TOKYO, Jun 05 (News On Japan) –
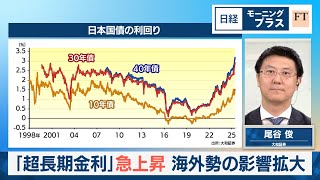
Japan’s super-long-term authorities bond yields—overlaying 30- and 40-year maturities—have climbed sharply in latest months, reaching their highest ranges in years. The upward momentum has additionally pushed up 10-year yields, that are generally used as a benchmark in monetary markets.
The shift is being attributed to a mixture of home and worldwide elements, with rising affect from abroad buyers standing out as a key driver.
Talking on the development, Daiwa Securities Chief Market Strategist Kotani, who has over 20 years of expertise within the bond market, outlined 4 predominant elements behind the rise. First, the nominal financial progress charge is a significant determinant of long-term rates of interest. Japan’s nominal GDP progress for fiscal 2023 was 3.7%, a determine that will seem excessive however contains inflation. This inflationary part helps larger long-term yields.
Second, the chance premium related to Japanese authorities debt is increasing. Japan’s fiscal place stays among the many weakest of superior economies, and with the ruling celebration dropping its majority within the decrease home final autumn, political uncertainty has additional elevated threat.
The third issue is world monetary instability. Since a significant reshuffling within the U.S. Treasury market in April, issues about U.S. fiscal sustainability—exacerbated by credit standing downgrades and tax minimize debates—have fueled a worldwide reassessment of sovereign debt threat.
The fourth issue is structural adjustments in provide and demand. On the availability facet, Japan’s Ministry of Finance has step by step shifted towards issuing longer-maturity bonds. In the meantime, demand has weakened: the Financial institution of Japan has scaled again its large bond purchases beneath its coverage normalization efforts, lowering a significant supply of demand.
Amongst institutional patrons, life insurers historically spend money on long-term bonds to match their long-term liabilities. Nevertheless, a regulatory transition happening from fiscal 2020 by way of 2023 pressured these insurers to build up giant quantities of long-term bonds. With the brand new guidelines now in impact as of this fiscal yr, that purchasing stress has largely subsided.
This shift in demand is having notable penalties. Whereas the federal government holds vital volumes of super-long-term bonds, rising yields imply falling costs. As of the top of March, 13 state-affiliated establishments reported unrealized losses totaling 16.8 trillion yen on their bond holdings. Bonds issued 10 years in the past with 40-year maturities have fallen to under half their unique value.
Though these are solely paper losses for now, they might materialize if the bonds are offered. The priority is that such losses could immediate some buyers to promote preemptively to keep away from additional declines. Nevertheless, insurers and different long-term holders are typically required to keep up belongings that match their liabilities, limiting their means to dump holdings freely.
Within the longer run, rising yields could improve the enchantment of insurance coverage merchandise that supply steady returns, thereby bringing capital again into the super-long bond market and stabilizing demand.
Amid these shifts, overseas buyers have emerged as a dominant pressure. Latest information present that overseas patrons have been buying greater than 2 trillion yen value of Japanese authorities bonds in some months—an unprecedented tempo. The Japan Bond Market now faces a brand new dynamic by which the worldwide funding neighborhood is taking part in an more and more decisive position in shaping home rate of interest developments.
Supply: テレ東BIZ