Ever marvel why urine is yellow or why pores and skin appears to be like yellow in individuals with jaundice? Scientists have identified for greater than a century that urobilin is the chemical accountable for that yellow shade. However the enzyme accountable for making urobilin was a thriller…till not too long ago. Researchers on the Nationwide Library of Medication (NLM) found the answer in an surprising place: the intestine microbiome. Their findings may also help us higher perceive sure well being circumstances, how our our bodies work, and why some infants get jaundice.
Why does urine look yellow?
When your physique replaces outdated purple blood cells, it creates bilirubin. This substance then strikes to your intestine, the place it both will get absorbed again into the bloodstream or is damaged down right into a chemical known as urobilinogen. Your kidneys then flip urobilinogen into urobilin—this makes your urine yellow.
Whereas researchers knew about this course of, one piece of the puzzle was nonetheless lacking: What causes bilirubin to interrupt down into urobilinogen? However researchers at NLM and the College of Maryland Corridor Lab not too long ago discovered the lacking puzzle piece—a key enzyme known as bilirubin reductase.
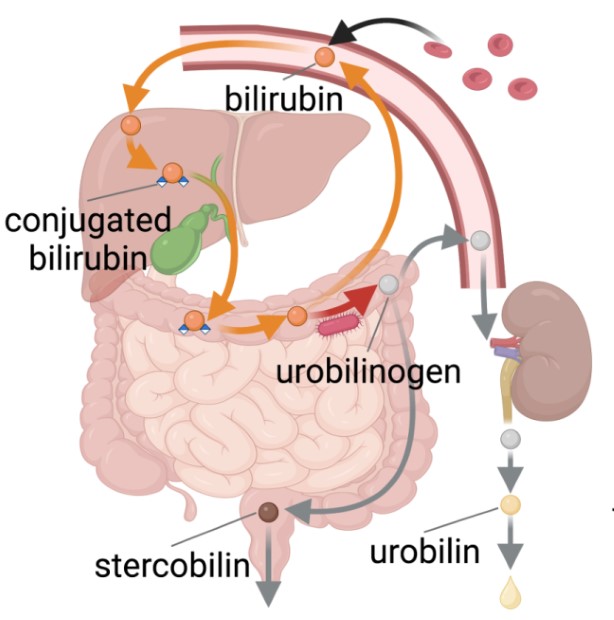
When the physique breaks down purple blood cells, bilirubin is produced. Bilirubin strikes to the intestine, the place it’s both absorbed into the blood once more or was urobilinogen. This urobilinogen is distributed to the kidneys and transformed to the waste product urobilin, which makes urine yellow.
How did researchers uncover this?
Their first step was to discover a group of micro organism that might scale back bilirubin. Many intestine micro organism want low-oxygen environments to outlive. That is laborious to do in a lab setting, so the scientists additionally used laptop experiments to have a look at the genomes of a number of micro organism at a time. A genome is your entire set of DNA directions present in a cell. is your entire set of DNA directions present in a cell.
Then from the bacterial genomes, researchers waded by way of all that bacterial information to search out the gene that encoded the enzyme that breaks down bilirubin.
“We had been capable of affirm their features after which have a look at larger image developments, like the connection of that gene to completely different sorts of illnesses,” mentioned Keith Dufault-Thompson, Ph.D., a workers scientist in NLM’s Division of Intramural Analysis (DIR).
Why does this analysis matter?
More often than not, our our bodies break down bilirubin on daily basis with none points. However when one thing goes flawed, bilirubin can construct up within the blood. This could result in well being issues equivalent to jaundice, during which your pores and skin and the whites of your eyes flip yellow. Jaundice is frequent in infants and folks with liver illness. It will possibly result in ache, fevers, listening to loss, and even mind harm in extreme instances.
Researchers wished to see how the bilirubin reductase enzyme impacts our well being. After their discovery, they analyzed information from previous research on the intestine microbiome (the ecosystem of micro organism and different microbes that stay within the intestines). They took genetic samples from the microbiomes of wholesome adults, younger infants, and sufferers with inflammatory bowel illness (IBD) and looked for the gene that produces bilirubin reductase. Xiaofang Jiang, Ph.D., a principal investigator within the NLM DIR, and her crew discovered that about 70% of infants don’t have the bacterial gene key to producing bilirubin reductase of their first month of life. This will likely clarify why jaundice impacts many newborns—their intestine microbiomes aren’t as developed. The examine additionally confirmed that greater than 30% of adults with IBD don’t have the bacterial gene current, both.
This new analysis might result in higher outcomes for infants and different individuals with these circumstances. It will possibly additionally train us extra in regards to the intestine microbiome’s function in total human well being.
What’s subsequent for this analysis?
Because the bilirubin reductase discovery, the analysis crew went again to have a look at earlier information on intestine microbiomes. They wish to see how the enzyme developed within the intestine setting.
Dr. Dufault-Thompson mentioned this work might assist us perceive bilirubin-reducing micro organism and pave the way in which for brand new therapies. Because of this examine, the crew can be taught extra about what sort of features intestine micro organism can do and the way they have an effect on our our bodies. These embrace how microbes metabolize (break down) synthetic sweeteners and various kinds of hormones.
“These tasks have helped us broaden our understanding of the impression of microbes on human well being and display the big selection of features that our microbiomes perform,” he mentioned.
*This text was tailored from the NLM Director’s Musings from the Mezzanine weblog. Learn the original article to be taught extra about this examine and the researchers behind it.