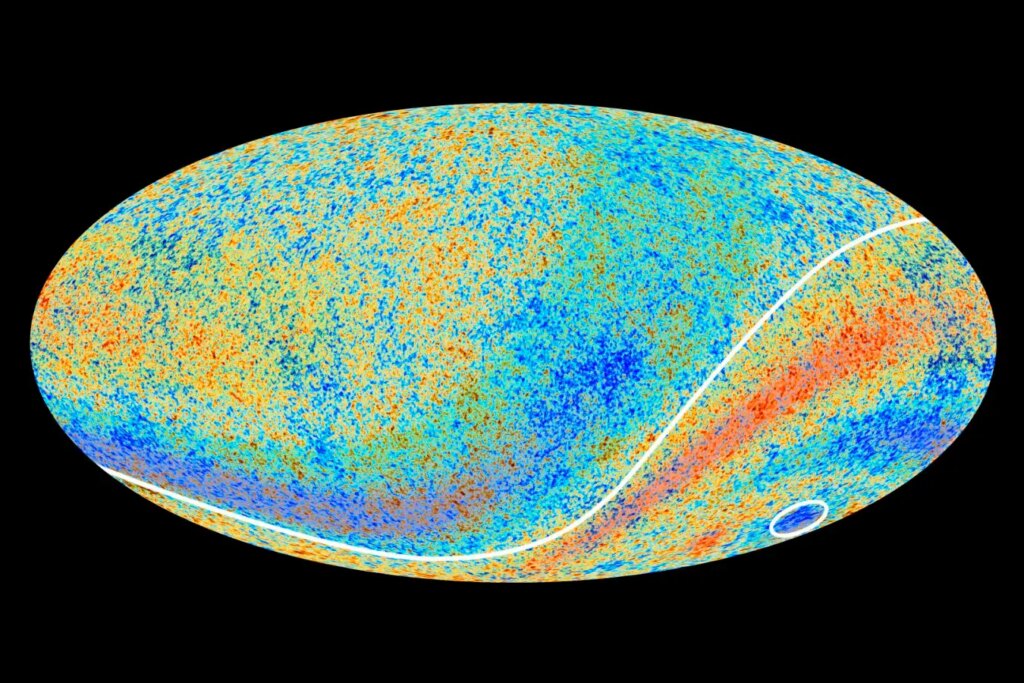
An asymmetry within the common temperature of the cosmic microwave background doesn’t match the usual mannequin of cosmology ESA/Planck Collaboration
An anomaly within the temperature of the universe has lengthy stumped physicists, and a brand new evaluation of information from a number of radio telescopes has solely deepened the thriller of what’s inflicting it.
This bizarre streak is seen within the afterglow of the big bang – the radiation that has been touring in the direction of us because the starting of time, referred to as the cosmic microwave background (CMB). Physicists agree our view of the universe, or place inside it, shouldn’t be in any method distinctive, so that they anticipate the CMB to look roughly the identical in all instructions. However measurements present in any other case: there may be an axis alongside which the CMB goes from colder to hotter. That is referred to as a dipole, and Lukas Böhme at Bielefeld College in Germany and his collaborators have now proven how deeply odd it’s by turning to information from radio telescopes.
Böhme says the existence of a dipole within the CMB isn’t a surprise by itself, however its measurement doesn’t match up with our strongest fashions of cosmology. Radiation emitted from a transferring supply or measured by somebody who’s transferring – and the Earth, our photo voltaic system and our entire galaxy are all transferring – will shift to be hotter or colder relying on that movement, as a result of Doppler impact and different relative movement results that stem from the theory of special relativity. However the dipole the researchers have been observing for many years corresponds to movement about ten instances sooner than anticipated.
To get a greater view of this discrepancy, Böhme and his colleagues analysed information from six telescopes that gather radio waves. After a cautious evaluation, they narrowed the information right down to the three they discovered most exact and analysed it in accordance with a brand new mannequin of the place radio waves come from within the sky. Böhme says their strategy was much like dividing up the sky into pixels and thoroughly figuring out what number of sources of radiation are contained in every. But, even with this painstaking adjustment, the dipole thriller continued.
Dragan Huterer on the College of Michigan says the brand new discovering is fascinating precisely due to how cautious the workforce’s evaluation was. It’s a fairly important step in the direction of establishing the dipole as an undisputable truth concerning the CMB, which might be a giant deal, he says. It is because it might suggest we both don’t perceive one thing concerning the construction of our neighbourhood throughout the cosmos, or the whole universe shouldn’t be as whilst our most successful theories recommend it must be. Nevertheless, Huterer says radio astronomy measurements are notoriously tough to make exact so there may nonetheless be systematic errors within the information.
A part of the problem comes from the actual fact all radio indicators telescopes gather are faint, says Böhme. “It is a actually small factor that we need to measure. It’s actually arduous to calibrate your [radio] survey to be so exact,” he says. However this isn’t the one proof for the dipole we have now. Infrared radiation coming from quasars appears to buttress the radio wave measurements, however it is going to actually be as much as future telescopes so as to add extra accuracy into the image and reduce the dipole thriller, says Böhme.
Reference: Bodily Evaluation Letters, forthcoming
Subjects: