurodegenerative illness.2,4
Dietary methods that mix heme sources, equivalent to lean meats, with non-heme sources like legumes, grains, leafy greens, and millets, together with enhancers like vitamin C, can be utilized to enhance iron absorption. Total, selling balanced, evidence-based vitamin is the simplest method to forestall each deficiency and overload, safeguarding lifelong well being.10
References
- “Anaemia.” [Online]. Obtainable from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/anaemia
- Obeagu, E. I. (2025). Iron homeostasis and well being: understanding its function past blood well being – a story evaluate. Annals of Drugs & Surgical procedure, 87(6):3362-3371. DOI:10.1097/MS9.0000000000003100, https://journals.lww.com/annals-of-medicine-and-surgery/fulltext/2025/06000/iron_homeostasis_and_health__understanding_its.42.aspx?context=latestarticles
- Man, Y., Xu, T., Adhikari, B., et al. (2021). Iron supplementation and iron-fortified meals: a evaluate. Crucial Evaluations in Meals Science and Vitamin 62(16):4504–4525. DOI:10.1080/10408398.2021.1876623, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10408398.2021.1876623
- Gao, Q., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2025). Function of iron in mind growth, growing older, and neurodegenerative illnesses. Annals of Drugs 57(1). DOI:10.1080/07853890.2025.2472871, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/07853890.2025.2472871
- Larsen, B., Bourque, J., Moore, T. M., et al. (2020). Longitudinal growth of mind iron is linked to cognition in youth. The Journal of Neuroscience 40(9):1810–1818. DOI:10.1523/jneurosci.2434-19.2020, https://www.jneurosci.org/content/40/9/1810.long
- Esquivel, M. Okay. (2022). Vitamin Advantages and Concerns for Complete Meals Plant-Primarily based Consuming Patterns. American Journal of Life-style Drugs 16(3); 284. DOI:10.1177/15598276221075992, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/15598276221075992
- Stoffel, N. U., Von Siebenthal, H. Okay., Moretti, D., & Zimmermann, M. B. (2020). Oral iron supplementation in iron-deficient ladies: How a lot and the way usually? Molecular Points of Drugs 75; 100865. DOI:10.1016/j.mam.2020.100865, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098299720300364
- Castanho, T. C., Amorim, L., et al. (2020). Iron Standing is Related to Temper, Cognition, and Useful Capacity in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Research. Vitamins, 12(11):3594. DOI:10.3390/nu12113594, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/11/3594
- “Iron” [Online]. Obtainable from: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/.
- Anitha, S., Kane-Potaka, J., Botha, R., et al. (2021). Millets Can Have a Main Impression on Bettering Iron Standing, Hemoglobin Degree, and Lowering Iron Deficiency Anemia–A Systematic Evaluate and Meta-Evaluation. Frontiers in Vitamin 8; 725529. DOI:10.3389/fnut.2021.725529, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.725529/full
Additional Studying
Final Up to date: Sep 29, 2025

