The panel additionally referred to as for restrictions on HFSS meals advertising — particularly towards kids and for necessary warnings round faculties and on digital platforms |Picture used for representational objective solely
| Picture Credit score: Getty Photographs through AFP
A collective of public well being consultants, scientists, authorized professionals, and client rights advocates on June 3, 2025 issued a renewed name to the Central authorities to adopt mandatory front-of-pack warning labels on food and beverage products excessive in fats, sugar, and salt (HFSS). The demand was made throughout a digital press convention convened to launch a nationwide Place Assertion on Entrance-of-Pack Diet Labelling (FOPNL).
The occasion, organised by the Diet Advocacy in Public Curiosity (NAPi), introduced collectively greater than 25 well being and civil society organisations which have endorsed the Place Assertion.
The context for the convention was the Supreme Court docket’s commentary throughout a listening to in April 2025 on a public curiosity litigation regarding deceptive meals packaging and insufficient labelling practices. The Court docket famous that a number of broadly consumed packaged meals merchandise, lacked clear front-of-pack info concerning their well being dangers. It directed the Meals Security and Requirements Authority of India (FSSAI) to revise and finalise its pending 2022 draft regulation on FOPNL inside a three-month timeframe.
The Place Assertion offered on the convention requires the immediate implementation of interpretive warning labels on HFSS merchandise to allow knowledgeable client decisions and stem the rising tide of non-communicable ailments (NCDs) in India.
Ok. Srinath Reddy, former president of the Public Well being Basis of India, highlighted the hazards of ultra-processed meals (UPFs), likening their well being claims to the paradox of respiratory polluted air. “Saying ultra-processed meals offers vitamins is like saying polluted air additionally offers oxygen,” he stated. Audio system Arun Gupta, Nationwide Convener of NAPi, elaborated on India’s regulatory delays and referred to as for a coverage that displays world well being requirements.
Chandrakant Lahariya of the Basis for Individuals-centric Well being Programs, offered scientific findings from India, reiterating that HFSS meals are instantly linked to the rise in way of life ailments. Diabetologist Banshi Saboo highlighted the alarming enhance in diabetes and weight problems, stating that client decisions are closely influenced by misleading packaging and unregulated well being claims.
Ashim Sanyal, chief working cfficer at VOICE( Voluntary Organisation in Curiosity of Shopper Schooling) addressed the problem of label literacy and the confusion brought on by star-based or site visitors mild labelling techniques, whereas senior advocates M.R. Rajendran Nair and Rajiv Shankar Dvivedi detailed the Supreme Court docket’s observations within the ongoing PIL looking for stricter meals labelling laws.
Extremely-processed meals typically have larger sugar content material in comparison with minimally processed meals, picture from the convention discussing meals content material and the necessity for clear labelling.
| Picture Credit score:
Particular Association

Name for WHO-alinged nutrient profiling mannequin
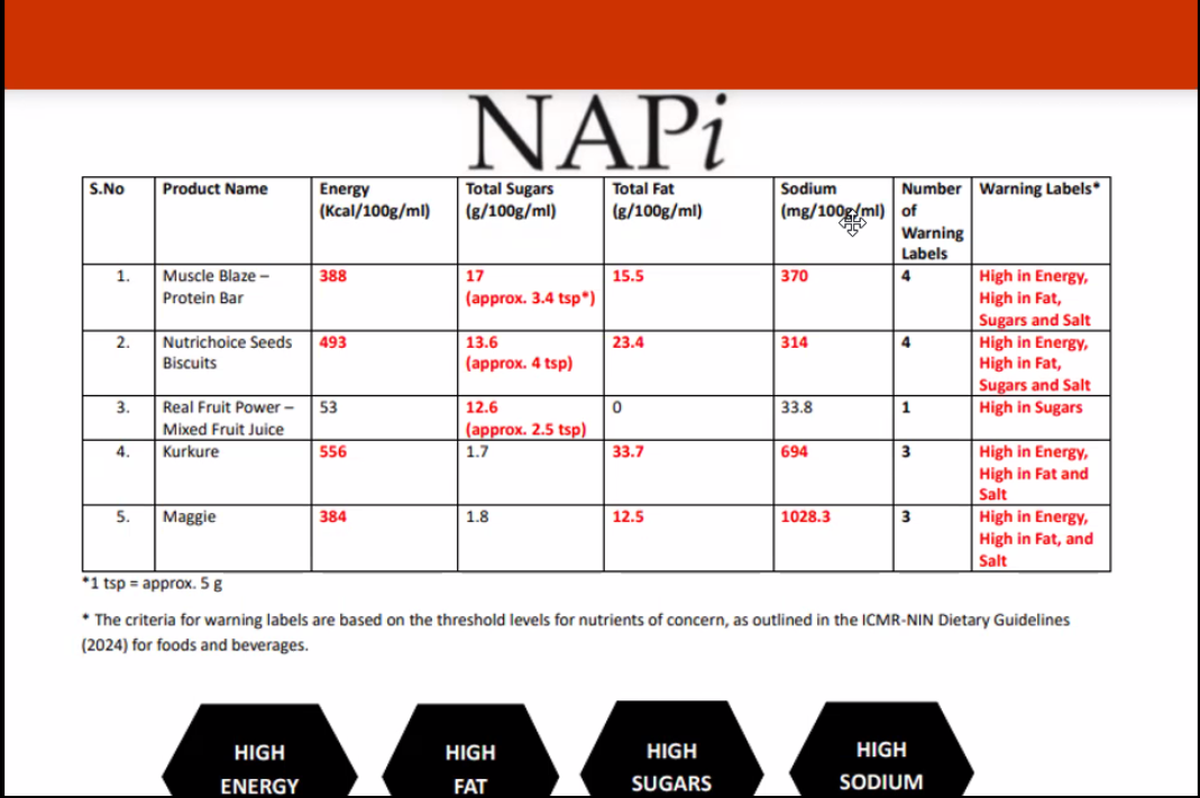
In India, a multi-state trial performed in 2022 by the Worldwide Institute for Inhabitants Sciences (IIPS), Mumbai and CMR – NIN in India with over 2,800 members confirmed that warning labels outperformed all different types of labelling in enabling shoppers to establish unhealthy merchandise. A separate examine by ICMR-NIN confirmed that transient publicity to such labels led to measurable adjustments in buying selections.
Audio system additionally mentioned the Indian Diet Score (INR), a star-based system proposed by the FSSAI, saying that it fails to alert shoppers about well being dangers. As a substitute, they identified, it creates a “well being halo” round processed meals merchandise that must be averted, not inspired.
Drawing on worldwide examples, the panel referred to Chile’s use of black octagonal warning labels that state “Excessive in Sugar,” “Excessive in Salt,” or “Excessive in Fats.” The introduction of those labels resulted in a 24 % drop in sugary beverage consumption throughout the first yr of implementation. Mexico adopted related warning labels after years of rising weight problems. These techniques are based mostly on nutrient profiling fashions really helpful by the WHO, they usually have proven that clear, interpretive warnings are more practical than numeric or star-based labels in influencing client behaviour and business practices.

Chile makes use of black, octagonal warning labels (often called “excessive in” labels) on packaged meals and drinks that exceed sure nutrient thresholds for sugar, sodium, saturated fats, and/or energy. These labels are mandated by the Chilean Regulation of Meals Labeling and Promoting
| Picture Credit score:
Particular Association

Crucially, the Assertion requires the Indian authorities to safeguard labelling legal guidelines from being weakened in worldwide commerce negotiations, akin to the continued India–UK Free Commerce Settlement.
Revealed – June 06, 2025 10:19 am IST
