By Ignacio Campomanes, Nina Dannaoui-Johnson, Annie (Yu-Lin) Lee, and Joseph Lemoine
Desk of contents
The harmful authoritarian narrative
A harmful perception has taken root globally: that political freedom is just not important to prosperity and should even be an impediment to financial development. This report demonstrates that this narrative is just not supported by rigorous empirical proof. Quite the opposite, the Indexes present that political freedom does result in stronger long-term development. In reality, the method of democratization alone offers a mean 8.8 % enhance to gross home product (GDP) per capita after twenty years in comparison with its autocratic friends.
The deterioration of political freedom that started in 2012 stays an ongoing pattern affecting nations throughout all areas and revenue ranges. The persevering with erosion of core political rights, corresponding to freedom of expression and affiliation, in addition to the weakening of institutional checks on government energy, together with judicial and legislative oversight, are alarming developments highlighted on this 2025 replace of the Freedom and Prosperity Indexes.
The advantages of political liberalization take time to materialize. Policymakers have to be persistent and affected person earlier than reaping the rewards of liberalization. And the identical logic doubtless applies in reverse: Declines in political freedom could not have instant financial penalties, however they carry long-term dangers. Complacency within the face of democratic backsliding could in the end jeopardize the prosperity of the following technology.
Though the Freedom and Prosperity Indexes presently seize this decline of freedom most clearly within the political dimension, the outlook for the rule of regulation and financial freedom is just not a lot better. The erosion of democratic establishments and oversight mechanisms will doubtless contribute to declines within the rule of regulation and financial governance. Executives unchecked by legislatures or civil society are much less more likely to be held accountable for bureaucratic inefficiency or corruption, and extra more likely to pursue dangerous financial insurance policies.
The authoritarian narrative have to be challenged with rigorous analysis and evidence-based evaluation. Historical past exhibits that it was free establishments—political, authorized, and financial—that enabled as we speak’s most developed nations to flee poverty and obtain outstanding prosperity over the previous 2 hundred years. The Freedom and Prosperity Heart stays dedicated to this mission, working alongside 1000’s of freedom advocates all over the world to safeguard and advance the establishments that foster long-term prosperity.
What do the Freedom and Prosperity Indexes measure?
The Atlantic Council’s Freedom and Prosperity Center was created with the mission to extend the well-being of individuals in every single place—and particularly of the poor and marginalized in creating nations—via unbiased, data-based analysis on the connection between freedom and prosperity. The cornerstone of this undertaking is the Freedom and Prosperity Indexes: a rigorous effort to evaluate the evolution of freedom and prosperity all over the world, going again three many years.
The 2 indexes are primarily based on well-established theoretical definitions of the ideas of freedom and prosperity, matched with revered empirical measures produced by worldwide establishments, together with the United Nations, the World Financial institution, the V-Dem undertaking, or Fraser Institute.
The Freedom Index
We consider freedom comprehensively, as a mixture of a political dimension (democracy and particular person rights), a authorized dimension (the rule of regulation), and an financial dimension (free-market financial system). Due to this fact, the Freedom Index aggregates three subindexes (political, authorized, and financial), every masking a number of elements.
The Freedom Index consists of three equally weighted subindexes: political, authorized, and financial
The political subindex measures the extent to which governments and lawmakers are conscious of the calls for of residents and respect their particular person rights and liberties. The extra democratic the political system, and the extra it permits for residents to oppose and contest these in energy, the extra public insurance policies are anticipated to replicate the preferences of a majority of the inhabitants. The political subindex has 4 elements: (1) elections; (2) political rights; (3) civil liberties; and (4) legislative constraints on the manager.
The authorized subindex measures the diploma to which a rustic abides by the rule of regulation—that’s, whether or not residents and authorities officers are certain by and abide by the laws and legal guidelines of the land. It thus displays certainty, stability, and predictability. The authorized subindex consists of 5 elements: : (1) readability of the regulation; (2) judicial independence and effectiveness; (3) forms high quality and corruption; (4) safety; and (5) informality.
The financial subindex is designed to measure whether or not most financial exercise in a rustic is guided by the ideas of free and aggressive markets. An economically free society enhances the incentives to work and make investments. Companies and people may seize the features of an environment friendly allocation of sources guided by the worth mechanism, and absolutely exploit the financial potential of its inhabitants. The financial subindex contains 4 elements: (1) property rights; (2) commerce freedom; (3) funding freedom; and (4) ladies’s financial freedom.
We scale every part so that each one have the identical vary (0–100), and compute every subindex because the unweighted common of its elements. Lastly, we arrive at a Freedom Index rating for every nation for every year, once more utilizing the unweighted common of the three subindexes.
With the intention to supply an intuitive and easy illustration of the variations in freedom throughout nations, we assign considered one of 4 freedom classes (Excessive Freedom, Average Freedom, Low Freedom, and Lowest Freedom) to every country-year commentary. To take action, we use the Freedom Index rank for every year, labeling the extent of freedom of the primary quartile of nations as “Excessive Freedom” (those who rank 1–41), “Average Freedom” for these within the second quartile (rating 42–82), “Low Freedom” the third quartile (rating 83–123), and “Lowest Freedom” these within the backside quartile (rating 124–164).
The Prosperity Index
The Prosperity Index additionally takes a broad view, going past the measurement of pure materials well-being and together with further social elements that we see as essential for the dialogue of a “affluent society.” The Prosperity Index has six elements: (1) revenue; (2) well being; (3) schooling; (4) inequality; (5) minorities; and (6) surroundings. The primary three elements seize particular person flourishing, whereas the final three assess whether or not prosperity is shared and sustainable.
Revenue per capita is essentially the most extensively used indicator of prosperity in financial and social science analysis. A affluent society is essentially one which has escaped generalized poverty and distress, and that generates sustained financial development. The expectation of a protracted and wholesome life and the chance to accumulate data are additionally extensively thought-about to be customary dimensions of a holistic view of human flourishing.
A affluent society requires that materials well-being is shared amongst residents and never concentrated in a small group. The elements of inequality and minorities are supposed to seize the diploma of inclusiveness in a rustic. We measure inequality when it comes to revenue, which can be extremely correlated with schooling and well being inequality. The minorities part captures the absence of discrimination relating to entry to public companies and alternatives, primarily based on ethnic, social class, language, gender, political affiliation, and different concerns.
Lastly, prosperity must be sustainable in the long term, and thus we embrace within the Prosperity Index a measure of environmental high quality. This part is an equally weighted common of three sub-components, which cope with the huge variation in nations’ stage of improvement. First, we assess the cleanliness of a rustic’s manufacturing processes utilizing the ratio of carbon dioxide emissions to GDP per capita (each in logs). Second, we seize the implications of environmental high quality for human life, utilizing the speed of deaths from air air pollution. Third, we think about the truth that within the least developed nations residents might be uncovered to unclean environments each day, so we use entry to wash cooking applied sciences at a family degree as a proxy.
As we do for the Freedom Index, we assign considered one of 4 prosperity classes (Excessive Prosperity, Average Prosperity, Low Prosperity, and Lowest Prosperity) to every country-year commentary. To take action, we use the Prosperity Index rank for every year, labeling as “Excessive Prosperity” the primary quartile of nations (those who rank 1–41), “Average Prosperity” these within the second quartile (rating 42–82), “Low Prosperity” the third quartile (rating 83–123), and “Lowest Prosperity” these within the backside quartile (rating 124–164).
The state of Freedom and Prosperity all over the world
International freedom continues to say no
The Freedom Map (linked under) illustrates the worldwide panorama of freedom in 2024, as measured by our three subindexes (political, authorized, and financial). Freedom stays erratically distributed the world over, with scores starting from a excessive of 93.8 in Denmark to a low of 16.9 in Afghanistan. The persistent low scores for some nations over a number of years (generally many years) spotlight persistent gaps in institutional capacities and financial freedom, notably in fragile and authoritarian states.
Discover Freedom and Prosperity world map
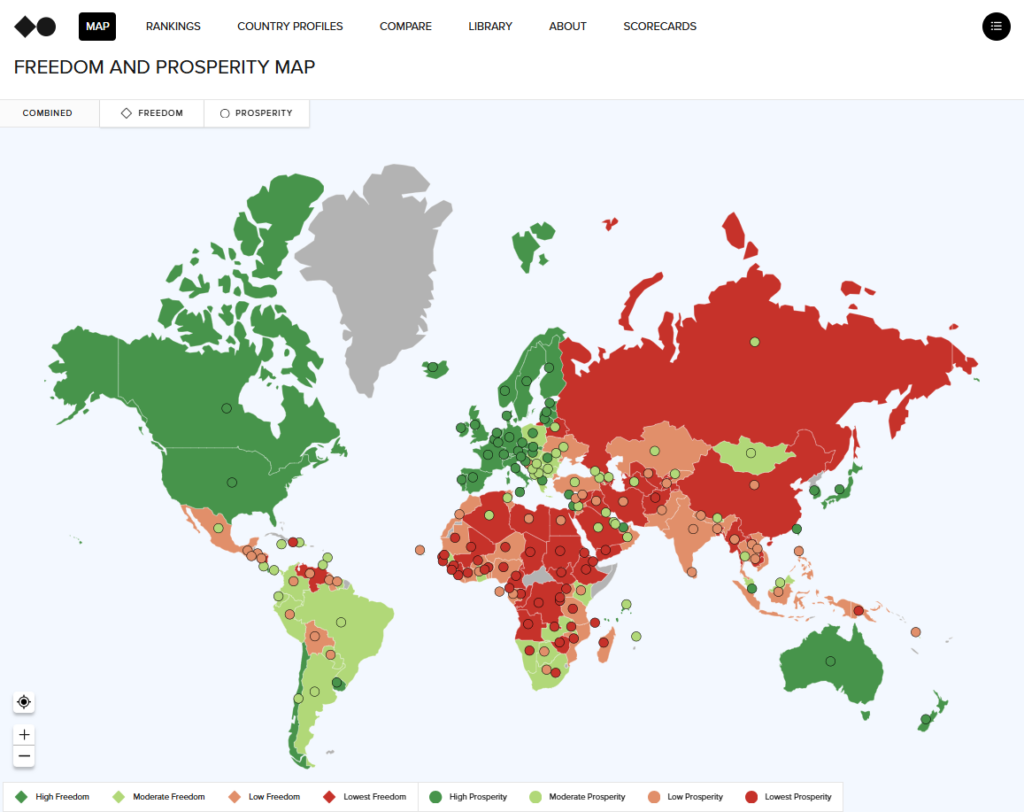
The Indexes rank 164 nations all over the world. Use our website to discover thirty years of knowledge, examine nations and areas, and look at the subindexes and indicators that comprise our Indexes.
Detailed Freedom Index scores and rankings for every nation can be found in Desk 1. which additionally highlights adjustments in rank over the previous 12 months.
As a result of institutional reform is usually a gradual and gradual course of, the general international distribution of freedom has remained fairly steady over the previous three many years. Western European nations proceed to dominate the highest of the Freedom Index, alongside Australia and New Zealand. Variations in scores amongst these nations are small, which helps clarify seemingly massive adjustments in rank, corresponding to Finland dropping three positions or Germany falling 5, even within the absence of main adjustments.
That mentioned, it’s noteworthy that each Canada (ranked twentieth) and america (twenty second) have misplaced floor relative to their European friends, falling 4 and three positions, respectively. Vital actions throughout the prime quartile embrace Poland’s reversal of its latest democratic backsliding: It has gained eight positions within the 2025 Index and reentered the “Excessive Freedom” class after eight years. In distinction, Slovakia’s efficiency is trigger for concern, dropping eight positions following an almost four-point decline in its Freedom rating.
Among the many center two quartiles, categorized as “Average Freedom” and “Low Freedom,” we observe extra dynamic shifts. On the constructive facet, the biggest enhancements have been seen in Guatemala (up 26 positions), Vietnam (up 21), South Africa (up 13), and Jordan (up 12). The sharpest declines have been recorded in Georgia (down 22 positions), Burkina Faso (down 17), and Mozambique (down 13).
Sadly, mobility throughout the “Lowest freedom” class stays restricted. This group continues to incorporate many nations from Sub-Saharan Africa and Central Asia. China (ranked 143rd) and Russia (145th), regardless of being two of the world’s most populous and geopolitically important nations, stay firmly entrenched within the lowest tier, exhibiting little progress towards better freedom.
Desk 1. Freedom Index scores and rating for 2024
Trying past the newest scores, the Freedom Index’s thirty-year protection permits us to uncover some fascinating dynamics. Determine 3 exhibits the evolution of the Freedom Index and its three subindexes since 1995 at a worldwide degree. Probably the most putting—and worrying—pattern is the detrimental evolution of the political subindex over the previous twelve years. Democratic regression began in 2013, nicely earlier than the COVID-19 disaster, accelerated throughout the pandemic, and continues as we speak. The worldwide common rating of the political subindex in 2024 is just like that of 1999, erasing 25 years of progress.
Determine 3. Political subindex is now on the identical degree as in 1999—a twenty-five-year low
The erosion of political freedom previously decade is a generalized pattern that impacts nations in any respect ranges of improvement, and throughout all areas of the world. Most notably, each the political subindex and the authorized subindex have declined by greater than two factors globally.
Determine 4 exhibits that the OECD nations (these with the best ranges of revenue on the planet, most of them well-established democracies) have skilled a decline in all three subindexes since 2014. For this group, the sharpest declines within the political subindex have occurred in Turkey, Mexico, Greece, and Hungary, every shedding greater than ten factors over the previous decade. Within the authorized subindex, which assesses the rule of regulation, Canada and america rank because the fourth- and sixth-largest decliners, respectively. Their scores dropped considerably resulting from a marked deterioration within the “readability of the regulation” part, which evaluates whether or not authorized norms are clear, clear, steady, and constantly enforced.
Determine 4. OECD scores have declined throughout all three freedom subindexes previously decade
Declines within the political subindex are important throughout all areas, as proven in Determine 5. with South and Central Asia experiencing the biggest fall (-6.12 factors on common), adopted by Center East and North Africa (-5.27) and Sub-Saharan Africa (-5.16). Equally, authorized freedom has fallen in all areas aside from South and Central Asia, however you will need to remember the fact that this area nonetheless exhibits the worst common rating on this subindex.
Determine 5. The democratic decline has continued to worsen throughout all areas
The erosion of political freedom has been essentially the most salient and generalized pattern in latest instances. We are able to look at what has been driving this by wanting on the evolution of the political subindex elements. Determine 6 presents the share change of every part for the reason that political subindex peak in 2012. All three have decreased within the final twelve years, though with barely completely different timing and power. Modifications within the elements measuring elections, civil liberties, and legislative constraints on the manager are comparatively minor till 2019, however worsen considerably throughout the pandemic (2019–2021) and proceed to say no nicely after the world got here again to relative normality.
The deterioration of the political rights part has been sustained and really sturdy since 2012, accumulating a lack of greater than 10 %. It appears clear that the restrictions imposed throughout the extraordinary circumstances of the COVID-19 disaster have been solely an accelerator of a course of already incubated, as political regression began nicely earlier than 2019, and continues as much as at the present time.
Determine 6. All elements of political freedom have declined since 2012
Till now, our evaluation has centered on international and regional easy averages, the place every nation carries equal weight within the combination traits, no matter its inhabitants dimension, geographic space, or GDP. Determine 7 examines how political freedom has developed for the typical particular person worldwide. It compares the worldwide improvement of the political subindex utilizing a easy nation common (blue) versus a population-weighted common (orange).
Determine 7. Inhabitants-weighted averages present decrease political freedom scores and a sharper decline
Two associated information stand out. First, the extent of political freedom skilled by the typical citizen of the world is considerably decrease than the nation common would point out. Second, its erosion over the previous decade has been a lot steeper after we look at it via population-weighted averages. It is because nations with bigger populations carry extra weight in population-based averages, that means their declines in political freedom impression the worldwide pattern way over these in less-populous nations.
China is a giant issue explaining the previous, because it contains greater than 17 % of the world inhabitants and has ranked among the many backside ten nations on the political subindex, and all its elements, since 1995. India, essentially the most populous nation on the planet, is the principle driving issue of the latter, with a plummeting pattern in political freedom since 2014 (-14 factors). Vital declines in a number of different populous nations have additionally contributed to the steep downward pattern, corresponding to Russia (-14.5), Indonesia (-11.8), and Bangladesh (-9.8).
Whereas the political and authorized subindexes have declined since 2014, the financial subindex exhibits constructive progress over the identical interval. In reality, two of its elements, property rights safety and, most notably, ladies’s financial freedom, are the one areas of your complete Freedom Index to have improved globally since 2014 (see Determine 8). Ladies’s financial freedom, particularly, has risen by practically seven factors globally since 2014, and by nearly twenty-three factors since 1995.
Determine 8. Solely ladies’s financial freedom presents important enchancment within the final decade
Just about each nation within the Index has skilled enhancements in ladies’s participation in financial affairs previously decade. It’s encouraging to look at that a few of the largest will increase on this part have taken place in nations that had the bottom scores simply ten years in the past. The Gulf monarchies (particularly the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and Bahrain), along with some African nations corresponding to Gabon and Democratic Republic of the Congo, current important expansions in ladies’s rights. Nevertheless, you will need to acknowledge that this measure is proscribed to financial rights solely, and that additional progress is required if these nations are to meet up with essentially the most superior nations of Western Europe.
Discover Freedom and Prosperity world map
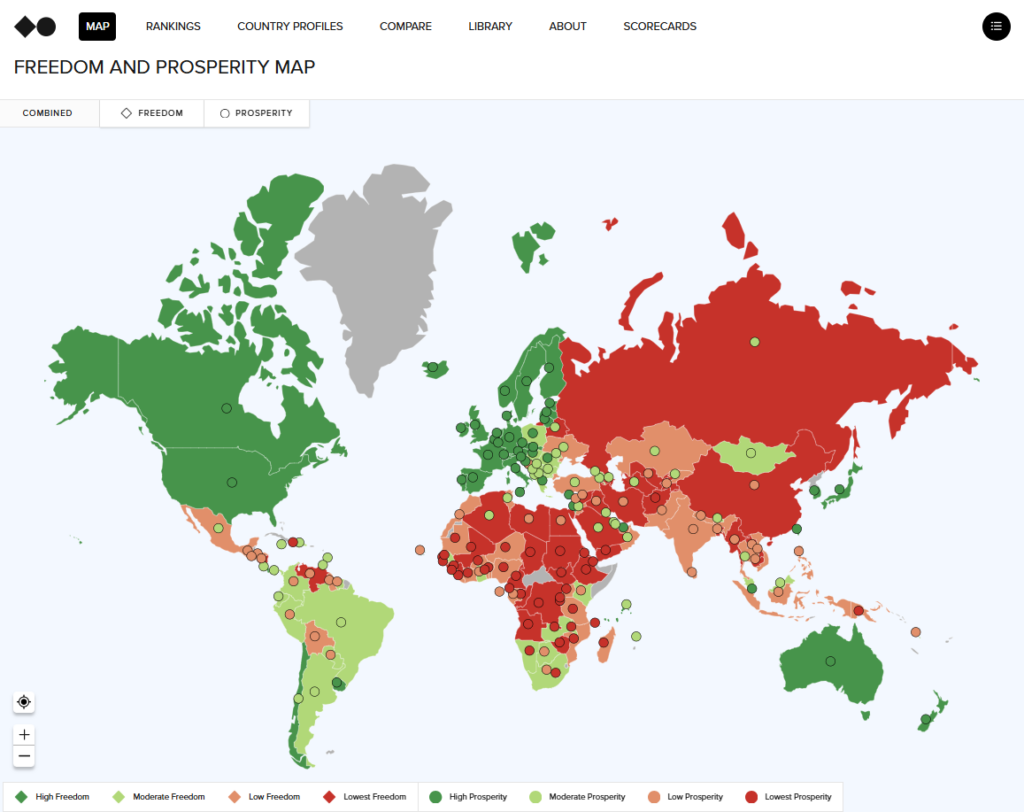
The Indexes rank 164 nations all over the world. Use our website to discover thirty years of knowledge, examine nations and areas, and look at the subindexes and indicators that comprise our Indexes.
Rising international prosperity, however worsening therapy of minorities
The Prosperity Map (linked under) exhibits the scenario of prosperity across the= world based on the six prosperity elements (revenue, well being, inequality, surroundings, minorities, schooling) in 2024. Detailed scores and rankings for every nation might be present in Desk 2. The overall distribution of prosperity is just like that of freedom, with the Western world topping the highest quartile (“Excessive Prosperity”), and Africa being the least affluent area.
Desk 2. Prosperity Index scores and rating for 2024
Giant actions within the rating place of particular nations in a single 12 months are nearly unimaginable because the elements of prosperity fluctuate solely regularly and in the long run. Nonetheless, we do observe clear traits when wanting on the evolution of prosperity and its elements since 1995 (Determine 9). Most putting is the dramatic enchancment of schooling globally, rising by greater than twenty factors. The obvious stagnation within the final two years is the product of an absence of knowledge from our most popular supply (the UN’s Human Growth Index). The disruptions attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic are solely evenly seen, however these don’t appear to have obstructed the generalized constructive pattern towards rising years of schooling throughout the globe, and particularly in creating areas.
Different noticeable traits within the elements of the Prosperity Index (Determine 9) embrace: A U-shape evolution of revenue inequality, which worsened from 1995 to 2005 however has improved since. Regular features in well being outcomes till 2019, adopted by a pointy decline as a result of COVID-19 pandemic and a partial restoration. Constant enchancment in environmental high quality. And a visual decline within the therapy of minorities since 2019.
General, the massive image is obvious: The world is turning into extra affluent. Nevertheless, the precise driving forces of this course of fluctuate considerably between areas and ranges of improvement.
Determine 9. Prosperity has improved throughout all elements since 1995, however the therapy of minorities has worsened previously decade
Determine 10 exhibits the 2024 rating within the Prosperity Index for all seven areas of the world (the tip of every arrow), in addition to the scale and path of change in every area’s rating since 2014 (starting of the arrow). The substantial variations in ranges of prosperity between areas is in no way a novel discovering, however it’s at all times essential to bear in mind these disparities when discussing how the completely different areas have developed lately.
Determine 10. The International South has been catching up in total prosperity since 2014, however a major hole stays (ten-year change on the Prosperity Index)
Sub-Saharan Africa and South and Central Asia are essentially the most improved areas since 2014, with a lot of that efficiency attributable to substantial will increase within the well being, surroundings, and schooling scores. Nonetheless, additionally it is price noticing that though decreases within the minorities part are generalized throughout the globe, the autumn in South and Central Asia is the biggest within the International South. This pattern could also be attributable to the deterioration of political freedom within the area (see above).
Determine 11. The therapy of minorities has worsened throughout all areas previously decade
North America is the one area by which total prosperity has declined over the previous decade, a pattern that warrants a number of vital caveats. First, as beforehand famous, North America nonetheless maintains a major lead in total prosperity in comparison with different areas, except for Europe. This benefit holds throughout most elements of the Prosperity Index. Second, the first driver of the area’s decline is a drop within the minorities part of the Index. In each america and Canada (the area’s solely two nations in our grouping, which locations Mexico with Latin America and the Caribbean) this indicator has skilled a notable downturn lately. This decline is probably going linked to extra restrictive immigration insurance policies, which can have diminished entry to public companies and financial alternatives for non-nationals and minority teams.
Is political freedom wanted for development and prosperity?
We now flip to a deeper query on the coronary heart of the Freedom and Prosperity Heart’s mission:
What’s the relationship between freedom and prosperity?
In different phrases:
Is freedom the surest path to long-term improvement and well-being?
Prosperity and total freedom are intently related
Within the 2024 Freedom and Prosperity Report, we introduced substantial proof of a powerful and constant affiliation between freedom and prosperity. Determine 12 offers an up to date visible abstract of this hyperlink, exhibiting a transparent constructive correlation (0.71) between the 2 Indexes throughout all nations in 2024: Nations with better freedom are inclined to get pleasure from larger ranges of prosperity.
Final 12 months’s report additional supported this discovering by analyzing adjustments over time fairly than one-off snapshots—an method that helps management for potential econometric issues. Even then, the constructive relationship held: International locations that improved most of their freedom scores since 1995 additionally skilled the biggest features in prosperity. As well as, we explored the long-term impression of a major enhance in freedom (a freedom “shock”) and once more discovered substantial constructive results on prosperity.
Determine 12. There’s a sturdy constructive correlation (0.71) between the Freedom Index and Prosperity Index
Is political freedom disconnected from financial development?
Having established a powerful constructive relationship between total freedom and prosperity, we now take a better take a look at the connection between every of the three freedom subindexes—political, authorized, and financial—and the varied elements of the Prosperity Index (Desk 3). Whereas every of the liberty subindexes is positively correlated with all prosperity elements, the power of those relationships varies.
One clear sample emerges: The authorized subindex, which displays the standard of the rule of regulation, exhibits the strongest correlation with practically all prosperity elements (except for inequality). Against this, the political subindex is the one least strongly correlated with practically all prosperity elements (except for minorities).
Desk 3. The authorized subindex (rule of regulation) correlates most strongly with prosperity (2024)
Some may argue that this sturdy relationship is pushed primarily by the wealthiest nations, corresponding to these in Western Europe, North America, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand, which have a tendency to attain excessive in each freedom and prosperity. To check this, we re-ran the evaluation, excluding these high-income OECD nations and focusing solely on the remaining 126 non-OECD nations. The power of the correlations decreased, however the relationships remained constructive in practically all circumstances. The one exception was for the inequality part, the place the correlation was basically zero. This will doubtless be defined by the Kuznets curve, a widely known financial principle that means inequality tends to rise within the early phases of improvement earlier than falling as nations develop richer. Since non-OECD nations span a variety of improvement phases, it’s unsurprising that inequality patterns are inconsistent amongst them, weakening the general correlation.
One of many standout findings from the international knowledge—that the authorized subindex relates way more strongly than the political subindex to prosperity—can be repeated on this non-OECD-country evaluation. For instance, the correlation between political freedom and GDP per capita is simply 0.17—3 times decrease than the correlation for the authorized subindex.
Determine 13 illustrates this divergence by plotting 2024 scores within the authorized and political subindexes in opposition to revenue per capita for non-OECD nations. On the left graph (political subindex), a number of nations—together with Gulf monarchies, Belarus, Russia, and China—rating low on political freedom however nonetheless get pleasure from comparatively excessive revenue ranges. Conversely, we additionally see various nations with sturdy political freedom scores (above 75) that carry out poorly when it comes to revenue, clustered within the backside proper of the graph.
Determine 13. At first look, political freedom alone is just not strongly associated to development
These findings increase difficult questions: Ought to we conclude that political freedom is just not vital for financial development, and solely marginally associated to broader prosperity? Ought to the worldwide group focus solely on strengthening the rule of regulation in creating nations as the best strategy to enhance revenue? And if political rights don’t seem to drive development, ought to we be much less involved concerning the international democratic backsliding seen lately?
These could seem like logical observations primarily based on the information—however a deeper dive into the Indexes, and the explanatory components behind them, reveals that also they are simplistic, and deceptive.
Components masking the democracy-growth nexus
The easy correlations don’t account for a number of vital components which will obscure the true relationship between political freedom and financial development. First, democratization is commonly a disruptive course of, producing basic adjustments to a rustic’s institutional framework via the growth of key political rights and civil liberties. Within the quick time period, such political transformations can generate uncertainty and require important adjustment from financial actors as they adapt to new guidelines, norms, and energy dynamics.
Furthermore, democratization is steadily triggered by financial crises. Whereas such crises could assist mobilize civil society and create momentum for reform, in addition they place a heavy burden on newly democratic governments. Political scientists have described this because the “tumultuous youth” of democracy, that’s, a section marked by instability and delayed returns. In consequence, the time horizon used to evaluate the impression of democratization is essential: The financial results of elevated political freedom could solely turn out to be seen within the medium to long run.
Take the case of Gambia, one of many nations that has made the biggest features in political freedom over the previous decade, following a serious democratization course of starting in 2017. It’s too early to completely assess the financial advantages of those reforms, particularly contemplating the numerous exterior shock of the COVID-19 pandemic between 2019 and 2021.
One other limitation of easy cross-sectional correlations is that they overlook the beginning circumstances below which nations undertake political reform. Some nations start democratization with sturdy authorized and financial establishments already in place, whereas others don’t. The Freedom Index is especially helpful right here, because it disentangles—and independently measures—the political, authorized, and financial dimensions of freedom. For instance, a rustic can obtain excessive efficiency on rule of regulation with out being democratic, simply as it’s attainable to have a vibrant democracy with weak rule of regulation. This raises an vital query: To what extent do the rule of regulation and financial freedom form the connection between political liberalization and financial development? Specializing in the connection between political freedom and the rule of regulation, we are able to think about two attainable situations, relying on whether or not they perform as substitutes or enhances:
- If substitutes: Political freedom might be particularly useful in nations with weak rule of regulation, that means enhancements in both dimension may spark financial development independently.
- If enhances: The advantages of democratization could rely upon having a powerful authorized basis already in place. On this case, solely nations that democratize after establishing strong authorized establishments would see important financial features, whereas these missing such foundations could not.
Lastly, when evaluating the consequences of political freedom, it’s crucial to outline the proper comparability teams. The “therapy group” ought to consist of nations which have undergone substantial and lasting will increase in political freedom—not these with marginal or short-term adjustments. On the identical time, the “management group” have to be fastidiously chosen to function a reputable benchmark—nations which have remained politically unchanged however are just like the “therapy” nation in different related traits.
The subsequent subsection outlines a extra rigorous evaluation of the political freedom-economic efficiency relationship, taking these methodological challenges under consideration.
A refined evaluation of political freedom and financial development
To raised perceive the connection between political freedom and financial development, we revert to our evaluation of 126 non-OECD nations, now over the interval 1995–2019. We deliberately finish the interval earlier than the COVID-19 pandemic to keep away from distortions attributable to its unprecedented financial disruptions.
Because the political subindex is a steady measure, we set a threshold rating of fifty. Each country-year commentary of fifty or above is classed as “democratic”, and any rating under is “autocratic.” Acknowledging that this threshold is considerably arbitrary, we additionally examined different cutoffs—forty-five, sixty, and the pattern median (65.9)—to evaluate the robustness of our outcomes. Various the cutoff doesn’t considerably have an effect on the outcomes. Primarily based on the 50-point threshold, we’re capable of categorize nations into 4 distinct teams, primarily based on their political trajectories over time:
- At all times Autocracies: International locations that remained under the fifty-point threshold all through your complete interval. This group consists of twenty-five nations, corresponding to China (Determine 14).
- Democratizers: International locations that began under the brink in 1995 however crossed above it by 2019, indicating a sustained shift towards democracy. This group consists of twenty-one nations, corresponding to Nigeria.
- Autocratizers: International locations that began above the brink in 1995 however fell under it by 2019, indicating democratic backsliding. There are 9 nations on this group, corresponding to Venezuela.
- At all times Democracies: International locations that remained above the brink all through your complete interval. That is the biggest group, with seventy-one nations, corresponding to Botswana.
Determine 14. An “At all times Autocracy”, a “Democratizer”, an “Autocratizer”, and an “At all times Democracy.” Political subindex scores (1995–2019) for one exemplar nation from every of the 4 sorts, grouped by political freedom traits
We then examine the group of Democratizers in opposition to the group of “At all times Autocracies,” as this creates the clearest counterfactual: What occurs when a rustic democratizes versus when it stays authoritarian? This comparability entails a complete of forty-six nations: twenty-one “Democratizers” and twenty-five “At all times Autocracies.”
To look at the long-term impression of democratization on financial efficiency, we use native linear projections as our fundamental analytical software. This technique is nicely suited to handle the issues mentioned within the earlier subsection, particularly relating to timing and variation throughout nations. In easy phrases, the approach entails working a sequence of regressions that estimate how a democratization “shock” (i.e., a major enhance in political freedom) impacts actual GDP per capita over time. We undertaking these results for as much as twenty years into the longer term, plotting the estimated impression for every year.
For every “Democratizer” nation, we establish the 12 months of democratization because the one with the biggest single-year enhance within the political subindex, for instance, 1999 within the case of Nigeria. Native linear projections additionally permit for the inclusion of vital management variables. Particularly, we embrace: (1) nation mounted results to account for time-invariant traits (corresponding to geography or historic establishments) which may affect development no matter political regime; and (2) 12 months mounted results to regulate for international shocks or traits that would have an effect on all nations in a given 12 months (corresponding to monetary crises or commodity value shifts).
These controls assist isolate the true impact of democratization from broader nationwide or international occasions that would in any other case bias the evaluation.
Democracy favors financial development
Determine 15 exhibits the cumulative impact of democratization on GDP per capita over a twenty-year interval, evaluating nations that skilled a democratization shock or episode with those who remained autocratic. The outcomes are clear: Democratization has a constructive and substantial long-term impression on financial development. On common, nations that democratize obtain GDP per capita ranges 8.8 % larger than their autocratic counterparts after twenty years.
Determine 15 additionally helps our earlier perception about timing: The financial advantages of political liberalization don’t seem instantly. On common, it takes round six to eight years for the expansion dividends of democracy to turn out to be seen—and round ten to 12 years for these advantages to be absolutely realized.
Determine 15. Democratization generates a lift in GDP per capita of 8.8 % (in contrast with nations that remained autocratic)
To discover the interplay between political freedom and the rule of regulation, we divided the democratization episodes into two classes:
- Excessive authorized subindex rating at time of democratization (above the median rating)
- Low authorized subindex rating at time of democratization (under the median)
We discover that democratization results in long-term financial features in each teams, however the impact is extra pronounced in nations with weaker authorized establishments on the time of democratization. In these circumstances, GDP per capita had grown 12.3 % after twenty years, measured in opposition to their autocratic counterparts. In distinction, for nations that democratized below comparatively sturdy rule of regulation circumstances, the achieve was extra modest, at 5.3 % over the identical interval.
These findings counsel a level of substitutability between political and authorized freedom: The place the rule of regulation is weak, political liberalization performs a extra crucial position in unlocking development potential.
Political freedom as a linchpin of prosperity
This thirtieth 12 months of the Freedom and Prosperity Indexes presents a posh image. Encouragingly, our Prosperity Index exhibits broad development, although important regional disparities and challenges persist. Conversely, political freedom and the rule of regulation are in decline throughout the board. Whether or not in OECD or non-OECD nations, or throughout areas, all are experiencing a downturn. Our political subindex, which measures the extent to which a nation upholds civil liberties, democratic legislature, and the political rights of its constituents, reveals the more and more dire state of world democracy—sinking to its lowest level in twenty-five years.
Whereas prosperity encompasses way over simply revenue, sustained financial development stays a crucial pillar of long-term well-being. Our evaluation offers compelling proof that democratization contributes meaningfully to long-term financial development, even when its results take time to materialize. Over twenty years, nations that democratize obtain per capita GDP that’s 8.8 % larger than their autocratic friends. Whereas the rule of regulation emerges as a constantly sturdy predictor of prosperity, our evaluation additionally exhibits that political freedom performs a significant and unbiased position, notably in contexts the place authorized establishments are weak.
Political liberalization can act as a strong catalyst for progress, particularly when it helps right institutional deficits. On the identical time, the impression of democracy on development is just not computerized or instant; it relies on timing, nationwide circumstances, and the broader institutional surroundings. This underscores a central perception of the Freedom and Prosperity Indexes: that freedom, when exercised in its full political, authorized, and financial dimensions—is not only an ethical crucial, however a realistic path to shared prosperity.
Learn the Freedom and Prosperity Indexes methodology
The Indexes rank 164 nations all over the world. Use our website to discover thirty years of knowledge, examine nations and areas, and look at the subindexes and indicators that comprise our Indexes.
Authors
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Will Mortenson and Christine Hutchinson for his or her invaluable contributions, and the crew at Soapbox for his or her help with knowledge visualization.
The Freedom and Prosperity Indexes are a creation of the Atlantic Council’s Freedom and Prosperity Heart. The middle’s mission is to extend the well-being of individuals in every single place—and particularly of the poor and marginalized in creating nations—via unbiased, data-based analysis on the connection between freedom and prosperity.
Associated content material
Discover this system

The Freedom and Prosperity Center goals to extend the prosperity of the poor and marginalized in creating nations and to discover the character of the connection between freedom and prosperity in each creating and developed nations.
