Problem #1: Analysis collaborations
A number of research offered empirical proof of a pointy decline in analysis productiveness over the primary 20 years of the 21st century, regardless of a rise within the variety of researchers (see Bloom et al., 2020 and the literature mentioned therein). There look like many causes for this, together with challenges in coordination and communication throughout numerous fields. From a sensible perspective, one attainable answer can be to encourage the formation of nationwide and worldwide analysis infrastructures (RIs) to learn from economies of scale.
However are these coalitions fascinating within the first place? And if that’s the case, how ought to they perform? Our first problem lies in establishing coordination mechanisms that allow them to be possible and efficient.
Inside particular areas of primary analysis, possible coalitions may take the type of what we name “digital labs”. Digital labs include distributed groups of researchers and technicians who work remotely on numerous parts of a given drawback, integrating their work by means of digital or in-person workshops.
Digital labs supply the potential to beat communication boundaries by using technological options that assist kind analysis communities.Footnote 2 In these communities, groups can uncover others working in associated, adjoining, and even seemingly unrelated areas, and who could possess the abilities and experience to fill key gaps of their analysis agenda. This flexibility is especially priceless in rising fields, the place the necessity for cross-disciplinary experience could solely turn into obvious as analysis progresses. As an example, “science of science” research that discover previous relational buildings between scientists or scientific disciplines may yield insights into the origins of scientific discovery (Fortunato et al., 2018) or assist goal particular scientific goals.
As mentioned in Appendix A, digital labs, when mixed with bodily labs, can speed up and improve scientific collaborations within the type of enhanced RIs, fostering extra environment friendly cross-disciplinary analysis networks.
Problem #2: Governance and regulation
Correct governance, well-designed incentives, and the allocation of possession rights are important for the profitable creation of latest mental property by means of joint efforts among the many individuals of a enterprise (Lerner and Wulf, 2007; Tian and Twite, 2011). It’s important that particular person contributors and organizations handle the sharing of knowledge successfully by means of collaborative agreements that deal with each scientific and enterprise objectives.
Regulatory our bodies may also have alternatives to rethink the necessities and restrictions they’ve established for numerous types of analysis and subsequent commercialization. Importantly, whereas these protocols form the frameworks used for translational science in most domains, a lot of them are nonetheless comparatively new.
To be clear, what we’re suggesting is that researchers from trade, authorities and the personal sector would profit from managed, generally coordinated, appeals for extra eyes or minds on particular facets of attention-grabbing issues, together with assurances that their contributions will likely be acknowledged and rewarded. It stays an open (and empirical) query whether or not this strategy can be greatest achieved by means of consortia, collectively funded analysis initiatives, a market for experience and information, or another kind.
On this regard, the regulator’s problem of balancing the safety of mental property rights (IPR) with the era of constructive externalities from Open Science represents a fancy panorama of trade-offs. On the one hand, IPR safety can stimulate innovation by granting creators unique management over their work, permitting them to get well their investments and generate monetary returns. Then again, overly restrictive IPR regimes can hinder the dissemination of information, restrict collaboration, and delay follow-on innovation. Fairly the other, Open Science approaches, which emphasize openness, transparency, and sharing of analysis outcomes, can speed up scientific progress, promote collaboration, and drive societal affect, at the price of undermining personal innovation incentives.
An environment friendly and efficient analysis ecosystem must stability the rights of creators with the advantages of openness and sharing, notably in areas resembling information sharing, open entry publishing, and collaborative analysis. Versatile licensing fashions, resembling open licenses and Inventive Commons licenses, might help obtain this stability by permitting for the free use and reuse of analysis outputs whereas nonetheless offering safety for mental property (see European Fee, 2022). Open Science can complement IPR safety by selling the event of latest concepts and improvements. A balanced strategy to IPR safety and Open Science can foster a analysis surroundings that encourages collaboration, accelerates scientific breakthroughs, and finally advantages society as an entire (Crouzier, 2017).
Problem #3: Accelerating funding
Though funding is commonly mentioned as the first problem to enabling SIT (or “long-shot”) investments, it’s mockingly the one for which we already appear to have a few of the most well-developed options. We describe SIT investments as “lengthy pictures” within the sense of Hull et al. (2019), as they function the next traits: (a) a really low chance of success; (b) a very long time horizon; (c) substantial upfront capital necessities; however which additionally get pleasure from (d) extraordinary industrial returns upon success. Conversely, we confer with scientific investments that provide no direct financial returns and lack speedy sensible purposes—pushed purely by a elementary curiosity to uncover the universe’s underlying truths—as “blue-sky” analysis.
Science-focused funding automobiles can probably mitigate long-shot and blue-sky analysis issues by using outcomes from fashionable portfolio principle. This strategy offers steering on structuring funding portfolios to cut back volatility (danger) whereas sustaining engaging return profiles relative to particular person investments within the quick and the long term.
On this regard, current work by monetary economists has demonstrated that risk-pooling buildings can function the idea for efficient funding automobiles that present longer-term capital for analysis, whereas delivering aggressive market-rate returns for buyers. Most notably, a brand new class of spinoff securities often known as Analysis-Backed Obligations (RBOs)—particularly, debt and fairness securities backed by the pool of underlying drug property issued by ‘mega-funds’ to lift capital and finance the event of pipeline medicine in its portfolio—are designed to fund portfolios of pooled long-shot analysis investments in candidate medical therapies for most cancers and uncommon genetic illnesses by making the most of portfolio diversification to subject high-quality (and thus decrease price) portfolio-level debt (Fernandez et al., 2012; Fagnan et al., 2014).
Equally structured monetary automobiles may play a key function in rising funding in different areas of scientific analysis. Importantly, these new buildings do not require buyers to forgo monetary returns to realize constructive analysis impacts. As an alternative, they’re designed to supply engaging risk-adjusted return profiles whereas additionally producing affect.
Nonetheless, not all R&D challenges are appropriate for automobiles resembling RBOs. For instance, the present state-of-the-art in Alzheimer’s analysis, together with the dearth of viable AD (Alzheimer Illness) remedy initiatives seems to make funding analysis in that space by way of an RBO construction troublesome as a result of a particularly excessive chance of failure and an absence of applicable diversification choices this present day (Fagnan et al., 2014). Thus, whereas the RBO strategy has broad applicability throughout many scientific domains—past simply the pharmaceutical trade—and has proven early successes in biomedical analysis, there are nonetheless areas the place this strategy might not be appropriate. In such settings, given the big scale of funding required and the exceedingly low ex-ante chance of success, it could be that solely a well-funded, socially motivated entity, like a authorities company, can guarantee adequate capital and funding self-discipline to fund analysis.
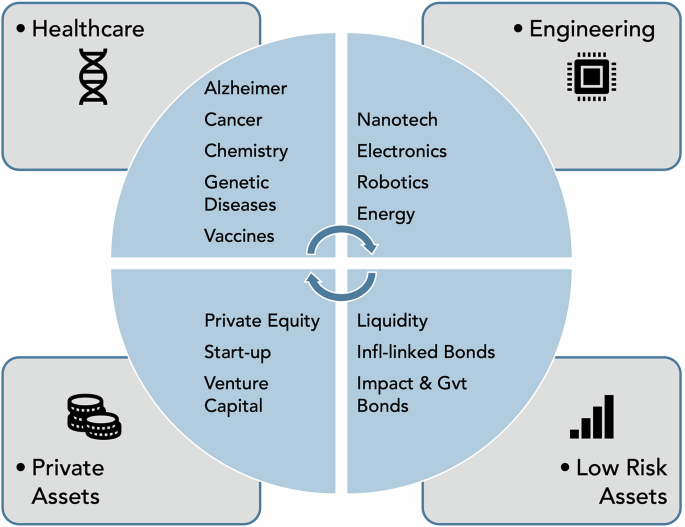
At this level, one would possibly surprise the right way to manage a science-based funding automobile (or Science-Primarily based Fund, SBF) in apply. A attainable construction is summarized in Fig. 1. On this instance, the fund would deal with a number of broad scientific goals, spanning a number of phases of R&D—from primary analysis to the interpretation of promising discoveries, and finally, commercialization.
The Determine depicts the organizational construction of a Science-Primarily based Fund. Investments are diversified between Non-public Belongings (Pure and Secondary Market of profitable Enterprise Capital, particularly Non-public Fairness and Begin-up) and Low Threat Belongings (investments in liquid property to offer interim returns to the fund and scale back the general portfolio danger). Non-public Belongings are investments in healthcare and engineering sectors, spanning from Alzheimer, Most cancers, Chemistry, Genetic Illnesses, Vaccines, on the one hand, to Nanotechnology, Electronics, Robotics, Power, on the opposite. Excessive and low-risky analysis initiatives are mixed with low-risky monetary devices beneath a cross-funding strategy through which returns from monetary automobiles and backup (low-risky) investments, along with rotational portfolio reallocations, are used to efficiently fund lead (high-risky) initiatives.
Notably, such broad funding mandates require applicable organizational architectures to reduce inside potential company prices between principals (buyers in and sponsors of the funding automobiles) and brokers (the managers of the automobiles).Footnote 3 The funding automobile could be sponsored in numerous methods. Examples embrace public sector coalitions of presidency companies, personal sector coalitions of enterprise capitalists and different institutional funding professionals, and public-private partnerships.
Problem #4: Roles and alternatives for governments and public establishments (GPI)
Governments and public establishments can play numerous key roles to extend the feasibility of analysis ecosystems and to encourage their realization. A few of these roles embrace:
-
1.
Unbiased Mission Analysis. One of many benefits of built-in analysis agendas and techniques is that they provide the potential to scale up funding in R&D by channeling personal capital, together with capital from monetary buyers who wouldn’t have particular experience in a specific analysis discipline. Not like conventional enterprise capitalists, such buyers are sometimes not able to guage the deserves or technical particulars of a selected venture. Public Establishments, within the type of new companies, can develop requirements for unbiased initiatives’ scores or rankings relative to their anticipated marginal contribution to enhancing scientific data and their environmental and societal impacts, whereas concurrently offering regulatory readability on the trail to future commercialization.
Virtually, it will likely be helpful to additional section analysis features into units of very broad goals. For instance, it could be advantageous to make use of totally different score methodologies and metrics to guage proposed initiatives relying on whether or not their goal is to (e.g.):
-
Advance primary data in some space—with no different particular aim or with objectives which might be possible unknown on the time of the analysis. (Such initiatives could also be of little curiosity to personal buyers); or
-
Translate analysis outcomes into industrial purposes within the type of long-term dangerous investments which have a aim, like decreasing or curing most cancers. (Such initiatives usually contain intensive high personal buyers);
-
Mission pooling. In instances the place public-private collaborations do make sense on either side, members of the general public sector can facilitate these collaborations by offering incentives for pooling initiatives that advance science in these fields the place trade funding is inadequate or non-existent.
-
On this context, GPIs can leverage their pure authority to:
-
i.
Convene individuals and act as clearing homes for info;
-
ii.
Create incentive applications and tax reduction;
-
iii.
Make direct funding (as mentioned within the subsequent level).
-
i.
Frequent apply utilized by governments and economists to guage the socio-economic-financial impacts of funding initiatives is the cost-benefit evaluation (CBA). We recommend a extra concerned generalized analysis strategy, through which analysis investments are evaluated primarily based on native (nationwide/trade/agency) and world (world economic system) prices and advantages utilizing a general-equilibrium mannequin to compute how a lot every nation ought to put money into science and the place to focus on primary and utilized analysis, as in Gersbach et al. (2023).
-
-
2.
Minimal return assure. If a pool of initiatives may be made giant and diversified sufficient, it’s affordable to count on that investments in them will likely be remunerated, with a probably extraordinary upside potential. Nonetheless, figuring out the worth of a share in such an funding may be troublesome because of the very giant uncertainty surrounding future cashflows. It’s usually onerous sufficient to estimate future cashflows that may accrue for translating analysis that has already been developed (however not but commercialized), and much tougher nonetheless to take action for earlier stage analysis and IP.
On this context, GPIs may scale back investor uncertainty by means of some type of draw back safety, both by:
-
Offering direct ensures, thereby decreasing danger for personal investments (by protecting the first-loss piece, for instance);
-
Buying shares of a Science-Primarily based Fund or designated courses of RBO securities that may stand in a first-loss positioning within the capital construction (maybe doing so at beneath market charges if wanted) (Fagnan et al., 2013);
-
Offering buy ensures for the ensuing merchandise which might be dropped at market. It may be proven that investments within the type of backstop ensures, for instance, have the potential to amplify and multiply authorities investments by attracting historically reluctant personal buyers to take part (Fagnan et al., 2013).
-
Such types of initiatives could also be a game-changer in motivating innovation, since government-funded funding companies are in a position to develop experience in higher figuring out goal companies for subsidies and in evaluating their price construction (Bayar et al., 2019).