1 Introduction
Parkinson’s illness (PD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative dysfunction characterised by core motor signs, collectively often called Parkinsonism. These signs sometimes embrace bradykinesia, marked by sluggish motion, and are sometimes accompanied by relaxation tremor or rigidity (Postuma et al., 2015). Alongside these motor signs, PD presents a spectrum of non-motor signs akin to fast eye motion sleep conduct dysfunction (RBD), constipation and despair (Mehndiratta et al., 2011). Non-motor signs can manifest at any stage of PD, generally serving as prodromal indicators previous motor signs (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 2004; Lee and Koh, 2015). Each motor and non-motor signs considerably impression the standard of life for people with PD (Santos García et al., 2019), with non-motor signs generally changing into the first complaints prompting medical visits (Frucht, 2004; O’Sullivan et al., 2008). In accordance with a scientific evaluate of the World Burden of Illness (GBD) 2016, PD affected ~6.1 million individuals worldwide, leading to 3.2 million incapacity adjusted life years (DALYs) (GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators, 2018). PD sometimes emerges in people aged over 50, and its prevalence elevated with age (GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators, 2018). By 2019, China had change into one of many high 5 international locations with the very best prevalence of PD instances and related DALYs (Zhong and Zhu, 2022), with projections indicating a steady rise in each prevalence and DALYs (Chen et al., 2022).
Varied antiparkinsonian drugs have been developed for the administration of PD, together with levodopa (both alone or with a dopa decarboxylase inhibitor), dopamine agonists, monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) inhibitors, catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitors, anticholinergics, and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2017; Grimes et al., 2019; Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Group from Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Association and Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Group from Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, 2020; Pringsheim et al., 2021; Waller et al., 2021). Nonetheless, these pharmacotherapies usually include inevitable unwanted effects. For example, dopamine agonists, thought-about a first-line remedy, could exacerbate sure non-motor signs akin to impulse management problems, extreme sleepiness, and psychotic signs (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 2004; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2017). One other first-line medicine, Levodopa, usually results in motor issues like dyskinesia, motor fluctuations, and “sporting off” phenomena throughout the middle-to-late levels of PD (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 2004; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2017), imposing vital burdens on sufferers (Santos-García et al., 2020).
Regardless of the provision of adjunctive pharmacotherapies and surgical interventions for motor issues and non-motor signs, adjunctive pharmacotherapies have limitations in medical effectiveness with extra unwanted effects (Waller et al., 2021). Furthermore, surgical procedure is commonly contraindicated in aged sufferers with superior PD (Dewey, 2004). There’s an unmet want for efficient and secure therapies to help standard antiparkinsonian methods, which can improve medical effectiveness in controlling motor and non-motor signs all through PD course, decrease the dangers of medication-induced motor issues in early levels of PD, and enhance administration of motor issues in superior levels (Dewey, 2004; LeWitt and Chaudhuri, 2020; Rukavina et al., 2021).
In mild of the challenges outlined above, an rising variety of PD sufferers have a tendency to hunt complementary and different therapies, akin to natural drugs, acupuncture, and different modalities, to reinforce and complement their anti-Parkinson’s administration (Rajendran et al., 2001; Ferry et al., 2002; Tan et al., 2006; Kim et al., 2009; Lökk and Nilsson, 2010; Pecci et al., 2010). Notably noteworthy is the recognition of conventional natural drugs, particularly Chinese language natural drugs (CHM), amongst Asian PD sufferers (Tan et al., 2006; Kim et al., 2009; Lin et al., 2021). CHM, deeply rooted in a historical past spanning hundreds of years in China, locations emphasis on individualized syndrome differentiation (Li et al., 2011). Though medical tips suggest Chinese language drugs therapies for PD, encompassing the remedy of each motor and non-motor signs, in addition to motor issues (Cho et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2020; Li W. et al., 2021; Luo et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Zhao and Liu, 2021; Yun and Liu, 2022), it’s acknowledged that sure guideline suggestions lack strong proof from high-quality analysis (Liu et al., 2020; Zhao and Liu, 2021). Whereas some current tips derive their medical suggestions from proof obtained via randomized managed trials (RCT) and RCT-based systematic evaluations, such proof usually faces constraints by way of generalizability and medical applicability (Green and Glasgow, 2006; Sanson-Fisher et al., 2007). In managed settings, PD sufferers are sometimes prescribed standardized formulation together with Ping chan granule, Cong rong shu jing granules, and Hua tan jie yu granules (Chen et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020a; Gu et al., 2023). Nonetheless, these formulation had been normally tailor-made to particular sufferers and should not successfully deal with the various signs of PD sufferers in real-world conditions. Actual-world medical apply experiences are essential for informing evidence-based approaches to treating PD with Chinese language drugs (Black, 1996; Dreyer, 2022). Moreover, the medical traits of PD sufferers who search Chinese language drugs, and after they begin to search Chinese language drugs therapies for PD remained unclear. Given the complexity of PD signs and issues, it is very important perceive sufferers’ main considerations, the signs that almost all trouble them, and their remedy preferences. As a basic part of evidence-based apply, sufferers’ preferences and values deserves in-depth exploration to optimize Chinese language drugs therapies for people with PD.
To handle these gaps, we carried out a retrospective evaluation of digital medical information (EMRs) from a tertiary Chinese language drugs hospital. The purpose was to discover and summarize real-world clinicians’ experiences in prescribing Chinese language drugs to PD sufferers, and determine the traits of PD sufferers receiving preliminary CHM therapies. The insights gained from this evaluation will contribute useful info to assist evidence-based medical apply of Chinese language drugs for PD.
2 Strategies
The research collected and analyzed knowledge of the present EMRs from outpatient departments at Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese language Medication (GPHCM), a tertiary hospital offering built-in Chinese language and traditional drugs for PD sufferers in China (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, 2021). The research proposal was reviewed and accepted by the Human Analysis Ethics Committee (HREC) of GPHCM (ZE2023-392-01) with waived knowledgeable consent.
2.1 Knowledge search and screening
Outpatient EMRs with a first-listed analysis of PD, whether or not confirmed or suspected, had been recognized within the digital EMR system of GPHCM between July 2018 and June 2023. Solely affected person encounters (PEs) for the preliminary medical visits for Parkinsonism had been retrieved out of those EMRs, and exported to an Excel sheet, with help offered by the Data Know-how Division of GPHCM.
Eligibility screening was carried out by Shaohua Lyu, a clinician specializing in PD and neurological situations. Observe-up PEs with preliminary encounters exterior the analysis timeframe and preliminary PEs missing detailed descriptions of medical historical past (together with signs) had been excluded. Any uncertainty was resolved via session with a senior PD specialist (X Luo or Q Su).
2.2 Standing of analysis
As medical analysis could or could not have been definitively established throughout the preliminary go to (CAER Inc, 2023), the standing of the first-listed PD analysis on the preliminary go to was additional categorized into three classes: (1) A “confirmed analysis,” if the affected person had obtained a proper PD analysis earlier than visiting the studied hospital; (2) A “suspected analysis,” if the affected person’s signs and complaints had been indicative of parkinsonism, however a confirmed PD analysis had not been established on the preliminary visits; (3) An “unclear standing of analysis,” when there was inadequate info to find out whether or not a PD analysis has been established from the preliminary PEs (Shah et al., 2019).
2.3 Knowledge extraction
Common info akin to age, illness length (time from the onset of motor signs), onset age, and gender, visited departments, typical motor signs, widespread motor issues, and non-motor signs together with particulars of prescriptions together with herb components of prescribed CHM decoctions, names and herb components of patented Chinese language natural drugs merchandise (PCHMPs), acupuncture, and names of antiparkinsonian drugs, had been extracted by Shaohua Lyu and double-checked by Zhenhui Mao.
Extracted motor signs included bradykinesia, relaxation tremor, rigidity and postural instability (Postuma et al., 2015). Motor issues comprised dyskinesia and motor fluctuations, which encompassed the “on-off” phenomenon and/or “sporting off” (Freitas et al., 2017). These issues could both signify the progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in nature or outcome from levodopa-induced unwanted effects (Kim et al., 2020). Non-motor signs extracted throughout this research encompassed constipation, musculoskeletal ache, fatigue, orthostatic hypotension, stressed legs, sweating, swallowing dysfunction, salivation, cognitive impairment, urinary issues, hallucinations and delusions, anxiousness and/or despair, extreme daytime sleepiness, and sleep disturbance (together with RBD) (Chaudhuri et al., 2007; Carroll et al., 2021).
2.4 Knowledge standardization
Numerous descriptions of the identical PD symptom within the EMRs textual content had been standardized utilizing widespread medical phrases. For example, rigidity in arms, legs or neck had been standardized as rigidity, no matter the precise areas talked about within the textual content. Herbs being processed in several methods had been additionally standardized. For instance, zhi huang qi (fried huang qi) was simplified as huang qi as no distinction was noticed of their nature. An identical strategy was taken with gan cao and zhi gan cao, in addition to zhi qiao and chao zhi qiao. It ought to be famous that zhi qiao, zhi shi and chen pi are all fruit peels collected at varied levels from the identical plant (Citrus aurantium L.). Nonetheless, the previous two share an identical perform, whereas chen pi has a distinguishing position in Chinese language drugs concept and was separated from the opposite two herbs throughout frequency evaluation. Scientific names generally used Latin names and conventional Chinese language names of the herbs concerned on this research are launched in Table 1.
2.5 Knowledge evaluation
IBS SPSS statistics (model 28.0, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was employed for the descriptive analyses of sufferers’ traits and remedy info. Categorical variables had been introduced as frequency and share, whereas steady variables had been expressed as imply with commonplace deviation. Moreover, IBS SPSS Modeler 18.0 was utilized to generate affiliation guidelines between herbs and signs, using the Apriori algorithm.
3 Outcomes
3.1 Abstract of the analysis process
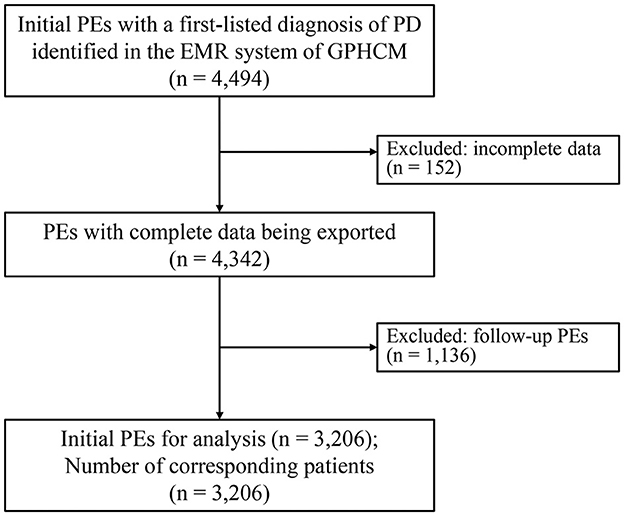
A complete of 4,494 outpatient initials PEs with a first-listed analysis of PD had been recognized and exported from the EMR system of GPHCM. In the course of the screening process, 152 PEs had been excluded for incomplete knowledge, and 1,136 PEs had been excluded as a result of they had been follow-up PEs quite than preliminary PEs. Finally, 3,206 PEs, every comparable to a person affected person, had been included within the analyses (Figure 1).
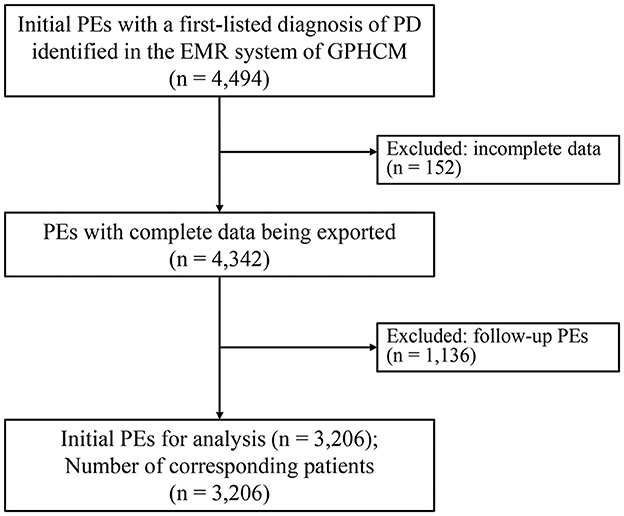
Determine 1. Flowchart of the research (EMRs, digital medical information; PD, Parkinson’s illness; PE, affected person encounter).
3.2 Scientific options of all sufferers
3.2.1 Demographics and common traits
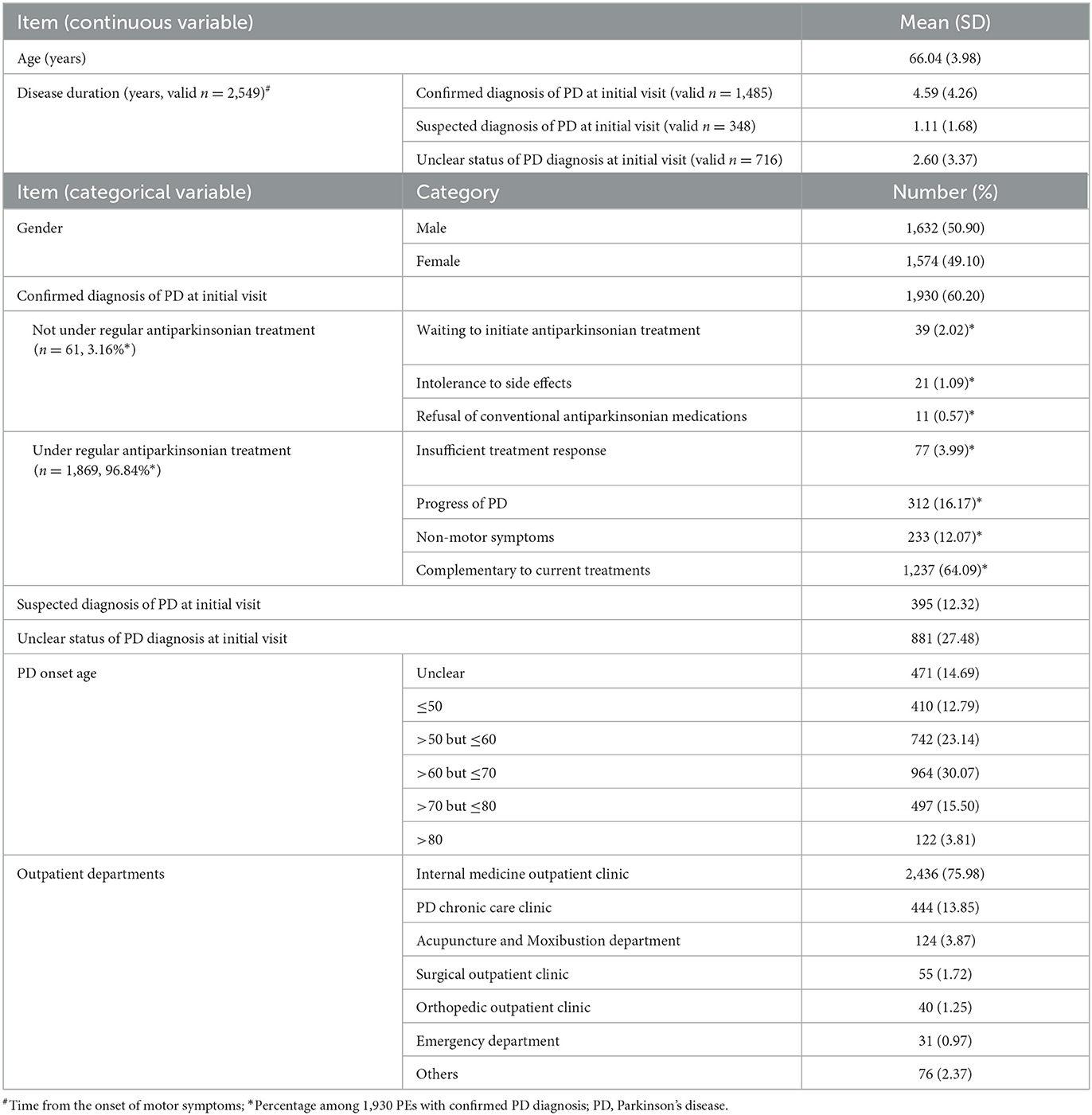
There have been 3,206 sufferers concerned on this research as every of the included PEs corresponds to 1 particular person affected person. Out of the three,206 eligible sufferers with a first-listed analysis of PD, 1,632 (50.90%) had been male. The typical age of the sufferers was 66.04 ± 3.98 years previous, with probably the most continuously reported onset age of parkinsonism falling throughout the vary of 60 to 70 years (n = 964, 30.07%). Illness length from the onset of motor signs was obtainable type 2,548 (79.48%) of the sufferers. Amongst these with a confirmed PD analysis (n = 1,485), the imply illness length was 4.59 ± 4.26 years, whereas sufferers with suspected PD analysis (n = 348) had a mean illness length of 1.11 ± 1.68 years. PD sufferers sought medical care in varied outpatient departments throughout their preliminary visits to the hospital. The most typical one was the interior drugs outpatient division (n = 2,436, 75.98%), adopted by PD persistent care clinic (n = 444, 13.85%) (Table 2).
Amongst 1,930 sufferers with a confirmed analysis of PD, 61 (3.16%) opted to not endure common antiparkinsonian drugs. This choice could also be attributed to unwanted effects intolerance, a deliberate option to postpone remedy initiation at early stage, or a refusal to be prescribed standard antiparkinsonian drugs. The remaining 1,869 (96.84%) sufferers had adhered to common standard antiparkinsonian drugs. Amongst this cohort, 1,237 (64.09%) sufferers sought extra Chinese language drugs remedy alongside their present therapies therapies with out offering detailed causes. Different particular causes for searching for Chinese language drugs concerned inadequate remedy response to traditional drugs, the “sporting off” of medicines as PD progressed to superior levels, and inadequate reduction of non-motor signs (Table 2).
3.2.2 Scientific manifestations of sufferers with first-listed analysis of PD
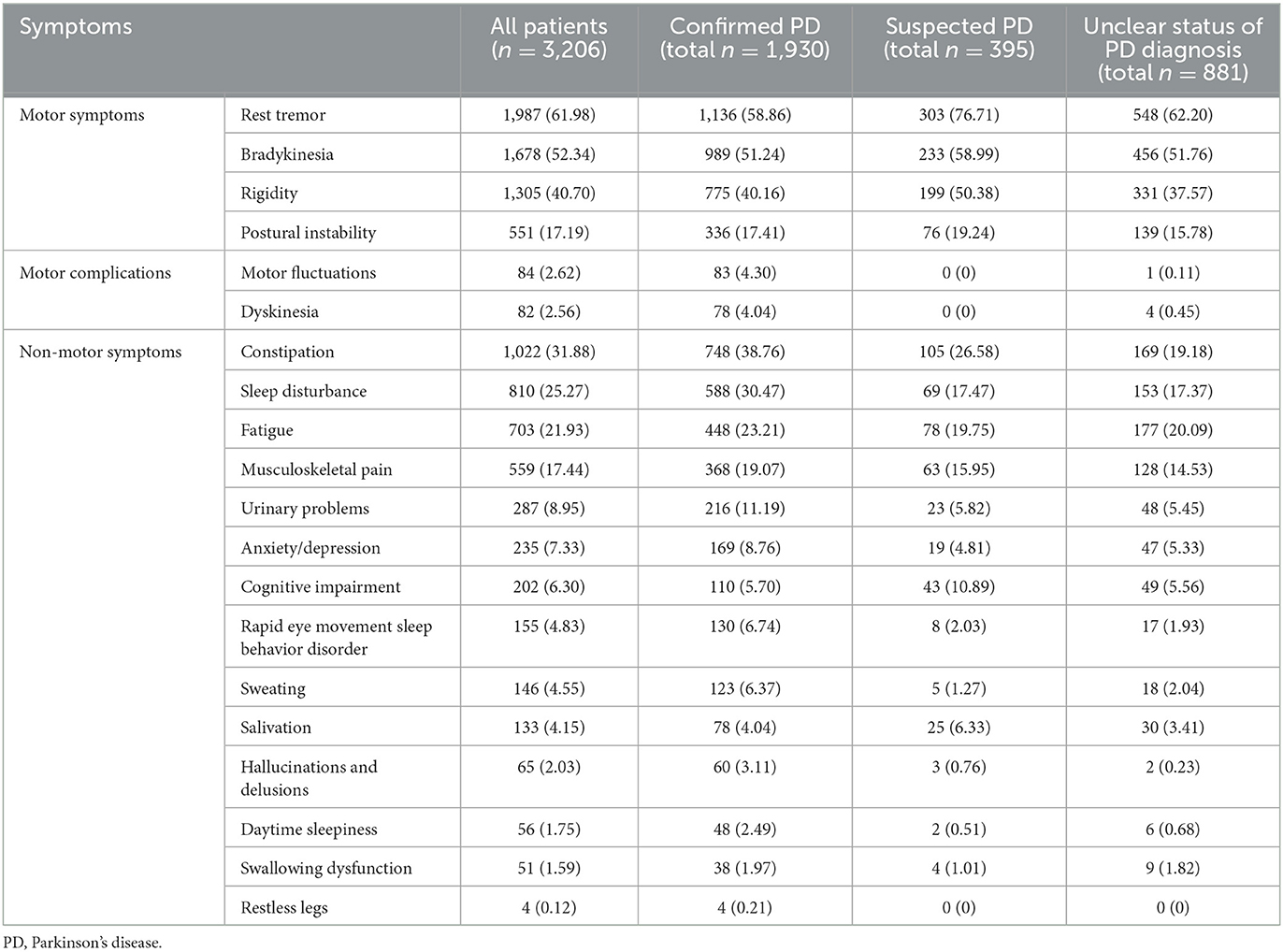
Relaxation tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity and postural instability represent the 4 typical motor signs, both recorded individually or in varied mixtures by the three,206 PEs. Amongst these signs, relaxation tremor emerged as probably the most continuously documented symptom by 1,987 (61.98%) PEs, adopted by bradykinesia (n = 1,678, 52.34%) and rigidity (n = 1,305, 40.70%). Postural instability was recorded by a restricted variety of PEs, particularly 551 (17.19%). The proportion of relaxation tremor and rigidity had been notably excessive amongst sufferers with suspected PD analysis in accordance with preliminary examinations.
Motor issues weren’t widespread among the many preliminary PEs, with solely 84 (2.62%) recording motor fluctuations, and 82 (2.56%) documenting dyskinesia. Motor issues had been predominantly reported amongst sufferers with a confirmed analysis of PD (Table 3).
On this research, a complete of 15 non-motor signs had been analyzed, with 4 of them recorded by over 10% of the PEs. These signs included constipation (n = 1,022, 31.88%), sleep disturbance (n = 810, 25.27%), fatigue (n = 703, 21.93%) and musculoskeletal ache (n = 559, 17.44%). Notably, these non-motor signs had been reported not solely by sufferers with a confirmed PD analysis, but additionally by these with suspected or unclear PD analysis (Table 3).
3.3 Remedies
Antiparkinsonian drugs are really helpful for managing Parkinsonism or helping within the institution or differentiation of a PD analysis based mostly on sufferers’ responses to drugs (Postuma et al., 2015). Moreover, Chinese language drugs can also be really helpful for Parkinsonism following the precept of syndrome differentiation (Yun and Liu, 2022). The regularity of remedy, each standard and Chinese language drugs, was carried out based mostly on the included PEs, whatever the standing of PD analysis.
3.3.1 Therapy classes
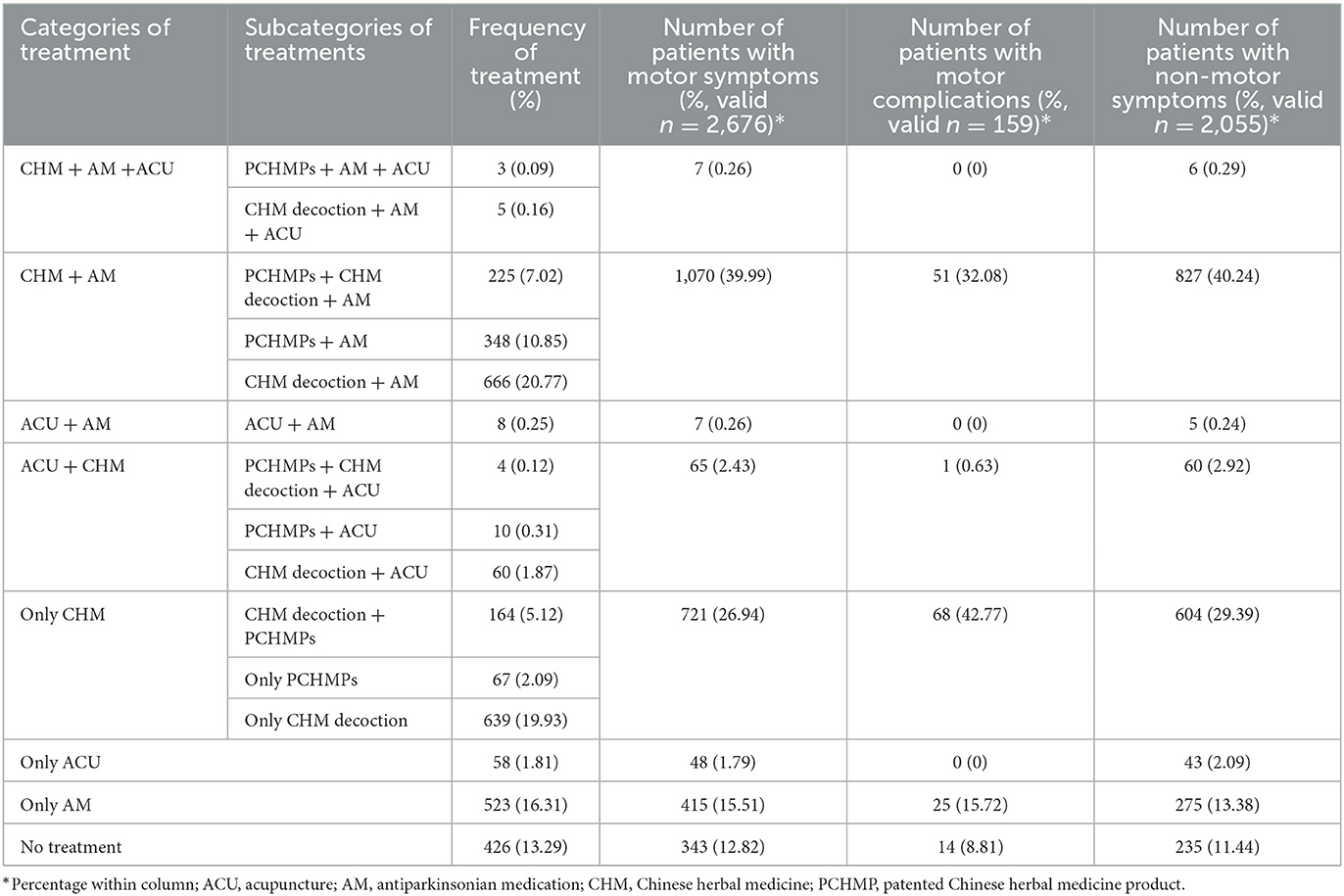
Among the many 3,206 sufferers, 426 sufferers underwent examinations with out receiving therapies. Antiparkinsonian drugs had been prescribed for 1,778 (55.46%) sufferers, both as a standalone remedy (n = 523, 16.31%) or together with CHM and/or acupuncture (n = 1,255, 39.15%). CHM was prescribed for two,191 (68.34%) sufferers, both as a standalone remedy (n = 870, 27.14%) or at the side of antiparkinsonian drugs and/or acupuncture (n = 1,321, 41.20%). Notably, CHM decoction was extra generally prescribed than PCHMPs (1,763 vs. 821). Acupuncture was restricted in use, being administrated to solely 148 PD sufferers. Integration of CHM and antiparkinsonian drugs had been the commonest remedy class amongst sufferers with motor signs (39.99%) and non-motor signs (40.24%), whereas single use of CHM was the commonest remedy for sufferers with motor issues (Table 4).
3.3.2 Frequency evaluation of herbs
Among the many 1,764 PEs with prescriptions of CHM decoctions, probably the most continuously prescribed herb is Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. (gan cao) (n = 1,252), adopted by Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi) (n = 953), Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (bai zhu) (n = 948), Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui) (n = 844), and Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (di huang) (n = 753). It’s noteworthy that these high continuously used herbs are additionally categorized as dietary medicinal herbs in accordance with China National Health and Family Planning Commission (2018) and China National Health Commission (2020) (Table 1).
3.3.3 Associations guidelines between signs and herbs
Affiliation guidelines had been generated to unveil potential connections between PD signs and herbs, using the Apriori algorithm. Three parameters specifically assist, confidence and carry are introduced within the affiliation guidelines. Assist is the prevalence of antecedent and its minimal threshold is normally predefined to keep away from occasional co-occurrence (Agrawal et al., 1993; Xiong, 2021). Confidence displays the potential of co-occurrences of consequent and antecedent within the datasets consisting of antecedent, whereas carry is a price that represents the chance of a rise within the consequent given a selected antecedent (Han et al., 2011; Lu et al., 2020). All through this course of, Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. (dang shen), Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen/hong shen) had been grouped as one sort as a result of their comparable capabilities in Chinese language drugs concept (Zhong, 2016). As indicated in Table 5, the antecedent symptom of RBD was related to the resultant use of Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf. (da huang) (carry = 2.28), Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. (dang shen)/Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen/hong shen) (carry = 1.29), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi) (carry = 1.28), and Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui) (carry = 1.26). Motor fluctuations had been related to Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. (dang shen)/Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen/hong shen) (carry = 1.49), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi) (carry = 1.40), and Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui) (carry = 1.28). Dyskinesia elevated using Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui) (carry = 1.34) and Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. (dang shen)/Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen/hong shen) (carry = 1.32). Sadly, affiliation guidelines weren’t efficiently constructed for different non-motor signs.
3.3.4 Frequency evaluation of patented Chinese language natural drugs merchandise
Patented Chinese language natural drugs merchandise (PCHMPs) with a frequency exceeding 25 are detailed in Table 6. These PCHMPs had been predominantly formulated for neurological situations together with stroke, complications, coronary coronary heart illness, and so on., generally noticed amongst aged sufferers (State Pharmacopoeia Committee of China, 2020). Alternatively, they had been focused non-motor signs of PD, akin to constipation and musculoskeletal ache.
3.3.5 Frequency evaluation of antiparkinsonian drugs
Among the many preliminary PEs for sufferers with a first-listed analysis of PD, probably the most frequent prescribed antiparkinsonian medicine is Levodopa (n = 1,450), adopted by Dopaminergic agonist (n = 831), MAO-B inhibitors (n = 145), COMT inhibitors (n = 120), Amantadine (n = 32), and Anticholinergics (n = 30).
4 Dialogue
4.1 Abstract of outcomes
Primarily based on the evaluation of three,206 real-world EMRs, our research not solely synthesized first-hand medical experience in prescribing CHM for PD, but additionally recognized affected person’ traits and remedy classes. In abstract, our research contributes to evidence-based Chinese language drugs apply for PD, encompassing dimensions of medical experience, sufferers’ preferences and values (Sackett, 1997; Dawes et al., 2005; Yates, 2013).
Within the examinations of 348 preliminary PEs with a suspected PD analysis, the length from the onset of motor signs to the primary medical session was discovered to be 1.11 years, aligning with the common length of 15 months reported in a earlier survey in China (Wan et al., 2019). Nonetheless, nearly all of sufferers visited GPHCM after receiving a confirmed PD analysis, with a mean delay of 4.59 years from the onset of motor signs. Inside this group, some sufferers could have been following a routine of standard antiparkinsonian drugs with out concurrent Chinese language drugs remedy, whereas others could have beforehand undergone Chinese language drugs therapies elsewhere. At this stage, ~50% of sufferers could have already developed motor issues (Bhidayasiri and Truong, 2008; Kim et al., 2020). Regardless of this, the share of motor issues based mostly on the included real-world PEs was merely round 2.5%. This discrepancy could also be attributed to the restricted consciousness of motor issues amongst non-PD specialists from the interior drugs outpatient clinic, which constitutes over 75% of PD-related outpatient visits. There’s a want for schooling concentrating on non-PD specialists to reinforce their understanding of motor issues and promote optimum administration of motor issues within the later levels.
Earlier than visiting the studied Chinese language drugs hospital, 96.84% of sufferers adhered to common standard antiparkinsonian drugs, whereas a mere 3.16% deviated from common therapies. This smaller share comprised people both awaiting the initiation of antiparkinsonian therapies or these unable to tolerate the related unwanted effects. The delayed graduation of antiparkinsonian remedy till illness development is just not unusual amongst PD sufferers (Stocchi et al., 2015). Moreover, insupportable unwanted effects of antiparkinsonian drugs had been continuously reported (Rascol et al., 2003). Amongst these constantly on common therapies, the choice to hunt Chinese language drugs could also be influenced by elements akin to a suboptimal response to traditional antiparkinsonian drugs, the “sporting off” phenomenon as PD advances to later levels, and inadequate managements for non-motor signs.
Early analysis and intervention of non-levodopa for PD sufferers have been really helpful (Pan et al., 2015; Tinelli et al., 2016), regardless of ongoing controversies concerning the timing and techniques for the preliminary pharmacological remedy for PD (Waller et al., 2021). Elements contributing to the diagnostic delay in PD could embrace physicians’ unfamiliarity with PD symptomology (Wan et al., 2019). Given the substantial involvement of non-PD specialists, it could be crucial to teach clinicians on PD information as a technique to scale back diagnostic latency. In time period of remedy, initiating non-levodopa drugs early not solely alleviates troublesome PD signs but additionally delays the initiation of levodopa and its subsequent unwanted effects, probably slowing illness development (Murman, 2012). CHM has demonstrated potential as an efficient remedy at the side of standard antiparkinsonian drugs in enhancing motor signs, non-motor signs and high quality of life (Li et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020a; Gu et al., 2023; Jun et al., 2023) (Supplementary File 1). Nonetheless, the present research indicated that almost all PD sufferers initiated their Chinese language drugs intervention from GPHCM after 4.59 years from the onset of motor signs. To enhance early intervention in PD and improve prognosis, there’s a want for group schooling and promotion concerning the effectiveness of Chinese language drugs interventions, alongside efforts to enhance the provision and accessibility of CHM.
Relaxation tremor is recorded as probably the most continuously skilled motor symptom by over 60% of sufferers with both a confirmed or suspected PD analysis, given its widely known affiliation with PD (Baumann, 2012). In distinction, postural instability is documented by <20% of PEs, a prevalence in line with earlier report (16%) (Appeadu and Gupta, 2023). Constipation, sleep disturbance, fatigue and musculoskeletal ache are the distinguished non-motor signs documented within the EMRs, no matter the analysis standing. Their prevalence aligns with beforehand documented non-motor signs (Tanveer et al., 2018; Kwok et al., 2021; Li L. C. et al., 2021). Nonetheless, different non-motor signs akin to cognitive impairment, stressed legs, and daytime sleepiness in our research weren’t as prevalent as reported amongst middle-late-stage PD sufferers in different research (Kwok et al., 2021; Li L. C. et al., 2021). Non-motor signs like constipation, insomnia, anxiousness, and despair have been reported to exert the best unfavourable impression on the standard of life amongst PD sufferers (Duncan et al., 2014). Within the studied Chinese language drugs hospital, PCHMPs had been tailor-made to deal with these generally reported non-motor signs. For example, Zao ren an shen capsule will be prescribed for sufferers experiencing sleep disturbance (Birling et al., 2022), and Tong fu xing shen capsule is thought for its efficacy in addressing constipation amongst PD sufferers (Huang, 2012). Moreover, herb components of CHM decoctions may also be modified to focus on particular non-motor signs. For instance, Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (da huang) was continuously prescribed for constipation.
Within the studied Chinese language drugs hospital, built-in Chinese language and traditional drugs emerged as the preferred remedy technique, adopted by the only use of CHM and single use of antiparkinsonian drugs. Using acupuncture for PD was restricted, and its utilization regularity was not analyzed because of the inadequate obtainable info. Because the predominant remedy for PD, CHM decoctions had been analyzed in depth.
In comparison with beforehand revealed data-mining research for PD based mostly on Well being Insurance coverage Analysis Database in Taiwan Province of China (Chen et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2021), Gastrodia elata Blume (tian ma) and Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (da huang) maintained consistency in reputation amongst CHM prescriptions. Nonetheless, the excessive frequency of tonifying herbs like Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi), Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (bai zhu), Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui), Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen), and so on. was seldom reported within the Taiwan research (Chen et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2021). This disparity could also be attributed to using totally different datasets with geographical variations. Nonetheless, tonifying herbs had been continuously used for PD, as indicated by a literature evaluate (Gu and Yuan, 2023).
Eight out of the highest 15 most continuously used herbs in our research, together with Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi), Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (bai zhu), Citrus aurantium L. (chen pi), Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui), Cimicifuga heracleifolia Kom. (sheng ma), Bupleurum chinense DC. (chai hu) and Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. (gan cao), are the herb components of Bu zhong yi qi tang (BZYQT), a classical components broadly employed for neurodegenerative situations akin to Alzheimer’s Illness and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lim et al., 2018; Yang, 2023). BZYQT has been really helpful by medical tips for PD and PD-associated autonomous neurofunctional problems (Luo et al., 2021; Zhao and Liu, 2021). Moreover, the logical mixture of different herbs, together with Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (bai shao), Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui), Citrus aurantium L. (chen pi), Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen), Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (bai zhu), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi) and Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf (fu ling), contributes to the primary components of Ren shen yang rong tang (RSYRT). RSYRT was really helpful for motor issues of PD (Liu et al., 2020). Nonetheless, each classical formulation weren’t talked about in different Chinese language drugs medical tips for PD (Wu et al., 2020; Li W. et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Yun and Liu, 2022).
It’s noteworthy that motor fluctuations and dyskinesia had been prone to be managed utilizing Chinese language drugs herbs akin to Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui), Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. (dang shen)/Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen/hong shen), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi), in accordance with the affiliation guidelines. The findings may supply a novel perspective for motor fluctuations and dyskinesia, the place there’s a lack of environment friendly therapies (Liu et al., 2020). Though the precise mechanism and results of those herbs for motor fluctuations and dyskinesia require additional examination and exploration, the findings present a foundation for future analysis. It is usually fascinating to look at that RBD was related to prescribing Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf. (da huang), a herb particular for constipation, whereas RBD has been reported to be correlated with constipation (Kong et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023). This discovering indicated that PD-induced RBD could also be handled by way of anti-constipation herbs like Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf. (da huang).
4.2 Mechanism of herb actions
To assist the medical utilization of the above-mentioned herbs and formulation for PD, mechanisms of herb actions for PD had been summarized.
BZYQT has been broadly reported to deal with PD-induced constipation and orthostatic hypotension (Bi et al., 2014; Chen and Wang, 2014; Wu et al., 2018). It exhibited results in stopping discount of tyrosine hydroxylase and accumulation of alpha-synuclein within the gut of PD mouse mannequin (Bi and Gao, 2015). As well as, BZYQT additionally exerted anti-apoptosis, anti-dementia and neuroprotective results for ACL, Alzheimer’s illness and ischemic stroke fashions (Lim et al., 2018; Li Q. et al., 2022; Yang, 2023).
The adjunct use of RSYRT confirmed superior results in comparison with the only use of antiparkinsonian drugs for PD with a Chinese language drugs syndrome of Deficiency of qi and Blood in a RCT (Wen, 2013). Scientific trials additionally discovered RSYRT to be efficient in enhancing fatigue symptom (Xu et al., 2020), and anti-microinflammation in haemodialysis sufferers (Hsiao et al., 2015). Furthermore, RSYRT demonstrated anti-aging results by way of enhancing insulin resistance within the mind (Zhao, 2023).
Mechanisms of particular person herb actions for PD had been summarized in Supplementary File 2. These continuously used herbs exerted evident antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-apoptosis, anti-neuroinflammatory results, aside from Citrus aurantium L. [mainly involved anti-constipation effects (Yan et al., 2020; Gong et al., 2023)] and Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf [possessing antidepressant and sedative-hypnotic effects (Shah et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2020; Pang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2021; Kim et al., 2022)].
Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. (gan cao) is probably the most continuously used herb for PD. A RCT indicated that 6-weeks licorice consumption considerably improved PD signs with out severe antagonistic occasions (Petramfar et al., 2020). Water extracts of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. (gan cao) demonstrated neuroprotective results by way of regulating ERK-1/2 pathways and the mTORC1-AMPK1 axis, in addition to inhibiting MAO-2 motion in in vitro research (Karthikkeyan et al., 2021, 2022; Ramadan et al., 2022). Its energetic compounds like Licopyranocoumarin, glycyrurol, and isoliquiritigenin, exerted anti-apoptosis in opposition to oxidative stress (Hwang and Chun, 2012; Fujimaki et al., 2014).
Astragaloside IV and Calycosin are bioactive compounds of Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi), they might defend dopaminergic neuron in opposition to neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, forestall dopaminergic neurodegeneration and mitigate PD signs, by way of regulating signaling methods of TLR/NF-κb and MAPK, Nrf2, nfκb/NLRP3, JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/AKT/mtor, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways (Chan et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2017; Yang C. et al., 2019; Yang J. et al., 2019; Tan et al., 2020; Xia et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2021).
Atractylenolide I, atractylenolide III, and atractylodin are the primary bioactive compounds of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (bai zhu), they decreased microglial activation, conferred safety to dopaminergic neurons, protected dopaminergic neurons from apoptosis, inflammatory cytokines and oxidant protein, attenuated transcriptional actions of NF-κb and MAPK phosphorylation in PD mouse fashions or in vitro experiments (More and Choi, 2017a,b; Jeong et al., 2019; Li H. et al., 2022).
N-Butylidenephthalide is a bioactive compound extracted from Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui), it could actually enhance PD restoration effectivity in a PD mouse mannequin (Chi et al., 2018), and block egl-1 expression to inhibit apoptosis pathways in addition to elevate rpn-6 expression to reinforce exercise of proteasomes (Fu et al., 2014).
The compound of catalpol is extracted from Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (di huang), and it demonstrated antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective results in vitro (Tian et al., 2006; Bi et al., 2008a,b). Formulation consisting of Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (di huang) as a important ingredient exerted antiparkinsonian therapeutic results by way of modulating apoptosis via MAPK and TLR4/NF-κb signaling methods (Tseng et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2021; He et al., 2023).
Paeoniflorin is among the energetic compounds of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (bai shao), it exerted neuroprotective, anti-ferroptosis, anti-neuroinflammatory, antioxidant and anti-apoptosis results in PD mouse fashions and in vitro analysis, by way of regulating the α-synuclein/PKC-δ, Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3, Akt/Nrf2/Gpx4, ROS/pkcδ/NF-κb, and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways (Sun et al., 2012; Dong et al., 2015; Zheng et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022).
Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen) extracts and compounds have been broadly investigated for PD. Ginsenoside Rg1 exerted neuroprotective, anti-cytotoxicity and immunomodulatory results in 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced PD mouse fashions. Extra particularly, it regulated prefrontal cortical gabaergic transmission (Liu et al., 2019), moderated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (Zhou et al., 2016), restored motor capabilities to physiological degree, and attenuated lack of dopaminergic neurons within the substantia nigra and striatum (Jiang et al., 2015), diminished aberrant α-synuclein-mediated neuroinflammation (Heng et al., 2016). Ginsenoside Rg3 regulated glutathione cysteine ligase modulatory subunit and glutathione cysteine ligase regulatory subunit expression in rotenone-induced PD mice (Han et al., 2021) and downregulated apoptosis mediators, egl-1 and ced-3, and upregulation of sod-3 and cat-2 in vitro (Chalorak et al., 2021). Ginsenosides Rd and Re acted anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant results, and maintained blood-brain barrier integrity in MPTP-induced PD mice (Choi et al., 2018a), lowered oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, induced Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 expression and activated the twin PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways in vitro (Zhang et al., 2016; Qiao et al., 2022). Extract of Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen) may defend in opposition to dopaminergic neuronal loss of life (Van Kampen et al., 2014; Jun et al., 2015; Ryu et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2020b), cell stress (Van Kampen et al., 2014) and mitochondrial dysfunction (Liu et al., 2020b), cut back indices of irritation (Van Kampen et al., 2014; Ryu et al., 2018; Jeon et al., 2020), forestall apoptosis (Hu et al., 2011; Van Kampen et al., 2014), accumulation of α-synuclein aggregates (Van Kampen et al., 2014; Jeon et al., 2020) and MPTP-induced leaky intestine barrier (Jeon et al., 2020), stimulate endogenous antioxidant launch (Wang J. Y. et al., 2013), regulate neuronal formation and power metabolism for survival (Kim et al., 2018). Signaling methods concerned in these actions embrace the Bcl-2 household, the nuclear issue erythroid 2-related issue 2 pathways, NF-κB signaling pathways (Choi et al., 2018b; Jeon et al., 2021).
Extracts of Bupleurum chinense DC. (chai hu) exerted anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective results as they will alleviate mitochondria injury in MPTP-induced PD mouse fashions (Jeong et al., 2018), regulate nuclear receptor-related 1 protein (Sim et al., 2017), and suppress NF-κb-mediated inflammatory pathways (Park et al., 2015).
4.3 Implication for medical apply
The preliminary utility of Chinese language drugs in managing PD has been a topic of controversy. Nonetheless, Chinese language drugs therapies, significantly CHM, emerges as a promising non-levodopa intervention. These therapies will be prescribed both at the side of antiparkinsonian drugs or as standalone therapies for PD sufferers (Cho et al., 2018). Notably, the mixing of Chinese language and traditional drugs is believed to contribute considerably to enhance PD signs (Li and Le, 2021). Our research indicated PD sufferers present process common standard drugs would nonetheless search Chinese language drugs to reinforce their present therapies, when PD situation progressed with “wearing-off” phenomenon, or reluctance and/or intolerance to traditional remedy had been noticed. PD sufferers may provoke their antiparkinsonian remedy with CHM, as a substitute for standard drugs. When deciding on remedy strategies, varied elements ought to be considered, together with the sufferers’ age, particular person preferences, remedy responses, tolerance of medicines, the severity of PD by way of each non-motor and motor incapacity, impairment in high quality of life, and presence of comorbidities (Marsili et al., 2017; de Bie et al., 2020; Waller et al., 2021).
As beforehand mentioned, every herb ingredient in BZYQT exerts one or a number of actions, together with antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-apoptosis, anti-neuroinflammatory, anti-constipation, antidepressant, and sedative-hypnotic results. Moreover, BZYQT itself reveals potential anti-dementia and neuroprotective results (Lim et al., 2018; Li Q. et al., 2022; Yang, 2023). We advocate for the prescription of BZYQT within the administration of PD. Tailor-made modifications to the components will be carried out to deal with particular particular person non-motor signs, akin to incorporating Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf. (da huang) for constipation. Moreover, PCHMPs will be prescribed to cope with comorbidities or accompanying signs. For example, Suan zao ren capsule could also be thought-about for sleep disturbances.
Furthermore, lots of the frequent herbs, together with Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. (gan cao), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi), Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen), and so on., are categorized as dietary and natural dietary supplements (Coates et al., 2010; China National Health and Family Planning Commission, 2018; China National Health Commission, 2020). These will be offered as a part of “meals remedy” or “medicinal eating regimen remedy” (Wu and Liang, 2018), serving as useful dietary supplements in day by day self-management of people with PD.
4.4 Implication for future analysis
Sufferers with PD usually search complementary therapies to enhance each motor and non-motor signs (Ferry et al., 2002; Tan et al., 2006; Kim et al., 2009; Pecci et al., 2010; Wang Y. et al., 2013). RCT proof has demonstrated the efficacy of CHM for PD in managed settings with supportive findings from laboratory experiments. Nonetheless, the generalizability of this proof stays restricted in nature. Actual-world results of CHM for PD stay unsure and warrant additional exploration. As well as, present proof targeted on short-to-intermediate time period results of CHM for PD. Given the persistent and progressive nature of PD, investigating the extended results and security of long-term CHM for PD holds vital medical worth and deserves thorough exploration. Moreover, PD sufferers, particularly these in superior ages, usually exhibit comorbidities akin to Alzheimer’s illness, hypertension, and others. Investigating the multi-targeted results of CHM for these co-existing situations is an avenue awaiting exploration.
Within the current research, an affiliation was recognized between motor issues and using herbs akin to Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (dang gui), Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (huang qi), and Codonopsis pilosula Nannf. (dang shen)/Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. (ren shen/hong shen). This herb mixture could also be utilized for motor issues in future analysis, and its medical results deserve future examination. Equally, the exploration of treating RBD with anti-constipation herb like Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf. (da huang) can also be really helpful.
4.5 Limitations
Inevitable limitations ought to be acknowledged on this research. Firstly, the analysis relied on EMRs from a single hospital and didn’t retrieve earlier therapies exterior the studied hospital, limiting the generalizability and reliability of the findings, regardless of the hospital’s tertiary standing and the evaluation being based mostly on knowledge from over 3,000 sufferers. Secondly, the absence of recorded remedy response within the preliminary PEs embrace within the research diminishes confidence within the sensible effectiveness of the concluded CHM prescriptions for PD. Potential longitudinal research with quantitative measurements are wanted to higher confirm the regularity of “efficient” CHM prescriptions for PD. Thirdly, the timing and real-world effectiveness of Chinese language drugs intervention for PD stay unresolved points that warrant additional exploration.
5 Conclusion
The studied sufferers typically initiated their visits to GPHCM after receiving a PD analysis, sometimes 4.59 years after the onset of motor signs. These sufferers had been generally prescribed with CHM decoctions and PCHMPs, both as standalone therapies or at the side of antiparkinsonian drugs. Notably, BZYQT emerged as a basic prescription for PD, usually tailor-made to deal with each motor issues and non-motor signs. Whereas earlier analysis has demonstrated the antiparkinsonian results of BZYQT and its particular person natural parts in compound or extract varieties, a urgent want exists for rigorous medical trials to additional validate and discover its effectiveness for PD and optimize its integration into the therapeutic panorama for PD.
Knowledge availability assertion
The unique contributions introduced within the research are included within the article/Supplementary material, additional inquiries will be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics assertion
The research involving people had been accepted by the Human Analysis Ethics Committee (HREC) of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese language Medication. The research had been carried out in accordance with the native laws and institutional necessities. The ethics committee/institutional evaluate board waived the requirement of written knowledgeable consent for participation from the contributors or the contributors’ authorized guardians/subsequent of kin as a result of The research was carried out based mostly on digital medical information and the figuring out info of the medical information weren’t exported.
Writer contributions
SL: Conceptualization, Knowledge curation, Formal evaluation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software program, Writing – unique draft, Writing – evaluate & enhancing. CZ: Supervision, Writing – evaluate & enhancing. ZM: Knowledge curation, Writing – evaluate & enhancing. XG: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – evaluate & enhancing. ZL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – evaluate & enhancing. XL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – evaluate & enhancing. JS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – evaluate & enhancing. QS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – evaluate & enhancing.
Funding
The writer(s) declare monetary assist was obtained for the analysis, authorship, and/or publication of this text. This research was funded by the Nationwide Key Analysis and Improvement Program of China (no. 2019YFC1708601), the Particular Fund of State Key Laboratory of Dampness Syndrome of Chinese language Medication (SZ2021ZZ14), Nationwide Conventional Chinese language Medication Scientific Excellent Abilities Coaching Program for QS, and Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese language Medication for SL (YN2023MS13).
Acknowledgments
The authors lengthen gratitude to the Data Know-how Division of GPHCM for his or her invaluable assist in knowledge identification and exportation. Moreover, we acknowledged the contribution of numerous affected person knowledge, which has been essential to our research.
Battle of curiosity
The authors declare that the analysis was carried out within the absence of any business or monetary relationships that might be construed as a possible battle of curiosity.
Writer’s word
All claims expressed on this article are solely these of the authors and don’t essentially signify these of their affiliated organizations, or these of the writer, the editors and the reviewers. Any product which may be evaluated on this article, or declare which may be made by its producer, is just not assured or endorsed by the writer.
Supplementary materials
The Supplementary Materials for this text will be discovered on-line at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1362948/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
BZYQT, Bu zhong yi qi tang; CHM, Chinese language natural drugs; COMT, catechol-O-methyl transferase; DALYs, incapacity adjusted life years; EMR, digital medical information; GBD, World Burden of Illness; GPHCM, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese language Medication; MAO-B, monoamine oxidase-B; MPTP, 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; PCHMP, patented Chinese language natural drugs product; PD, Parkinson’s illness; PE, affected person encounter; RBD, fast eye motion sleep conduct dysfunction; RCT, randomized managed trial; RSYRT, Ren shen yang rong tang.
References
Agrawal, R., Imieliński, T., and Swami, A. (1993). “Mining affiliation guidelines between units of things in giant databases,” in Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD worldwide convention on Administration of information. Washington, DC: Affiliation for Computing Equipment, 207–216.
Appeadu, M. Ok., and Gupta, V. (2023). Postural Instability. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing.
Baumann, C. R. (2012). Epidemiology, analysis and differential analysis in Parkinson’s illness tremor. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 18, S90–S92. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(Nationwide Institute for Well being and Care Excellence, 2017)70029-3
Bhidayasiri, R., and Truong, D. D. (2008). Motor issues in Parkinson illness: medical manifestations and administration. J. Neurol. Sci. 266, 204–215. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2007.08.028
Bi, J., Jiang, B., Liu, J. H., Lei, C., Zhang, X. L., and An, L. J., et al. (2008a). Protecting results of catalpol in opposition to H2O2-induced oxidative stress in astrocytes main cultures. Neurosci Lett. 442, 224–227. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.07.029
Bi, J., Wang, X. B., Chen, L., Hao, S., An, L. J., Jiang, B., et al. (2008b). Catalpol protects mesencephalic neurons in opposition to MPTP induced neurotoxicity by way of attenuation of mitochondrial dysfunction and MAO-B exercise. Toxicol In Vitro. 22, 1883–1889. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2008.09.007
Bi, S., and Gao, H. (2015). Affect of selegiline mixed with center-supplementing and qi-boosting decoction on the expression of TH and α-syn in rats mannequin with Parkinson’s illness [司来吉兰联合补中益气汤对帕金森病模型大鼠结肠 TH,α-Syn 表达的影响]. J. Henan Univ. Chin. Med. 35, 512–514. doi: 10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2015.03.0218
Bi, S., Liu, B., and Gao, H. (2014). Scientific commentary on Bu-Zhong Yi-Qi decoction mixed with selegiline for Parkinson’s constipation [补中益气汤加减联合司来吉兰治疗帕金森病伴功能性便秘的疗效观察]. Guiding J. Trad. Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 20, 25–27. doi: 10.13862/j.cnki.cn43-1446/r.2014.11.009
Birling, Y., Zhu, X., Avard, N., Tannous, C., Fahey, P. P., Sarris, J., et al. (2022). Zao Ren An Shen capsule for insomnia: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Sleep. 45:zsab266. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab266
Chalorak, P., Sanguanphun, T., Limboonreung, T., and Meemon, Ok. (2021). Neurorescue results of frondoside A and ginsenoside Rg3 in C. elegans mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. Molecules 26:4843. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164843
Chan, W. S., Durairajan, S. S., Lu, J. H., Wang, Y., Xie, L. X., Kum, W. F., et al. (2009). Neuroprotective results of Astragaloside IV in 6-hydroxydopamine-treated main nigral cell tradition. Neurochem. Int. 55, 414–422. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.04.012
Chaudhuri, Ok. R., Martinez-Martin, P., Brown, R. G., Sethi, Ok., Stocchi, F., Odin, P., et al. (2007). The metric properties of a novel non-motor signs scale for Parkinson’s illness: outcomes from a world pilot research. Mov. Disord. 22, 1901–1911. doi: 10.1002/mds.21596
Chen, F., Chen, S., Si, A., Luo, Y., Hu, W., Zhang, Y., and Ma, J. (2022). The long-term pattern of Parkinson’s illness incidence and mortality in China and a Bayesian projection from 2020 to 2030. Entrance. Getting old Neurosci. 14:973310. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.973310
Chen, Ok. Y., Wu, M. Y., Yang, P. S., Chiang, J. H., Hsu, C. Y., Chen, C. Y., and Yen, H. R. (2018). Utilization of Chinese language natural drugs and its affiliation with the chance of fracture in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness in Taiwan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 226, 168–175. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.021
Chen, Ok. Z., Chen, S., Ren, J. Y., Lin, S., Xiao, M. J., Cheng, L., et al. (2021). Antidepressant impact of acidic polysaccharides from Poria and their regulation of neurotransmitters and NLRP3 pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 46, 5088–5095. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210610.705
Chen, M., and Wang, W. (2014). Effectiveness of Buzhong Yiqi decoction for constipation in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness [补中益气汤加减治疗帕金森病患者便秘症状的临床观察]. J. Cardio-cerebrovascular Dis. Integr. Chin. Western Med. 12, 59–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2014.01.0033
Chen, S. Y., Xiao, S. J., Lin, Y. N., Li, X. Y., Xu, Q., Yang, S. S., et al. (2020). Scientific efficacy and transcriptomic evaluation of congrong shujing granules () in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness and syndrome of Shen (Kidney) essence deficiency. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26, 412–419. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3080-0
Chen, Y., Xu, Q., Wu, L., Zhou, M., Lin, Y., Jiang, Y., et al. (2023). REM sleep conduct dysfunction correlates with constipation in de novo Chinese language Parkinson’s illness sufferers. Neurol. Sci. 44, 191–197. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06381-5
Chi, Ok., Fu, R. H., Huang, Y. C., Chen, S. Y., Hsu, C. J., Lin, S. Z., et al. (2018). Adipose-derived stem cells stimulated with n-Butylidenephthalide exhibit therapeutic results in a mouse mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. Cell Transplant. 27, 456–470. doi: 10.1177/0963689718757408
China Nationwide Well being Fee (2020). China Official Catalogue of Dietary Medicinal Herbs. Beijing: China Nationwide Well being Fee and China State Administration for Market Regulation.
China Nationwide Well being and Household Planning Fee (2018). China Official Catalogue of Dietary Medicinal Herbs. Beijing: China Nationwide Well being and Household Planning Fee.
Cho, Ok. H., Kim, T. H., Kwon, S., Jung, W. S., Moon, S. Ok., Ko, C. N., et al. (2018). Complementary and different drugs for idiopathic Parkinson’s illness: an evidence-based medical apply guideline. Entrance. Getting old Neurosci. 10:323. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00323
Choi, J. H., Jang, M., Nah, S. Y., Oh, S., and Cho, I. H. (2018a). Multitarget results of Korean Pink Ginseng in animal mannequin of Parkinson’s illness: antiapoptosis, antioxidant, antiinflammation, and upkeep of blood-brain barrier integrity. J. Ginseng. Res. 42, 379–388. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2018.01.002
Choi, J. H., Jang, M., Oh, S., Nah, S. Y., and Cho, I. H. (2018b). Multi-target protecting results of gintonin in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-mediated mannequin of Parkinson’s illness by way of lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Entrance. Pharmacol. 9:515. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00515
Coates, P. M., Betz, J. M., Blackman, M. R., Cragg, G. M., Levine, M., Moss, J., et al. (2010). Encyclopedia of Dietary Dietary supplements, 2nd Edn. New York, NY: Taylor and Francis Group.
Dawes, M., Summerskill, W., Glasziou, P., Cartabellotta, A., Martin, J., Hopayian, Ok., et al. (2005). Sicily assertion on evidence-based apply. BMC Med. Educ. 5, 1. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-5-1
de Bie, R. M. A., Clarke, C. E., Espay, A. J., Fox, S. H., and Lang, A. E. (2020). Initiation of pharmacological remedy in Parkinson’s illness: when, why, and the way. Lancet Neurol. 19, 452–461. doi: 10.1016/S1474-442230036-3
Dong, H., Li, R., Yu, C., Xu, T., Zhang, X., Dong, M., et al. (2015). Paeoniflorin inhibition of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by way of suppressing reactive oxygen species-mediated PKCδ/NF-κB pathway. Neuroscience 285, 70–80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.008
Duncan, G. W., Khoo, T. Ok., Yarnall, A. J., O’Brien, J. T., Coleman, S. Y., Brooks, D. J., et al. (2014). Well being-related high quality of life in early Parkinson’s illness: the impression of nonmotor signs. Mov. Disord. 29, 195–202. doi: 10.1002/mds.25664
Ferry, P., Johnson, M., and Wallis, P. (2002). Use of complementary therapies and non-prescribed medicine in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness. Postgrad. Med. J. 78, 612–614. doi: 10.1136/pmj.78.924.612
Freitas, M. E., Hess, C. W., and Fox, S. H. (2017). Motor issues of dopaminergic drugs in Parkinson’s illness. Semin. Neurol. 37, 147–157. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1602423
Fu, R. H., Harn, H. J., Liu, S. P., Chen, C. S., Chang, W. L., Chen, Y. M., et al. (2014). n-butylidenephthalide protects in opposition to dopaminergic neuron degeneration and α-synuclein accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans fashions of Parkinson’s illness. PLoS ONE 9:e85305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085305
Fujimaki, T., Saiki, S., Tashiro, E., Yamada, D., Kitagawa, M., Hattori, N., et al. (2014). Identification of licopyranocoumarin and glycyrurol from natural medicines as neuroprotective compounds for Parkinson’s illness. PLoS ONE 9:e100395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100395
GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Illness Collaborators (2018). World, regional, and nationwide burden of Parkinson’s illness, 1990-2016: a scientific evaluation for the World Burden of Illness Examine 2016. Lancet Neurol. 17, 939–953. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30295-3
Gong, Y., Liang, X., Dai, Y., Huang, X., Su, Q., Ma, Y., et al. (2023). Prokinetic results of Citrus reticulata and Citrus aurantium extract with/with out Bupleurum chinense utilizing multistress-induced delayed gastric emptying fashions. Pharm. Biol. 61, 345–355. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2173249
Inexperienced, L. W., and Glasgow, R. E. (2006). Evaluating the relevance, generalization, and applicability of analysis:points in exterior validation and translation methodology. Eval. Well being Prof. 29, 126–153. doi: 10.1177/0163278705284445
Grimes, D., Fitzpatrick, M., Gordon, J., Miyasaki, J., Fon, E. A., Schlossmacher, M., et al. (2019). Canadian guideline for Parkinson illness. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 191, E989–E1004. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.181504
Gu, C., and Yuan, C. (2023). TCM syndrome distribution and rule of medicine in Parkinson’s illness [帕金森病的中医证型分布和用药规律探析]. Shanghai J. Trad. Chin. Med. 47, 12–14.
Gu, S. C., Shi, R., Gaoag, C., Yuan, X. L., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Conventional Chinese language drugs pingchan granule for motor signs and capabilities in Parkinson’s illness: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled research. Phytomedicine. 108, 154497. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154497
Guo, Ok., Zhang, Y., Li, L., Zhang, J., Rong, H., Liu, D., et al. (2021). Neuroprotective impact of paeoniflorin within the mouse mannequin of Parkinson’s illness via α-synuclein/protein kinase C δ subtype signaling pathway. Neuroreport 32, 1379–1387. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001739
Han, J., Pei, J., and Kamber, M. (2011). Knowledge mining: Ideas and Strategies. Amsterdam: Elsevier
Han, Y., Wang, T., Li, C., Wang, Z., Zhao, Y., He, J., et al. (2021). Ginsenoside Rg3 exerts a neuroprotective impact in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s illness mice by way of its anti-oxidative properties. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 909:174413. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174413
He, Z. Q., Huan, P. F., Wang, L., and He, J. C. (2023). Compound dihuang granule adjustments intestine microbiota of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s Illness mice by way of inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Neurochem. Res. 48, 3610–3624. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04004-9
Heng, Y., Zhang, Q. S., Mu, Z., Hu, J. F., Yuan, Y. H., Chen, N. H., et al. (2016). Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates motor impairment and neuroinflammation within the MPTP-probenecid-induced parkinsonism mouse mannequin by concentrating on α-synuclein abnormalities within the substantia nigra. Toxicol Lett. 243, 7–21. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.12.005
Hsiao, P. J., Lin, Ok. S., Chiu, C. C., Chen, H. W., Huang, J. S., Kao, S. Y., et al. (2015). Use of conventional Chinese language drugs (Ren Shen Yang Rong Tang) in opposition to microinflammation in hemodialysis sufferers: an open-label trial. Compl. Ther. Med. 23, 363–371. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2015.03.002
Hu, S., Han, R., Mak, S., and Han, Y. (2011). Safety in opposition to 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+)-induced apoptosis by water extract of ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 135, 34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.02.017
Huang, Q. (2012). Effectiveness of Tongfu Xingshen Capsule for Constipation in Parkinson’s Illness: A Randomised Managed Trial [通腑醒神胶囊治疗帕金森氏病功能性便秘临床研究]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou College of Chinese language Medication.
Huang, Y. J., Hsu, N. Y., Lu, Ok. H., Lin, Y. E., Lin, S. H., Lu, Y. S., et al. (2020). Poria cocos water extract ameliorates the behavioral deficits induced by unpredictable persistent gentle stress in rats by down-regulating irritation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 258:112566. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112566
Hwang, C. Ok., and Chun, H. S. (2012). Isoliquiritigenin remoted from licorice Glycyrrhiza uralensis prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in dopaminergic neurons. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 76, 536–543. doi: 10.1271/bbb.110842
Jeon, H., Kim, H. Y., Bae, C. H., Lee, Y., and Kim, S. (2020). Korean Pink Ginseng regulates intestinal tight junction and irritation within the colon of a Parkinson’s illness mouse mannequin. J. Med. Meals. 23, 1231–1237. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2019.4640
Jeon, H., Kim, H. Y., Bae, C. H., Lee, Y., Koo, S., Kim, S., et al. (2021). Korean pink ginseng decreases 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced mitophagy in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Integr. Med. 19, 537–544. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2021.09.005
Jeong, J. S., Piao, Y., Kang, S., Son, M., Kang, Y. C., Du, X. F., et al. (2018). Triple natural extract DA-9805 exerts a neuroprotective impact by way of amelioration of mitochondrial injury in experimental fashions of Parkinson’s illness. Sci. Rep. 8:15953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34240-x
Jeong, Y. H., Li, W., Go, Y., and Oh, Y. C. (2019). Atractylodis rhizoma alba attenuates neuroinflammation in BV2 microglia upon LPS stimulation by inducing HO-1 exercise and inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:4015. doi: 10.3390/ijms20164015
Jiang, W., Wang, Z., Jiang, Y., Lu, M., and Li, X. (2015). Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates motor perform in an animal mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. Pharmacology 96, 25–31. doi: 10.1159/000431100
Jun, P., Zhao, H., Jung, I. C., Kwon, O., Han, C. H., Received, J., et al. (2023). Efficacy of natural drugs remedy based mostly on syndrome differentiation for Parkinson’s illness: a scientific evaluate and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled medical trials. Entrance. Pharmacol. 14:1108407. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1108407
Jun, Y. L., Bae, C. H., Kim, D., Koo, S., and Kim, S. (2015). Korean Pink Ginseng protects dopaminergic neurons by suppressing the cleavage of p35 to p25 in a Parkinson’s illness mouse mannequin. J. Ginseng Res. 39, 148–154. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2014.10.003
Karthikkeyan, G., Behera, S. Ok., Upadhyay, S. S., Pervaje, R., Prasad, T. S. Ok., Modi, P. Ok., et al. (2022). Metabolomics evaluation highlights Yashtimadhu (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.)-mediated neuroprotection in a rotenone-induced mobile mannequin of Parkinson’s illness by restoring the mTORC1-AMPK1 axis in autophagic regulation. Phytother. Res. 36, 2207–2222. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7449
Karthikkeyan, G., Prabhu, A., Pervaje, R., Pervaje, S. Ok., Modi, P. Ok., Prasad, T. S. Ok., et al. (2021). Knowledge on dose-dependent cytotoxicity of rotenone and neuroprotection conferred by Yashtimadhu (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) in an in vitro Parkinson’s illness mannequin. Knowledge Temporary 39:107535. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107535
Kim, D., Kwon, S., Jeon, H., Ryu, S., Ha, Ok. T., Kim, S., et al. (2018). Proteomic change by Korean Pink Ginseng within the substantia nigra of a Parkinson’s illness mouse mannequin. J. Ginseng Res. 42, 429–435. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.04.008
Kim, H., Park, I., Park, Ok., Park, S., Kim, Y. I., Park, B. G., et al. (2022). The constructive results of poria cocos extract on high quality of sleep in insomnia rat fashions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Well being. 19:6629. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116629
Kim, H. J., Mason, S., Foltynie, T., Winder-Rhodes, S., Barker, R. A., Williams-Grey, C. H., et al. (2020). Motor issues in Parkinson’s illness: 13-year follow-up of the CamPaIGN cohort. Mov. Disord. 35, 185–190. doi: 10.1002/mds.27882
Kim, S. R., Lee, T. Y., Kim, M. S., Lee, M. C., and Chung, S. J. (2009). Use of complementary and different drugs by Korean sufferers with Parkinson’s illness. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 111, 156–160. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2008.09.011
Kong, W. L., Huang, Y., Qian, E., and Morris, M. J. (2020). Constipation and sleep behaviour dysfunction affiliate with processing velocity and a focus in males with Parkinson’s illness over 5 years follow-up. Sci. Rep. 10:19014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75800-4
Kwok, J. Y. Y., Huang, T. W., Tretriluxana, J., Auyeung, M., Chau, P. H., Lin, C. C., et al. (2021). Symptom burden and unmet assist wants of sufferers with Parkinson’s illness: a cross-sectional research in asia-pacific areas. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 22, 1255–1264. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2020.09.012
Li, D., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Tong, Y., and Mei, X. (2011). Fundamental Concept of Conventional Chinese language Medication, 中医基础理论, revealed in Chinese language. Beijing: Individuals’s Medical Publishing Home.
Li, H., Wang, F., Zhou, Z., Jiang, X., Li, F., Feng, Y., et al. (2022). Atractylon, a novel dopamine 2 receptor agonist, ameliorates Parkinsonian like motor dysfunctions in MPTP-induced mice. NeuroToxicology 89, 121–126. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2022.01.010
Li, L. C., Chen, J., Zhu, X. B., Guo, M., Chen, Q., Fang, H. M., et al. (2021). Developments of issues in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness in seven main cities of China from 2016 to 2019. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 36, 274–278. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000370
Li, M., Yang, H. M., Luo, D. X., Chen, J. Z., and Shi, H. J. (2016). Multi-dimensional evaluation on Parkinson’s illness questionnaire-39 in Parkinson’s sufferers handled with Bushen Huoxue Granule: a multicenter, randomized, double-blinded and placebo managed trial. Compl. Ther. Med. 29, 116–120. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2016.09.008
Li, Q., Cao, M., Wei, Z., Mei, J., Zhang, Y., Li, M., et al. (2022). The protecting impact of Buzhong Yiqi decoction on ischemic stroke mice and the mechanism of intestine microbiota. Entrance. Neurosci. 16:956620. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.956620
Li, S., and Le, W. (2021). Parkinson’s illness in conventional Chinese language drugs. The Lancet Neurol. 20:262. doi: 10.1016/S1474-442230224-8
Li, W., Gan, J., and Liu, Z. (2021). Knowledgeable consensus on built-in conventional Chinese language and Western drugs administration for sleep problem in Parkinson’s Illness (2021 version) [帕金森病睡眠障碍中西医结合管理专家共识(2021)]. J. Shanghai Univ. Chin. Med. 35, 1–6.
Lim, H. S., Kim, Y. J., Sohn, E., Yoon, J., Kim, B. Y., Jeong, S. J., et al. (2018). Bojungikgi-Tang, a standard natural components, exerts neuroprotective results and ameliorates reminiscence impairments in Alzheimer’s Illness-like experimental fashions. Vitamins 10:1952. doi: 10.3390/nu10121952
Lin, C. H., Chiu, H. E., Wu, S. Y., Tseng, S. T., Wu, T. C., Hung, Y. C., et al. (2021). Chinese language natural merchandise for non-motor signs of Parkinson’s illness in Taiwan: a population-based research. Entrance. Pharmacol. 11:615657. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.615657
Liu, M., Hu, C., Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, Q., Fang, Y., et al. (2020a). Impact of Huatan Jieyu granules in remedy of Parkinson’s illness sufferers with sleep problem recognized as symptom sample of phlegma-heat-stirring wind. J. Tradit Chin. Med. 40, 461–466. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2020.03.015
Liu, M., Yu, S., Wang, J., Qiao, J., Liu, Y., Wang, S., et al. (2020b). Ginseng protein protects in opposition to mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration by inducing mitochondrial unfolded protein response in Drosophila melanogaster PINK1 mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. J. Ethnopharmacol. 247:112213. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112213
Liu, X., Zhang, J., Wang, S., Qiu, J., and Yu, C. (2017). Astragaloside IV attenuates the H2O2-induced apoptosis of neuronal cells by inhibiting α-synuclein expression by way of the p38 MAPK pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 40, 1772–1780. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3157
Liu, Y., Zong, X., Huang, J., Guan, Y., Li, Y., Du, T., et al. (2019). Ginsenoside Rb1 regulates prefrontal cortical GABAergic transmission in MPTP-treated mice. Getting old 11, 5008–5034. doi: 10.18632/growing older.102095
Liu, Z., Li, W., and Chen, H. (2020). The professional consensus on the analysis and remedy of built-in conventional Chinese language and Western drugs in Parkinson’s illness motion issues (2020) [帕金森病运动并发症中西医结合诊治专家共识 (2020)]. Chin. J. Neuroimmunol. Neurol. 27, 247–252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2963.2020.04.001
Lökk, J., and Nilsson, M. (2010). Frequency, sort and elements related to using complementary and different drugs in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness at a neurological outpatient clinic. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 16, 540–544. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2010.06.007
Lu, P. H., Keng, J. L., Kuo, Ok. L., Wang, Y. F., Tai, Y. C., and Kuo, C. Y. (2020). An Apriori algorithm-based affiliation rule evaluation to determine herb mixtures for treating uremic pruritus utilizing Chinese language natural tub remedy. Evid. Primarily based Compl. Alter. Med. 2020:8854772 doi: 10.1155/2020/8854772
Luo, X., Li, Z., Zhu, M., Xu, P., Guo, X., Wu, Z., et al. (2021). Conventional Chinese language drugs professional consensus on analysis and remedy of Parkinson’s illness (Tremor and Spasm illness) [帕金森病 (颤拘病) 中医临床诊疗专家共识]. J. Trad. Chin. Med. 62, 2109–2116. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.23.017
Marsili, L., Marconi, R., and Colosimo, C. (2017). “Chapter twelve – remedy methods in early Parkinson’s illness,” in Worldwide Assessment of Neurobiology, eds. Ok. P. Bhatia, Ok. R. Chaudhuri, M. Stamelou (New York, NY: Educational Press), 345–360.
Mehndiratta, M., Garg, R. Ok., and Pandey, S. (2011). Nonmotor symptom advanced of Parkinson’s illness–an under-recognized entity. J. Assoc. Physicians India. 59, 302–308.
Extra, S. V., and Choi, D. Ok. (2017b). Atractylenolide-I protects human SH-SY5Y Cells from 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium-induced apoptotic cell loss of life. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:1012. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051012
Murman, D. L. (2012). Early remedy of Parkinson’s illness: alternatives for managed care. Am. J. Managed Care 18:S183.
Nationwide Institute for Well being and Care Excellence (2017). Parkinson’s Illness in Adults (NICE guideline NH71). London: Nationwide Institute for Well being and Care Excellence
Nationwide Institute of Neurological Issues and Stroke (2004). Parkinson’s Illness: Challenges, Progress, and Promise. Bethesda, MD: Nationwide Institute of Neurological Issues and Stroke.
O’Sullivan, S. S., Williams, D. R., Gallagher, D. A., Massey, L. A., Silveira-Moriyama, L., Lees, A. J., et al. (2008). Nonmotor signs as presenting complaints in Parkinson’s illness: a clinicopathological research. Mov. Disord. 23, 101–106. doi: 10.1002/mds.21813
Pan, W., Liu, J., Chen, X., Wang, Q., Wu, Y., Bai, Y., et al. (2015). A sensible consensus guideline for the integrative remedy of Parkinson’s illness in Shanghai, China. Integr. Med. Int. 2, 56–62. doi: 10.1159/000435813
Pang, Y., Zhu, S., and Pei, H. (2020). Pachymic acid protects in opposition to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion damage by the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Metab. Mind Dis. 35, 673–680. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00540-3
Park, W. H., Kang, S., Piao, Y., Pak, C. J., Oh, M. S., Kim, J., et al. (2015). Ethanol extract of Bupleurum falcatum and saikosaponins inhibit neuroinflammation by way of inhibition of NF-κB. J. Ethnopharmacol. 174, 37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.039
Parkinson’s Illness and Motion Issues Group from Neurology Department of Chinese language Medical Affiliation and Parkinson’s Illness and Motion Issues Group from Neurology Department of Chinese language Medical Physician Affiliation (2020). Guideline for analysis and remedy of Parkinson’s illness in China (the fourth version) [中国帕金森病治疗指南(第四版)]. Chin. J. Neurol. 53:14. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113694-20200331-00233
Pecci, C., Rivas, M. J., Moretti, C. M., Raina, G., Ramirez, C. Z., Díaz, S., et al. (2010). Use of complementary and different therapies in outpatients with Parkinson’s illness in Argentina. Mov. Disord. 25, 2094–2098. doi: 10.1002/mds.23235
Petramfar, P., Hajari, F., Yousefi, G., Azadi, S., and Hamedi, A. (2020). Efficacy of oral administration of licorice as an adjunct remedy on enhancing the signs of sufferers with Parkinson’s illness, A randomized double blinded medical trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 247:112226. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112226
Postuma, R. B., Berg, D., Stern, M., Poewe, W., Olanow, C. W., Oertel, W., et al. (2015). MDS medical diagnostic standards for Parkinson’s illness. Mov. Disord. 30, 1591–1601. doi: 10.1002/mds.26424
Pringsheim, T., Day, G. S., Smith, D. B., Rae-Grant, A., Licking, N., Armstrong, M. J., et al. (2021). Dopaminergic remedy for motor signs in early parkinson illness apply guideline abstract. A report of the AAN guideline subcommittee. Neurology 97, 942–957. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012868
Qiao, J., Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, S., Zhao, W., Liu, S., et al. (2022). Neuroprotective impact of Ginsenoside Re in opposition to neurotoxin-induced Parkinson’s illness fashions by way of induction of Nrf2. Mol. Med. Rep. 25:12731. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12731
Rajendran, P. R., Thompson, R. E., and Reich, S. G. (2001). Using different therapies by sufferers with Parkinson’s illness. Neurology. 57, 790–794. doi: 10.1212/WNL.57.5.790
Ramadan, S., Sabry, M. M., Saad, M. A., Angeloni, S., Sabry, O. M., Caprioli, G., et al. (2022). Dismantling Parkinson’s illness with herbs: MAO-B inhibitory exercise and quantification of chemical constituents utilizing HPLC-MS/MS of Egyptian native market crops. Nat. Prod. Res. 36, 5766–5771. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.2013836
Rascol, O., Payoux, P., Ory, F., Ferreira, J. J., Brefel-Courbon, C., Montastruc, J. L., et al. (2003). Limitations of present Parkinson’s illness remedy. Annal. Neurol. 53, S3–S15. doi: 10.1002/ana.10513
Rukavina, Ok., Batzu, L., Boogers, A., Abundes-Corona, A., Bruno, V., Chaudhuri, Ok. R., et al. (2021). Non-motor issues in late stage Parkinson’s illness: recognition, administration and unmet wants. Knowledgeable Rev. Neurother. 21, 335–352. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2021.1883428
Ryu, S., Jeon, H., Koo, S., and Kim, S. (2018). Korean Pink Ginseng enhances neurogenesis within the subventricular zone of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated mice. Entrance. Getting old Neurosci. 10:355. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00355
Sackett, D. L., (ed.). (1997). Proof-Primarily based Medication. Seminars in Perinatology. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Sanson-Fisher, R. W., Bonevski, B., Inexperienced, L. W., and D’Este, C. (2007). Limitations of the randomized managed trial in evaluating population-based well being interventions. Am. J. Prev. Med. 33, 155–161. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2007.04.007
Santos García, D., de Deus Fonticoba, T., Suárez Castro, E., Borrué, C., Mata, M., Solano Vila, B., et al. (2019). Non-motor signs burden, temper, and gait issues are probably the most vital elements contributing to a poor high quality of life in non-demented Parkinson’s illness sufferers: Outcomes from the COPPADIS Examine Cohort. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 66, 151–157. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.07.031
Santos-García, D., de Deus Fonticoba, T., Suárez Castro, E., Aneiros Díaz, A., McAfee, D., Catalán, M. J., et al. (2020). Non-motor symptom burden is strongly correlated to motor issues in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness. Eur. J. Neurol. 27, 1210–1223. doi: 10.1111/ene.14221
Shah, A. D., Quinn, N. J., Chaudhry, A., Sullivan, R., Costello, J., O’Riordan, D., et al. (2019). Recording issues and diagnoses in medical care: creating steering for healthcare professionals and system designers. BMJ Well being Care Inf. 26:100106. doi: 10.1136/bmjhci-2019-100106
Shah, V. Ok., Choi, J. J., Han, J. Y., Lee, M. Ok., Hong, J. T., Oh, Ok. W., et al. (2014). Pachymic acid enhances pentobarbital-induced sleeping behaviors by way of GABAA-ergic programs in mice. Biomol. Ther. 22, 314–320. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2014.045
Sim, Y., Park, G., Eo, H., Huh, E., Gu, P. S., Hong, S. P., et al. (2017). Protecting results of a natural extract mixture of Bupleurum falcatum, Paeonia suffruticosa, and Angelica dahurica in opposition to MPTP-induced neurotoxicity by way of regulation of nuclear receptor-related 1 protein. Neuroscience 340, 166–175. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.10.029
State Pharmacopoeia Committee of China (2020). Chinese language Pharmacopoeia. Beijing: China Medical Science and Know-how Press.
Solar, R., Wang, Ok., Wu, D., Li, X., and Ou, Y. (2012). Protecting impact of paeoniflorin in opposition to glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells by way of Bcl-2/Bax sign pathway. Folia Neuropathol. 50, 270–276. doi: 10.5114/fn.2012.30527
Tan, L. C., Lau, P. N., Jamora, R. D., and Chan, E. S. (2006). Use of complementary therapies in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness in Singapore. Mov. Disord. 21, 86–89. doi: 10.1002/mds.20662
Tan, Y., Yin, L., Solar, Z., Shao, S., Chen, W., Man, X., et al. (2020). Astragalus polysaccharide exerts anti-Parkinson by way of activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to extend mobile autophagy degree in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 153, 349–356. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.282
Tanveer, Ok., Attique, I., Sadiq, W., and Ahmad, A. (2018). Non-motor signs in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness: a cross-sectional survey. Cureus 10:e3412. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3412
Tian, Y. Y., An, L. J., Jiang, L., Duan, Y. L., Chen, J., Jiang, B., et al. (2006). Catalpol protects dopaminergic neurons from LPS-induced neurotoxicity in mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures. Life Sci. 80, 193–199. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.09.010
Tinelli, M., Kanavos, P., and Grimaccia, F. (2016). The Worth of Early Analysis and Therapy in Parkinson’s Illness: A Literature Assessment of The Potential Scientific and Socioeconomic Affect of Concentrating on Unmet Wants in Parkinson’s Illness.
Tseng, Y. T., Chang, F. R., and Lo, Y. C. (2014). The Chinese language natural components Liuwei dihuang protects dopaminergic neurons in opposition to Parkinson’s toxin via enhancing antioxidative protection and stopping apoptotic loss of life. Phytomedicine 21, 724–733. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.11.001
Van Kampen, J. M., Baranowski, D. B., Shaw, C. A., and Kay, D. G. (2014). Panax ginseng is neuroprotective in a novel progressive mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. Exp. Gerontol. 50, 95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.11.012
Waller, S., Williams, L., Morales-Briceño, H., and Fung, V. (2021). The preliminary analysis and administration of Parkinson’s illness. Austr. J. Gen. Prac. 50, 793–800. doi: 10.31128/AJGP-07-21-6087
Wan, Y., Zhu, Y., Luo, Y., Han, X., Li, Y., Gan, J., et al. (2019). Determinants of diagnostic latency in Chinese language individuals with Parkinson’s illness. BMC Neurol. 19:120. doi: 10.1186/s12883-019-1323-5
Wang, J. Y., Yang, J. Y., Wang, F., Fu, S. Y., Hou, Y., Jiang, B., et al. (2013). Neuroprotective impact of pseudoginsenoside-f11 on a rat mannequin of Parkinson’s illness induced by 6-hydroxydopamine. Evid. Primarily based Complement Alternat. Med. 2013:152798. doi: 10.1155/2013/152798
Wang, L., An, H., Yu, F., Yang, J., Ding, H., Bao, Y., et al. (2022). The neuroprotective results of paeoniflorin in opposition to MPP(+)-induced injury to dopaminergic neurons by way of the Akt/Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 122:102103. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2022.102103
Wang, L., Yang, Y. F., Chen, L., He, Z. Q., Bi, D. Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2021). Compound dihuang granule inhibits nigrostriatal pathway apoptosis in Parkinson’s illness by suppressing the JNK/AP-1 pathway. Entrance. Pharmacol. 12:621359. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.621359
Wang, Y., Xie, C. L., Wang, W. W., Lu, L., Fu, D. L., Wang, X. T., and Zheng, G. Q. (2013). Epidemiology of complementary and different drugs use in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness. J. Clin. Neurosci. 20, 1062–1067. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2012.10.022
Wen, X. (2013). Treating 68 instances of tremble of qixue kuixu sort with the Renshen Yangrong decoction [人参养荣汤治疗气血亏虚型颤证68例]. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 5, 67–69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2013.03.039
Wu, C., Zhou, X., Xie, M., Lin, J., and Gao, L. (2020). Knowledgeable consensus for TCM preventive remedy of ailments: Parkinson despair and/or anxiousness [中医治未病· 帕金森抑郁和/或焦虑专家共识]. Chin. J. Inf. Trad. Chin. Med. 1, 1–5.
Wu, Q., and Liang, X. (2018). Meals remedy and medical eating regimen remedy of conventional Chinese language drugs. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 18, 1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.yclnex.2018.01.001
Wu, W., Zhang, Q., and Zhu, Y. (2018). Scientific research on Buzhong Yiqi decoction mixed with midodrine hydrochloride in remedy of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s illness [补中益气汤联合盐酸米多君治疗帕金森病直立性低血压疗效研究]. Shaanxi J. Trad. Chin. Med. 34, 713–716.
Xia, M. L., Xie, X. H., Ding, J. H., Du, R. H., and Hu, G. (2020). Astragaloside IV inhibits astrocyte senescence: implication in Parkinson’s illness. J. Neuroinflam. 17:105. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01791-8
Xu, Y., Wang, X. S., Chen, Y., Shi, Q., and Chen, T. H. (2020). A section II randomized managed trial of renshen yangrong tang natural extract granules for fatigue discount in most cancers survivors. J. Ache Symptom Handle. 59, 966–973. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.10.018
Xu, Z., Yang, D., Huang, X., and Huang, H. (2021). Astragaloside IV protects 6-hydroxydopamine-induced SH-SY5Y cell mannequin of Parkinson’s illness by way of activating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Entrance. Neurosci. 15:631501. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.631501
Yan, S., Hao, M., Yang, H., Solar, M., Wu, B., Yue, Y., et al. (2020). Metabolomics research on the therapeutic impact of the Chinese language herb pair Fructus Aurantii Immaturus and Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae in constipated rats based mostly on UPLC-Q/TOF-MS evaluation. Ann. Palliat. Med. 9, 2837–2852. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-280
Yang, C., Mo, Y., Xu, E., Wen, H., Wei, R., Li, S., et al. (2019). Astragaloside IV ameliorates motor deficits and dopaminergic neuron degeneration by way of inhibiting neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in a Parkinson’s illness mouse mannequin. Int0 Immunopharmacol. 75:105651. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.05.036
Yang, E. J. (2023). Mixed remedy with Bojungikgi-Tang (Buzhong Yiqi decoction) and riluzole attenuates cell loss of life in TDP-43-expressing cells. Chin. J. Integr. Med. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3557-8. [Epub ahead of print].
Yang, J., Jia, M., Zhang, X., and Wang, P. (2019). Calycosin attenuates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s illness by suppressing the activation of TLR/NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Phytother. Res. 33, 309–318. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6221
Yang, N., Liu, W., Ning, H., Liu, Z., Xu, L., Zhang, J., et al. (2021). Knowledgeable consensus on analysis and remedy of despair in Parkinson’s illness with built-in conventional Chinese language and Western drugs (2021 version) [帕金森病抑郁中西医结合诊断与治疗专家共识 (2021 年版)]. Chin. J. Contemp. Neurol. Neurosurg. 21:1027. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2021.12.002
Yates, C. (2013). Proof-based apply: the parts, historical past, and course of. Counsel. Final result Res. Eval. 4, 41–54. doi: 10.1177/2150137812472193
Yun, C., and Liu, Z. (2022). Knowledgeable consensus on built-in conventional Chinese language and Western drugs within the remedy of early stage Parkinson’s illness (2021) [中西医结合治疗早期帕金森病专家共识 (2021)]. Shanghai J. Trad. Chin. Med. 56, 1–6. doi: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2021.2110003
Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Ma, C., Yan, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2016). Ginsenoside Rd and ginsenoside Re supply neuroprotection in a novel mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 5, 52–61.
Zhao, J. (2023). 18F-FDG Autoradiography Mixed with Insulin to Consider the Impact of Renshen Yangrong Decoction on Native Mind Glucose Metabolism in Aged Mice [(LeWitt and Chaudhuri, 2020)F-FDG放射自显影技术结合胰岛素评价人参养荣汤对老年小鼠大脑局部葡萄糖代谢的研究] [Doctral Degree]. Changchun: Jilin College (2023).
Zhao, Y., and Liu, Z. (2021). Consensus among expers on the integration of Chinese and Western medicine for autonomous neurofunctional disorders induced by Parkinson’s disease (2020) [帕金森病自主神经功能障碍中西医结合诊治专家共识 (2020)]. J. Nanjing Univ. Trad. Chin. Med. 37, 6–12. doi: 10.14148/j.issn.1672-0482.2021.0006
Zheng, M., Liu, C., Fan, Y., Shi, D., and Zhang, Y. (2016). Protecting results of paeoniflorin in opposition to MPP(+)-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells. Neurochem. Res. 41, 1323–1334. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1834-z
Zhong, G. (2016). Chinese language Materia Medica [中药学], 1st Edn. Hong Kong: Conventional Chinese language Medication Publishing co.
Zhong, Q. Q., and Zhu, F. (2022). Trends in prevalence cases and disability-adjusted life-years of Parkinson’s disease: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Neuroepidemiology 56, 261–270. doi: 10.1159/000524208