Picture: Sanjay Kanojia/NurPhoto by way of Getty Photographs
Picture: Sanjay Kanojia/NurPhoto by way of Getty Photographs
Here’s a sector-wise evaluation of a few of Finances bulletins in 4 key areas: Infrastructure, Agriculture, Manufacturing and Consumption.
Infrastructure
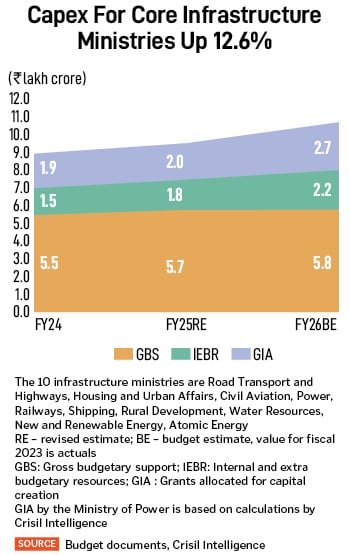
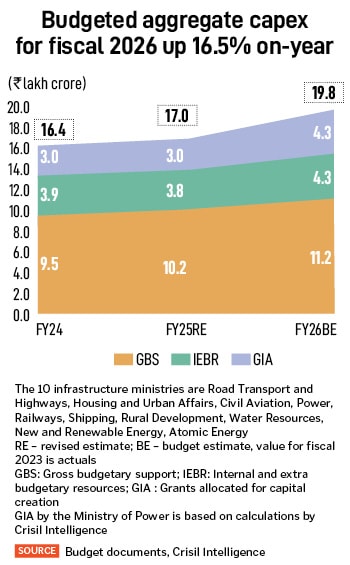
- Put up the pandemic, the central authorities’s capex outlay for infrastructure ministries has risen from Rs6.6 lakh crore in fiscal 2021 to Rs9.6 lakh crore in 2025 (compound annual development fee of 9.5 p.c). This has been spent on rural roads, highways, airports, railways and energy to enhance bodily connectivity, cut back logistics prices and improve competitiveness. Additional, with Rs10.7 lakh crore allocation for fiscal 2026, the stage is now set for improved personal sector participation, with a deal with selling PPP [public private partnership] initiatives throughout infrastructure ministries.
- The central authorities’s help to states via interest-free loans would possible increase state-level infrastructure improvement.
- The following section in asset monetisation is predicted to help potential reinvestment alternatives and assist the federal government meet its fiscal deficit goal.
- Granting of infrastructure standing to vessels of a sure dimension within the delivery business will give easy accessibility to lengthy tenure, low-cost funding to Indian ship producers, which is able to assist them purchase and function extra ships.
Additionally learn: Will the Union Budget boost the economy?
- The Maritime Growth Fund ensures substantial authorities help to the business, which is able to assist in growing home manufacturing while boosting worldwide commerce. This may assist strengthening India’s place within the international shipbuilding market and assist the nation grow to be among the many prime shipbuilders globally as per the Amrit Kaal Imaginative and prescient 2047.
- City infrastructure initiatives in areas pertaining to redevelopment of cities, water and sanitation, and metro rail improvement will obtain financing increase and enhance way of life for residents in city localities.
- Growth of smaller airports and helipads in hilly, aspirational and northeast areas would allow higher air connectivity within the distant places. This could allow environment friendly motion of passengers and cargo in these places.
Agriculture
- The outlay for the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare dipped ~3 p.c for fiscal 2026BE (budgeted estimates), in contrast with fiscal 2025RE (revised estimates). Allocation underneath schemes supporting sustainability, holistic agriculture improvement, local weather resilience and post-harvest administration witnessed development, starting from 8 p.c underneath the Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA) to 42 p.c in case of Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY). Nevertheless, allocation underneath the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana plunged 23 p.c.
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare additionally launched a number of schemes aimed in the direction of complete planning for fruits, greens and cotton, cultivation of makhana, high-yielding seed varieties and lowering import dependence for pulses, with a mixed corpus of ~Rs2,200 crore.
- The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying noticed a 37 p.c leap in allocation for fiscal 2026BE, in contrast with fiscal 2025RE. The Division of Fisheries obtained a considerable fillip (62 p.c over fiscal 2025RE) following the announcement of the Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Growth Fund launched to assist the event of infrastructure in marine and inland fisheries. The outlay for Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana grew to Rs2,465 crore for fiscal 2026 from Rs1,500 crore for fiscal 2025RE.
Additionally learn: Budget 2025: Government’s big push for agri growth
- The fundamental customs responsibility (BCD) on frozen fish paste (surimi) diminished to five p.c from 30 p.c, which is used for the manufacture of surimi analogue merchandise for exports. Additional, BCD on fish hydrolysate was diminished to five p.c from 15 p.c, which is used for the manufacture of aquatic feed
- Beneath Ministry of Chemical substances and Fertilisers, the outlay for the Division of Fertilisers dipped 14 p.c. Subsidy allocation for urea stays unchanged over fiscal 2025RE, whereas that for non-urea declined 6 p.c in fiscal 2026BE.
- Allocation for the Division of Rural Growth grew ~8 p.c for fiscal 2026BE. That for short-term employment programme underneath the Mahatma Gandhi Nationwide Rural Employment Assure Act, 2005, accounting for ~46 p.c share in whole allocation, remained at par with fiscal 2025RE. In the meantime, allocation for the scheme specializing in long-term improvement comparable to rural homes (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana or PMAY) witnessed a major leap of ~69 p.c over fiscal 2025RE.
- The Ministry of Meals Processing noticed a 56 p.c leap in allocation for fiscal 2026. Outlays for the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY) and Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Meals processing Enterprises Scheme (PM FME) jumped 43 p.c and 67 p.c, respectively. The production-linked incentive scheme received a 71 p.c increase to advertise Indian meals manufacturers globally.
Manufacturing
- The initiative on clear know-how manufacturing, complemented by the PLI scheme, is predicted to considerably increase the home manufacturing of EV batteries, thereby lowering the nation’s heavy reliance on imports (presently 90-95 p.c for EV batteries) and enhancing its international competitiveness in rising and inexperienced know-how sectors.
- The elimination of BCD on important supplies and capital items required for EV manufacturing demonstrates the federal government’s robust dedication to speed up EV adoption. It’s anticipated to facilitate the localisation of battery manufacturing, cut back manufacturing prices and allow large-scale manufacturing, thereby lowering India’s dependence on imports.
- India’s electronics exports surged to $29.1 billion in fiscal 2024 from $5.7 billion in fiscal 2015, with cellphones rising because the second-largest contributor to general exports this fiscal. Discount in BCD on digital elements is predicted to reinforce the competitiveness of Indian producers, who have been beforehand hindered by excessive tariffs, and allow them to higher compete with friends comparable to Vietnam. The decrease responsibility will cut back manufacturing prices, enhance margins and exports and end in larger integration with international worth chains.
Additionally learn: Budget 2025: Can the National Manufacturing Mission help turn India into a global manufacturing hub?
- India’s efforts to develop home manufacturing is being bolstered by the worldwide provide chain de-risking technique, which goals to capitalise on the nation’s export potential in key sectors comparable to electronics and prescription drugs. By positioning itself as a producing hub with an unlimited shopper market, India is poised to draw elevated investments and create new job alternatives, having already demonstrated spectacular export development in electronics (19 p.c CAGR) and prescription drugs (6 p.c CAGR) between fiscals 2016 and 2024, outpacing the nation’s general merchandise exports development of 5 p.c.
- India’s manufacturing sector logged a 7.5 p.c rise in employment to 1.85 crore individuals in fiscal 2023. Regardless of decrease manpower prices, labour productiveness is 30-50 p.c decrease than competing nations. Bridging this hole requires specialised expertise and technological capabilities, which could be achieved via Nationwide Centres of Excellence for Skilling, enabling India to leverage its demographic dividend.
- The introduction of the Funding Friendliness Index of States will allow states to benchmark their efficiency, establish areas of enchancment and share greatest practices. By fostering competitors, innovation and cooperation, this index will assist states create a conducive enterprise setting and stimulate development. India’s federal construction makes this index important as states play a important function in attracting investments.
- Allocation to the PLI scheme has jumped 87 p.c to Rs17,517 crore for fiscal 2026, geared toward driving development throughout industries and enhancing competitiveness. The rise in outlay is notable for electronics (accounting for over half of the allocation), textiles, white items and IT {hardware} sectors. Capex is predicted to peak within the subsequent two fiscals, adopted by incentive payouts, which is able to help the expansion of Indian companies and cut back import dependence.
Consumption
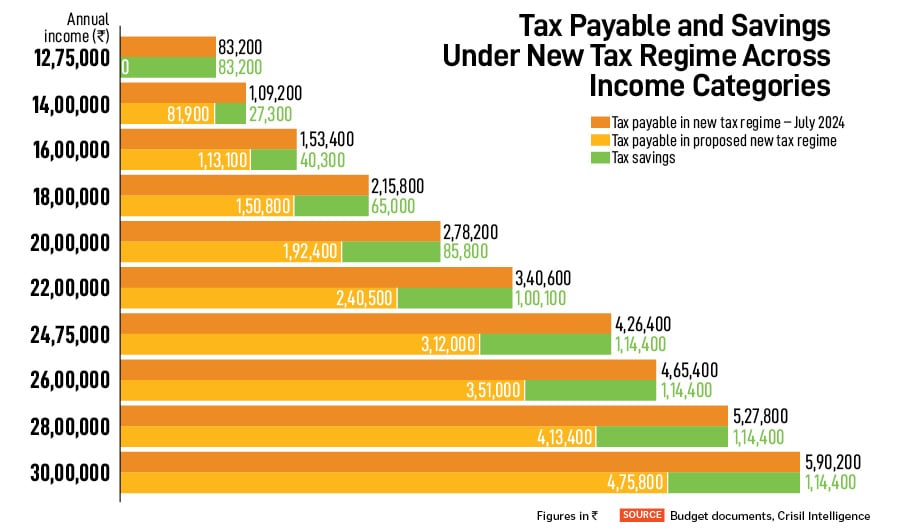
These incomes Rs12,75,000 yearly will obtain a tax advantage of Rs83,200 in contrast with the brand new tax regime of July 2024. For these not eligible for this profit, the revised tax slabs within the new regime will nonetheless enhance web money in hand by a most of Rs1,14,400 every year throughout revenue classes (this cover is for annual revenue over Rs24,75,000 within the proposed new tax regime).