Within the Nineteen Seventies, photographs from the NASA Mariner 9 orbiter revealed water-sculpted surfaces on Mars. This settled the once-controversial query of whether or not water ever rippled over the crimson planet.
Since then, an increasing number of proof has emerged that water as soon as performed a big function on our planetary neighbour.
For instance, Martian meteorites file proof for water again to 4.5 billion years in the past. On the younger aspect of the timescale, affect craters fashioned over the previous few years present the presence of ice under the surface today.
At this time the recent subjects deal with when water appeared, how a lot was there, and the way lengthy it lasted. Maybe essentially the most burning of all Mars water-related subjects these days is: had been there ever oceans?
A brand new examine published in PNAS immediately has made fairly a splash. The examine concerned a staff of Chinese language and American scientists led by Jianhui Li from Guangzhou College in China, and was based mostly on work achieved by the China Nationwide House Administration’s Mars rover Zhurong.
Knowledge from Zhurong present an unprecedented look into rocks buried close to a proposed shoreline billions of years previous. The researchers declare to have discovered seashore deposits from an historical Martian ocean.
Robert Citron/Southwest Research Institute/NASA
Blue water on a crimson planet
Rovers exploring Mars examine many features of the planet, together with the geology, soil and ambiance. They’re typically on the lookout for any proof of water. That’s partly as a result of water is an important issue for figuring out if Mars ever supported life.
Sedimentary rocks are sometimes a specific focus of investigations, as a result of they will include proof of water – and due to this fact life – on Mars.
For instance, the NASA Perseverance rover is presently trying to find life in a delta deposit. Deltas are triangular areas typically discovered the place rivers circulation into bigger our bodies of water, depositing giant quantities of sediment. Examples on Earth embrace the Mississippi delta in the US and the Nile delta in Egypt.
The delta the Perseverance rover is exploring is positioned inside the roughly 45km huge Jezero affect crater, believed to be the positioning of an historical lake.
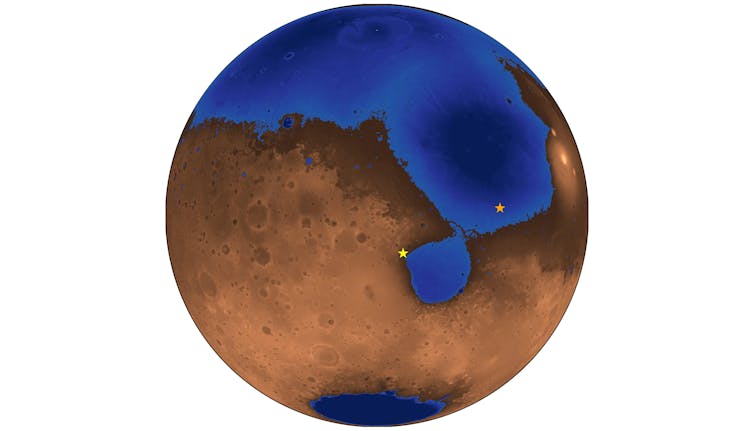
Zhurong had its sights set on a really completely different physique of water – the vestiges of an historical ocean positioned within the northern hemisphere of Mars.
ESA/DLR/FU Berlin
The god of fireside
The Zhurong rover is known as after a legendary god of fireside.
It was launched by the Chinese National Space Administration in 2020 and was energetic on Mars from 2021 to 2022. Zhurong landed inside Utopia Planitia, an unlimited expanse and the biggest affect basin on Mars which stretches some 3,300km in diameter.
Zhurong is investigating an space close to a sequence of ridges – described as paleoshorelines – that reach for 1000’s of kilometres throughout Mars. The paleoshorelines have beforehand been interpreted because the remnants of a global ocean that encircled the northern third of Mars.
Nonetheless, there are differing views amongst scientists about this, and extra observations are wanted.
On Earth, the geologic file of oceans is distinctive. Fashionable oceans are just a few tons of of thousands and thousands of years previous. But the worldwide rock file is riddled with deposits made by many older oceans, some a number of billions of years previous.
Hai Liu/Guangzhou University
What lies beneath
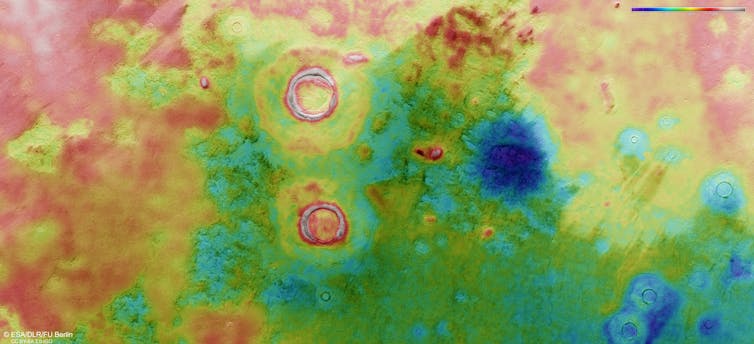
To find out if rocks in Utopia Planitia are in line with having been deposited by an ocean, the rover collected information alongside a 1.3km measured line often called a transect on the margin of the basin. The transect was oriented perpendicular to the paleoshoreline. The purpose was to work out what rock sorts are there, and what story they inform.
The Zhurong rover used a way known as floor penetrating radar, which probed all the way down to 100 metres beneath the floor. The information revealed many traits of the buried rocks, together with their orientation.
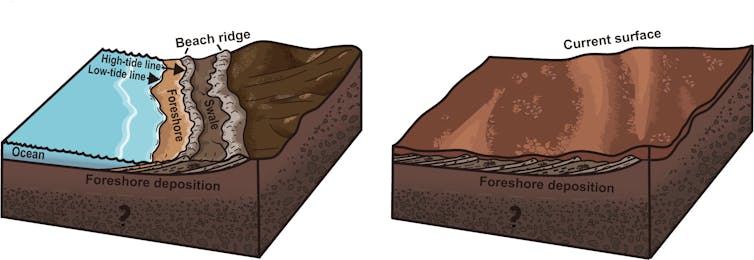
Rocks imaged alongside the transect contained many reflective layers which are seen by floor penetrating radar all the way down to not less than 30 metres. All of the layers additionally dip shallowly into the basin, away from the paleoshoreline. This geometry precisely displays how sediments are deposited into oceans on Earth.
The bottom penetrating radar additionally measured how a lot the rocks are affected by {an electrical} discipline. The outcomes confirmed the rocks usually tend to be sedimentary and aren’t volcanic flows, which might additionally type layers.
The examine in contrast Zhurong information gathered from Utopia Planitia with floor penetrating radar information for various sedimentary environments on Earth.
The results of the comparability is evident – the rocks Zhurong imaged are a match for coastal sediments deposited alongside the margin of an ocean.
Zhurong discovered a seashore.

NASA/JPL
A moist Mars
The Noachian interval of Martian historical past, from 4.1 to three.7 billion years in the past, is the poster youngster for a moist Mars. There’s considerable proof from orbital photographs of valley networks and mineral maps that the floor of Noachian Mars had floor water.
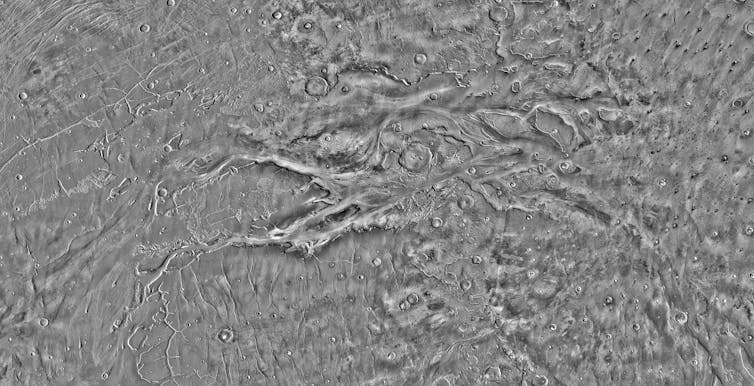
Nonetheless, there may be much less proof for floor water throughout the Hesperian interval, from 3.7 to three billion years in the past. Beautiful orbital photographs of enormous outflow channels in Hesperian land varieties, together with an space of canyons often called Kasei Valles, are believed to have fashioned from catastrophic releases of floor water, fairly than standing water.
By NASA / JPL-Caltech / Arizona State University
From this view, Mars seems to have cooled down and dried up by Hesperian time.
Nonetheless, the Zhurong rover findings of coastal deposits fashioned in an ocean might point out that floor water was secure on Mars longer than beforehand recognised. It could have lasted into the Late Hesperian interval.
This will likely imply that liveable environments, round an ocean, prolonged to newer occasions.
