A significant evaluate has raised alarm over the rising threat of PFAS air pollution in agricultural soils, with implications for meals security and human well being worldwide.
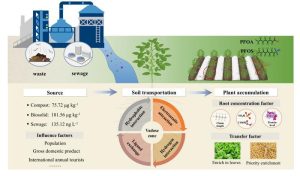
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), usually dubbed ‘eternally chemical compounds,’ are more and more getting into farmland by way of the recycling of biosolids and wastewater irrigation.
As soon as deposited in soil, these persistent pollution can infiltrate crops, doubtlessly contaminating the human meals chain.
The lengthy legacy of PFAS
First created within the Nineteen Forties, PFAS have been broadly utilized in merchandise resembling non-stick cookware, meals packaging, firefighting foams, textiles, and cosmetics.
Their sturdiness comes from the extraordinarily sturdy carbon–fluorine bonds that make them immune to pure breakdown.
Whereas this property has made PFAS worthwhile in manufacturing, it has additionally turned them into one of the persistent types of chemical air pollution.
Scientists have more and more linked PFAS publicity to severe well being dangers, together with hormone disruption, reproductive issues, and long-term toxicity.
Examine highlights agricultural dangers
The evaluate examined United Nations global waste data alongside 115 research papers spanning 2005 to 2025.
The findings recognized biosolids – nutrient-rich residues from sewage remedy crops – because the dominant supply of PFAS air pollution getting into farmland.
Geographic hotspots of contamination threat have been highlighted in Western Europe, Australia, and East Asia, the place wastewater reuse and biosolid utility are widespread.
How PFAS behave in crops
One of many examine’s most regarding revelations is how PFAS work together with crops. Longer-chain PFAS have a tendency to connect tightly to soil particles and accumulate in plant roots.
Shorter-chain PFAS, in contrast, are extremely cell, transferring with water by way of plant tissues and concentrating in edible components resembling leaves and grains.
Amongst staple crops, soybeans stood out as significantly susceptible, absorbing increased PFAS ranges because of their protein-rich composition in comparison with rice, wheat, and maize.
Weak PFAS rules go away gaps
Regardless of mounting proof of the hazards, international rules stay patchy. Only some nations, together with the USA, Germany, and Australia, have set limits on PFAS ranges in biosolids used for agricultural functions.
Nearly all of areas nonetheless lack enforceable requirements, leaving farmers and shoppers uncovered to hidden dangers.
Researchers emphasise that limiting using PFAS-contaminated waste is the best technique for stopping soil contamination, reasonably than relying solely on costly cleanup efforts.
Name for smarter monitoring
To sort out this rising problem, the evaluate recommends growing predictive fashions that mix soil traits with PFAS migration patterns.
Such instruments would assist regulators and farmers assess dangers extra precisely throughout numerous agricultural techniques. As round economic system practices increase worldwide, specialists warning that sustainable recycling should not come on the expense of spreading PFAS air pollution into the meals provide.

