The failed Soviet spacecraft Kosmos 482 will conclude its roughly 50-year jaunt by way of Earth’s orbit this weekend, with specialists predicting it might crash again to our planet as quickly as tonight (Might 9).
The latest predictions from the European Space Agency (ESA) reveal that the Kosmos 482 Descent Craft is poised to reenter Earth’s ambiance at roughly 2:26 a.m. EDT (06:26 GMT) on Saturday, Might 10. The uncertainty for the prediction is plus or minus 4.35 hours, giving us an estimated reentry window of roughly 10 p.m. EDT Friday (Might 9) to 7 a.m EDT Saturday, in accordance with ESA.
Kayhan House, a Colorado-based area know-how firm that is additionally been monitoring the craft, predicts a good narrower reentry window. At press time, the corporate’s latest estimate predicts a reentry time of two:28 a.m. ET (6:28 GMT) on Might 10, plus or minus 2.4 hours.
“The atmospheric density within the decrease altitudes (50 to 300 km) [30 to 185 miles] may be very unsure, which can lead to giant prediction uncertainties,” Derek Woods, senior astrodynamics engineer at Kayhan House, advised Reside Science in an e-mail.
The place will Kosmos 482 land?
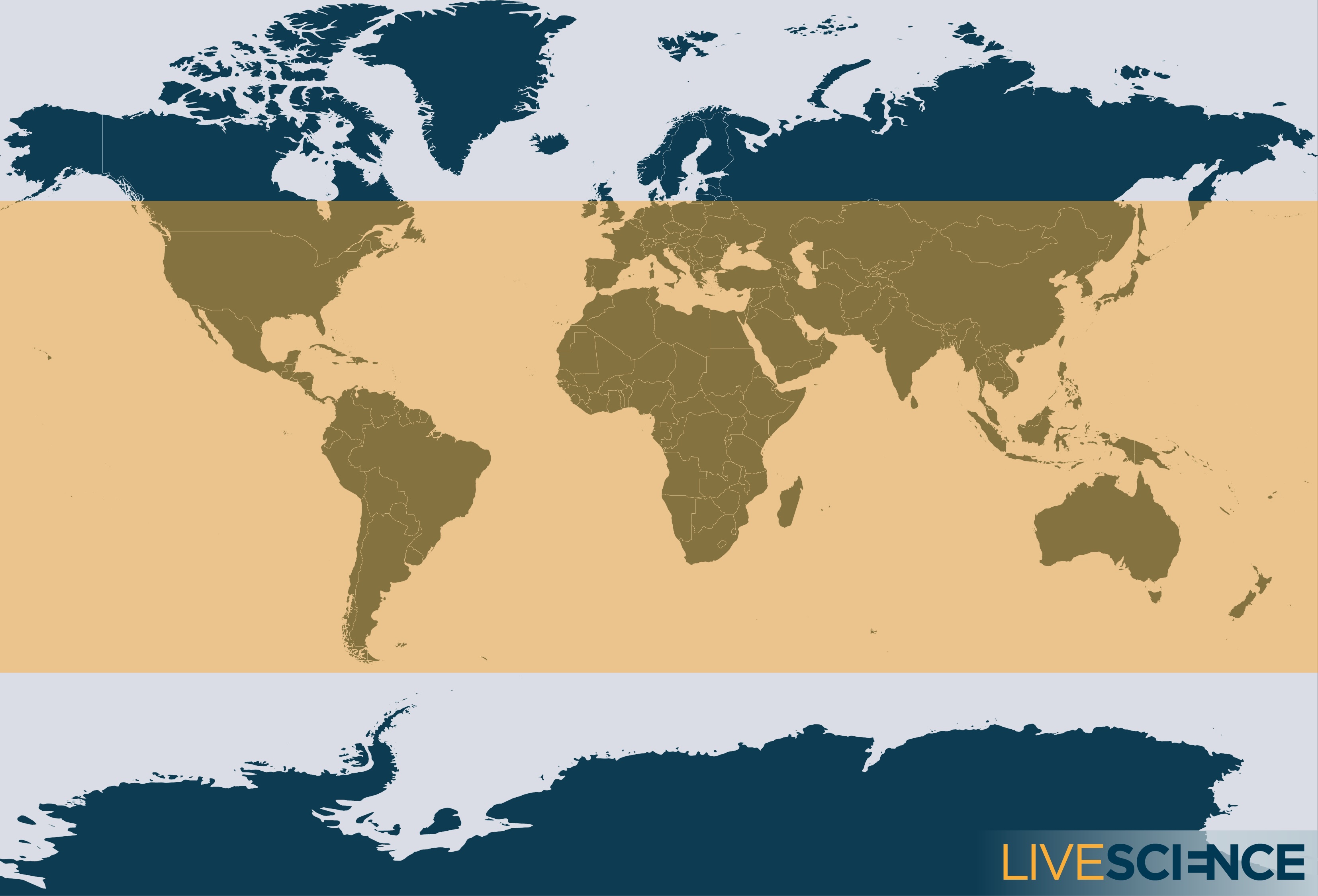
Falling like a meteor by way of the ambiance, the roughly 3-foot-wide (1 meter), 1,091 pound (495 kilograms) craft could hit virtually anywhere on the planet. It might land at any level between 52 levels north and 52 levels south — an infinite swath of the planet that features virtually each main populated space — in accordance with ESA.
Associated: Doomed Soviet spacecraft tumbling toward Earth may already have its parachute out, new images hint
Fortunately, the chances are overwhelmingly in favor of the spacecraft touchdown within the ocean, as most uncontrolled area junk reentries do. Specialists will not be capable to slim down the touchdown zone till hours earlier than the reentry occurs, because of the considerably unpredictable results of atmospheric drag.
The chance of the out-of-control spacecraft hitting an individual is “the standard one-in-several-thousand likelihood” related to falling area particles, Jonathan McDowell, an astrophysicist on the Harvard-Smithsonian Heart for Astrophysics, wrote in a blog post.
What’s Kosmos 482?
The Kosmos 482 probe was constructed and launched in 1972 as a part of the Soviet Union’s Venera mission to discover Venus. The Soviets efficiently launched the Venera 7 and eight probes, which had been the primary two spacecraft to efficiently land on Venus in 1970 and 1972, respectively.

Kosmos 482 was constructed as a sister probe to Venera 8. Nonetheless, attributable to a malfunction with the Soyuz rocket that launched it into area, the probe failed to attain sufficient velocity to achieve Venus, as a substitute getting caught in an elliptical, or oval-shaped, orbit round Earth for greater than 50 years — till now.
Designed to outlive a fiery fall by way of Venus’ ambiance, the Kosmos 482 Descent Craft is more likely to keep in a single piece because it crashes to Earth this weekend, Marco Langbroek, a lecturer in area situational consciousness at Delft Technical College within the Netherlands who first found the lander’s imminent return, wrote in a blog post. Will probably be touring at roughly 150 mph (242 km/h).
Half of a bigger downside
Whereas its intriguing historical past has earned the lander media consideration, Kosmos 482 is only one of greater than 1.2 million items of area junk in Earth’s orbit bigger than 0.4 inches (1 centimeter), in accordance with an ESA report printed in April.
Orbital collisions and uncontrolled reentries have gotten more and more frequent, with “intact satellites or rocket our bodies … now re-entering the Earth ambiance on common greater than thrice a day,” in accordance with the ESA report.
The bigger items of area junk come from a variety of spacecraft, rockets and boosters which are sufficiently big to outlive reentry and attain the bottom.
“We’re seeing an increase in reentries involving bigger objects that may partially survive and attain the floor,” Woods stated. “A few of these bigger objects are defunct area race-era objects like KOSMOS 428 DESCENT CRAFT. These objects had been in extremely eccentric orbits and at the moment are naturally decaying after many years in area.”
Because the variety of new satellites in Earth’s orbit will increase yearly, it should grow to be extra necessary than ever for missions to have “managed end-of-life plans for giant objects” and for area businesses to put money into particles removing know-how, Woods added.
