·July 14, 2025
Worldwide Financial Fund
The Challenge:
India has sustained a mean financial development fee of above 6 % for the previous three many years, with a fair stronger post-pandemic rebound – over 8 % yearly throughout 2021-2024. This quick tempo of growth has not solely lifted hundreds of thousands out of poverty and raised family incomes, but in addition elevated India’s position as a significant participant within the international economic system and key contributor to international development. India’s growth path has concerned making a direct transition from an agrarian to a service economic system, differing markedly from most Western and East Asian countries (and notably China) which have relied on increasing industrial sectors drawing labor from agriculture earlier than transitioning to a bigger service sector. The Indian authorities has set a aim to rework the nation to a developed economic system (Viksit Bharat) by the centenary of its independence in 2047. The query is how the nation can buttress its development trajectory in a shock-prone and more and more fragmented world. On this context, India’s expertise might provide worthwhile insights for different rising markets navigating comparable transitions.
India’s trajectory from agriculture straight to providers has meant that it largely bypassed phases of industrialization typical of different rising markets.
The Details:
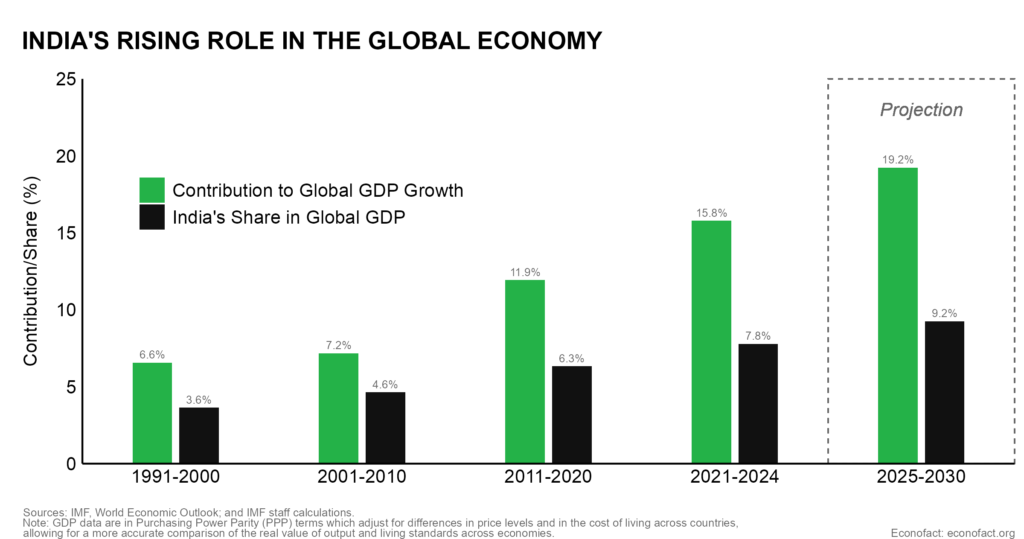
- India is now the quickest rising main economic system on the planet, with a excessive and rising contribution to international development. In Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) phrases (that’s after adjusting for variations in value ranges and the price of residing throughout international locations), India accounted for about 8.3 % of worldwide GDP in 2024 — up from lower than 3.5 % in 1990. It’s now the world’s fourth-largest economic system — behind solely China, the USA, and the European Union. In 2024, India contributed near 17 % to international GDP development, and IMF projections recommend that this contribution will rise to virtually 20 % over the following 5 years (see chart). This sustained development has translated into broad revenue good points and a big discount in poverty. In accordance with the World Bank, GDP per capita (PPP) has risen about tenfold over the previous three many years, whereas the speed of maximum poverty (revenue of $3/day or underneath) has fallen to about 5 % in 2022, down from over 45 % within the early Nineties.
- India’s financial journey has been distinctive, shifting directly from an agricultural base to a service-led structure. Agriculture’s share of worth added declined from about 30 % in 1990 to twenty % in 2024. On the identical time, the share of worth added within the providers sector grew from simply over 30 % of worth added to over 55 %, led by fast expansions in fields comparable to info know-how, finance, and journey. This transition has benefitted from advances in digital know-how and India’s widening base of educated center courses, which have allowed India to turn out to be a number one drive in enterprise service digital out-sourcing. India’s trajectory shifting from agriculture straight to providers has meant that India largely bypassed phases of industrialization which have been typical for the event of rising market economies comparable to Brazil or China.
- Will increase within the nation’s capital inventory and enhancements in productiveness have been key drivers for development, bolstered by landmark reforms. GDP development in India has shifted away from a labor-driven mannequin within the Nineteen Eighties to being more and more pushed by bodily capital and will increase within the effectivity of useful resource use for the reason that Nineties (see here and here). The shift has been linked to a number of instrumental reforms for the reason that Nineties. Particularly, the 1991 liberalization deregulated the economic system, opened it to overseas commerce and funding, and laid the inspiration for personal sector–led development. More moderen reforms have constructed on this momentum — for instance, introducing the Items and Companies Tax (GST) has helped unify the home market whereas investing in digital public infrastructure has enhanced monetary inclusion and repair supply. Collectively, these reforms have improved useful resource allocation, boosted productiveness, and strengthened the general enterprise local weather, catalyzing India’s transformation right into a fast-growing economic system.
- A prudent macroeconomic policy framework has underpinned India’s sustained development. The adoption of a versatile inflation goal regime for financial coverage in 2016 has helped anchor inflation expectations amid meals value volatility. Publish-pandemic fiscal deficits have remained inside targets, serving to to construct coverage credibility. Fiscal coverage has achieved consolidation amid a robust push in growth-enhancing public funding. Monetary sector reforms –-focusing on bettering the resilience of banks and non-bank monetary corporations, deepening monetary markets, and strengthening regulatory oversight — have enhanced monetary stability, as evidenced by improved financial institution capital, declining non-performing loans, and rising income.
- Reaching India’s aspirations of reaching high-income standing by 2047 would require sustaining robust development over the following twenty years — an more and more difficult aim within the present international setting. India would wish to develop at about 8 % yearly over the approaching many years to fulfill this goal, a tall order given historic development of 6.1 % on common over 1991-2024. In the meantime, elevated international commerce coverage uncertainty, rising protectionism, and geopolitical tensions pose exterior headwinds. One other main query will probably be how India will deal with advances in Synthetic Intelligence (AI). IMF research estimates that 26 % of Indians are in occupations with excessive AI publicity — 14 % in jobs the place AI might turn into largely complementary, probably elevating productiveness and earnings, however 12 % in occupations which are at the next threat of being displaced.
- A significant persevering with constraint on development, regardless of profitable previous financial reforms, is that India’s non-public capital inventory stays low in contrast with what is required to fulfill India’s developmental aspirations, partly reflecting remaining structural impediments to enterprise exercise. Whereas public funding has performed a outstanding position within the post-pandemic restoration, it must be strengthened by a sturdy revival in non-public funding to lift India’s productive capability and productiveness. Though non-public funding in India is comparatively excessive by rising market requirements, India’s capital inventory stays at only about one third of the level in other EMs when compared on a per-capita basis. Additional scaling up non-public funding is crucial to construct the capital inventory required for India’s transition to a developed economic system. The improved well being of company and monetary sector steadiness sheets offers a supportive backdrop, however there may be nonetheless restricted proof of widespread capability constraints that might result in a marked funding push. As well as, international financial coverage uncertainty and structural bottlenecks can weigh on investor sentiment and constrain funding, together with overseas direct funding. Cross-country evidence underscores that India nonetheless has room to meet up with best-performing rising market and international reform benchmarks, together with in judicial effectivity, credit score market entry, and commerce openness.
- With India’s comparatively younger inhabitants, labor’s contribution to development has been rising. However a good portion of India’s labor drive stays underutilized, and the favorable demographic window is progressively narrowing. Whereas labor has traditionally performed a comparatively restricted position in driving India’s development, its contribution elevated considerably throughout the post-pandemic interval, supported by rising labor drive participation and employment. This shift highlights the potential of India’s demographic dividend, outlined as the expansion advantages from an growing working age inhabitants. India’s working age inhabitants is projected to proceed to extend within the subsequent decade, in contrast to other countries like China that will experience a rising demographic drag as their populations age. Nevertheless, the expansion advantages from India’s rising youthful working-age inhabitants might be eroded by the excessive portion of the Indian workforce nonetheless employed in comparatively low-productivity and casual sectors. An additional constraint is that, regardless of notable good points lately, feminine labor drive participation stays comparatively low. With out a substantial growth in high-quality and formal-sector jobs, the complete advantages of the demographic alternative might go unrealized. Furthermore, the window to reap the demographic dividend is narrowing because the share of working-age inhabitants is projected to start out declining progressively after 2034.
- However current success in enterprise service exports, India stays a comparatively closed economic system that doesn’t take full benefit of potential worldwide commerce and funding alternatives. Whereas, just lately, efforts have been made to simplify and scale back tariff charges, India’s common tariff ranges stay excessive in comparison with peer rising markets. On the funding entrance, whereas FDI flows have declined broadly all over the world lately, the decline has been extra pronounced for India, whose share in international FDI has declined to about 2 % in 2023, from about 2½ % throughout 2014-19.
India’s expertise can also provide worthwhile classes for different international locations pursuing excessive and sustained development. A key takeaway is that macroeconomic stability – anchored by sound fiscal, financial, and monetary insurance policies – offers a important basis for sustained development. This must be strengthened by instrumental reforms. India’s service-led development mannequin, which distinguishes itself from the normal manufacturing-led development, additionally affords a possible different development trajectory for different rising economies. That stated, sustaining excessive development will turn out to be more and more difficult amid evolving structural headwinds each from exterior and inside forces. To satisfy these challenges, international locations must mobilize all engines of development inside the manufacturing and providers sectors, supported by a secure macroeconomic framework, continued reforms, and efficient coverage implementation.
Delivering India’s formidable imaginative and prescient for its economic system in 2047 would require vigorous reforms and insurance policies to completely unleash all engines of development — labor, capital, and productiveness. Key priorities embrace labor and product market reform, commerce and funding liberalization, and powerful coverage frameworks in assist of a secure financial setting. Complementary efforts — comparable to reforms in agriculture, land, and the judiciary, together with investments in training, expertise, public well being, and elevating feminine labor drive participation — will probably be important to speed up human capital accumulation and allow the shift towards extra productive sectors. By additional decreasing commerce boundaries and advancing commerce and funding agreements, India might entice overseas funding, improve export competitiveness, facilitate know-how switch, and strengthen international worth chain integration — serving to place India nicely in a quickly evolving international economic system.
Subjects: