A new astronomical picture reveals a one-of-a-kind deep area object that appears to look down at us on Earth just like the Eye of Sauron, portrayed as a flaming eye in The Lord of the Rings motion pictures. That object, proven right here, is known as a blazar, a jet of radiation issuing from a supermassive black gap, and it’s shining deep within the coronary heart of an energetic galaxy 3.5 billion light-years away.
Also referred to as PKS 1424+240, this blazar occurs to be one of many brightest within the sky. It has puzzled astronomers because it was found within the Seventies. Although its jet seems to maneuver sluggishly, it additionally appears to be one of many greatest emitters of gamma rays and high-energy neutrinos, these almost massless and chargeless ghost particles that abound throughout the universe. Sluggish and high-energy don’t typically go collectively, however the newly launched picture provides some recent clues to assist remedy the thriller.
PKS 1424+240 is a one-of-a-kind blazar
“That is the primary time we’ve ever received such a transparent image from contained in the jet,” says astrophysicist Yuri Kovalev on the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn in Germany. “We see emissions throughout the central brilliant area the place the supermassive black gap is.” Kovalev is the creator of a new study within the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics that stories that PKS 1424+240 is aligned in such a manner that astronomers on Earth can look down all the size of the jet.
Compiled from knowledge gathered throughout greater than 15 years of exact radio-telescope observations, the picture reveals that this explicit blazar is pointed nearly straight on the Earth, permitting an unprecedented have a look at what is occurring inside. The ringed layers seen within the picture symbolize a donut-shaped magnetic area on the base of the jet, which might be accountable for focusing the jet and accelerating particles like neutrinos. As a result of the jet is so intently aligned with the Earth, the high-energy neutrino emission might also be amplified by the results of particular relativity, boosting its brightness. On the identical time, the jet could solely seem like transferring slowly on account of so-called projection results. This explicit optical phantasm is why while you have a look at an oncoming practice that’s approaching head on, it appears to journey slowly, till it’s upon you.
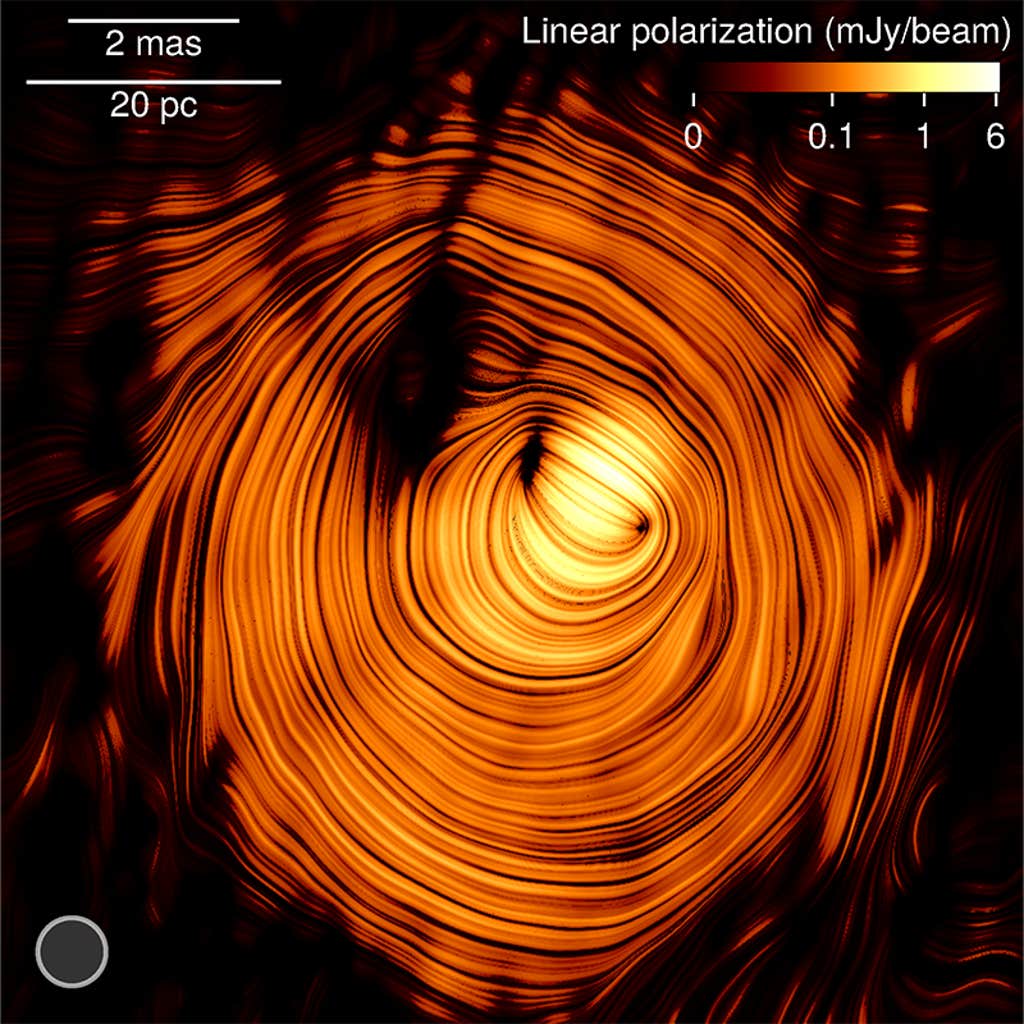
Kovalev and his colleagues have studied this explicit blazar since 2009 with a synchronized meeting of 10 radio-telescopes that stretches from Hawaii to the Caribbean. The synchronization of those telescopes means all the array successfully works like a single radio dish greater than 5,000 miles throughout.
Scientists aren’t positive why the supermassive black holes on the facilities of some galaxies form blazars, whereas most others don’t. Kovalev says the brand new research will assist researchers higher perceive the blazar jets and the highly effective, twisted magnetic fields on the heart of black holes which might be thought to create them.
“That is the primary time we’ve ever received such a transparent image from contained in the jet.”
Blazars are comparatively frequent—astronomers have now detected greater than 3,000 of them. However solely a couple of tenth of these emit high-energy neutrinos, which Kovalev thinks are created when comparatively heavy protons are accelerated to just about the velocity of sunshine close to the floor of the supermassive black gap. Protons are comparatively huge particles—about 1,800 instances heavier than an electron, and billions of instances heavier than a neutrino—and the truth that neutrinos are created in any respect is a clue to the method that creates them. “Excessive-energy neutrinos are a smoking gun for environment friendly proton accelerators,” he says, and so higher understanding how supermassive black holes can speed up such huge particles is an “thrilling and difficult drawback.”
Boston College’s Alan Marscher, a professor emeritus of astronomy who research blazars however who was additionally not concerned within the research, notes that Kovalev’s suggestion that the neutrinos type close to the floor of the central black gap isn’t the one believable rationalization for them. As a substitute, the neutrinos could have been created by magnetic shockwaves that happen inside a blazar jet because it expands, he says.
“PKS 1424+240 is a one-of-a-kind blazar,” says astrophysicist Raffaele D’Abrusco of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, who was not concerned within the research. “This very peculiar blazar occurs to have its jet nearly completely aligned to our line of sight … This particular orientation offers us an opportunity to straight examine areas of the jet which might be often not accessible.”
Metropolis College of Paris astrophysicist Matteo Cerruti, an skilled in blazars, provides that merely capturing the “Eye of Sauron” picture is itself extraordinary, as a result of the intense distance between PKS 1424+240 and Earth means a exact alignment is required to watch it with radio telescopes: “Getting observational proof of such a tiny viewing angle is an impressive end result.”
Lead picture: Y.Y. Kovalev et al.


