For the fourth yr in a row, NASA’s Curiosity rover has photographed iridescent clouds drifting throughout the Martian sky. The clouds seem in the identical place, on the similar time of yr.
On January 17, through the early Martian autumn, Curiosity’s Mastcam recorded these noctilucent, or “night-shining,” clouds for 16 minutes. The Solar’s rays scatter towards the clouds, creating colourful, “mother-of-pearl” clouds tinged with crimson and inexperienced.
Cloudgazing… on Mars! ☁️
@MarsCuriosity captured these colourful clouds drifting throughout the Martian sky. The iridescent, carbon dioxide ice formations provide clues about Mars’ ambiance and climate: https://t.co/HAp2FDFjhk pic.twitter.com/DEWV477X01— NASA (@NASA) February 11, 2025
Dry ice clouds
Common Martian clouds are composed of water ice, however researchers imagine that frozen carbon dioxide, or dry ice, makes up the noctilucent clouds. They float 60 to 80 kilometers above the floor of the Purple Planet, the place frigid temperatures trigger the carbon dioxide to condense into colourful, wispy clouds. Some plumes descend to 50 kilometers earlier than evaporating within the rising temperatures.
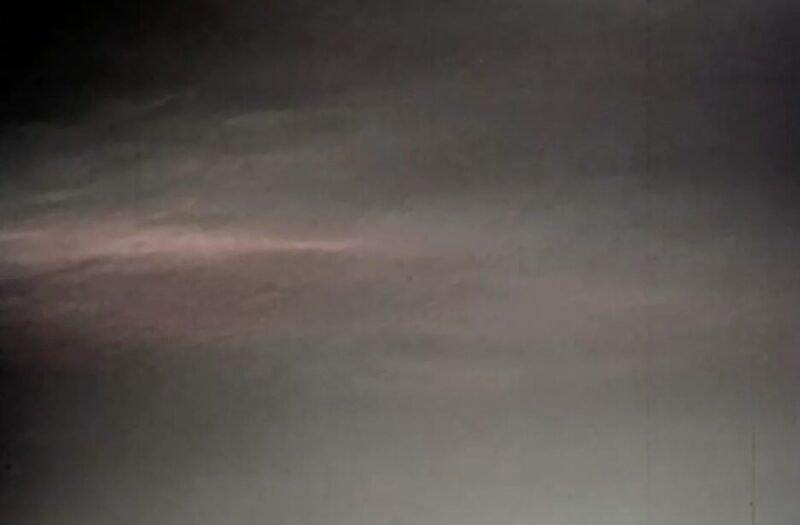

Photograph: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/SSI
Twilight clouds on Mars had been first noticed throughout NASA’s Pathfinder mission in 1997. Curiosity’s current observations mark the fourth time that these iridescent clouds have appeared over the Gale Crater within the planet’s southern hemisphere. They appear to come back on the similar time every year.
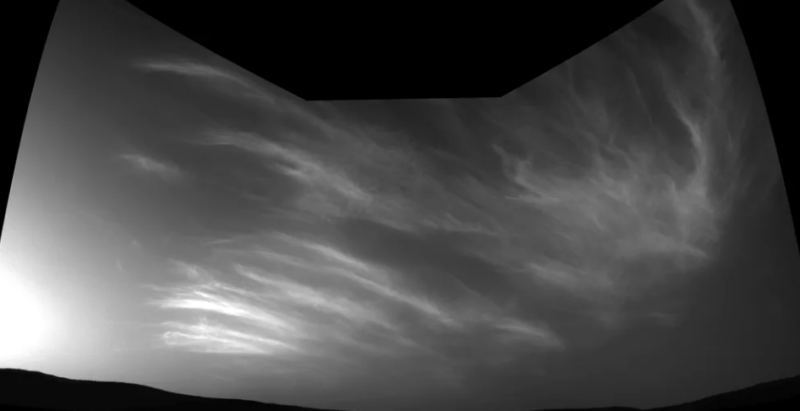
Noctilucent clouds on Mars seen by NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover, Could 17, 2019. Photograph: NASA/JPL-Caltech
This predictability has allowed scientists to plan their observations meticulously. Mark Lemmon, an atmospheric scientist on the Area Science Institute, recollects his preliminary encounter with these clouds: “At first, [I was sure] it was some shade artifact…Now it’s change into so predictable that we are able to plan our pictures prematurely.”
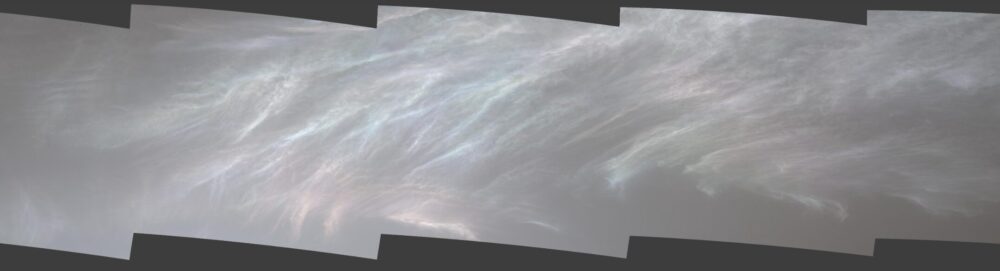
NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover noticed these mother-of-pearl clouds on March 5, 2021. Photograph: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Surprisingly, the twilight clouds don’t appear to type wherever else on the planet. One speculation is that atmospheric gravity waves assist generate the clouds. The waves cool the ambiance and create cool sufficient situations for the clouds to type.
That is, nevertheless, only a principle. “Martian gravity waves usually are not absolutely understood and we’re not totally certain what’s inflicting twilight clouds to type in a single place however not one other,” says Lemmon.
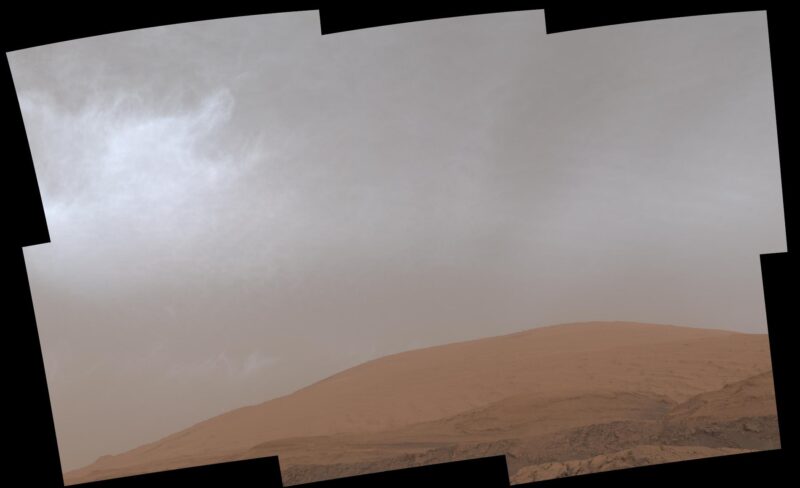

Clouds drifting over Mount Sharp on Mars, as seen by NASA’s Curiosity rover on March 19, 2021. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
