Residing in house presents many challenges, from excessive radiation to bone loss. Nonetheless, an often-overlooked issue is the microbial atmosphere inside spacecraft.
On Earth, people exist inside an enormous and complicated microbial ecosystem, however house habitats just like the Worldwide House Station (ISS) are extremely managed, enclosed environments the place microbial variety is drastically lowered.
This isolation poses each benefits and dangers. Whereas fewer pathogens could appear useful, the absence of useful microbes can weaken astronauts’ immune programs and contribute to well being issues.
Mapping the Microbiome of House
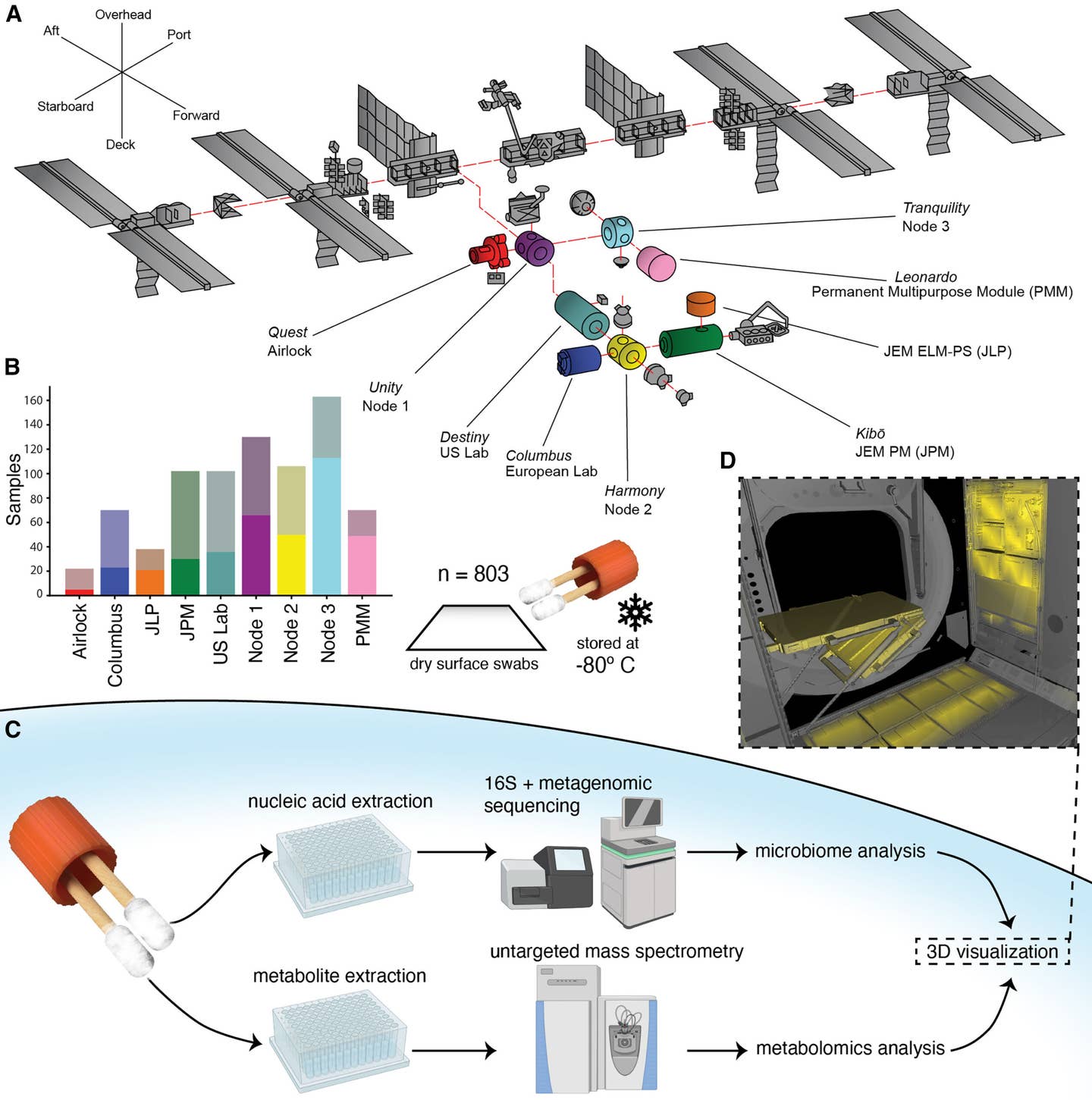
To know how the ISS atmosphere compares to these on Earth, researchers analyzed 803 floor samples throughout the station’s United States Orbital Section (USOS). This dataset was almost 100 occasions bigger than earlier research.
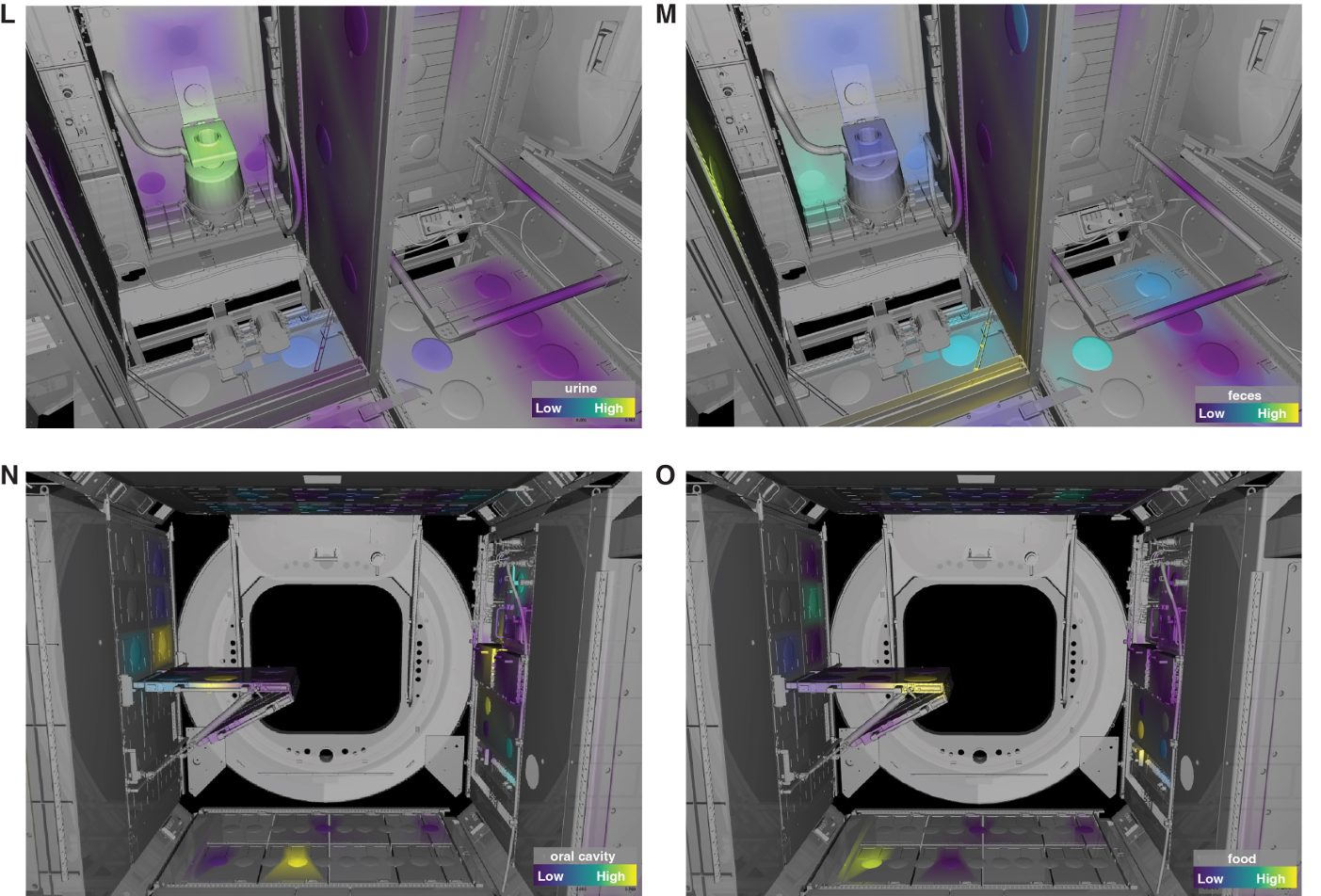
The samples had been used to create a high-resolution 3D mannequin of microbial and chemical distribution throughout the station’s surfaces. This allowed researchers to visualise how totally different areas of the ISS accumulate specific microbes and chemical compounds over time.
The outcomes confirmed that the station’s microbiome is overwhelmingly dominated by human-associated micro organism, primarily from pores and skin. The examine discovered stark variations between microbial communities in numerous ISS modules, relying on their major perform.
For instance, meals preparation and eating areas contained microbes linked to meals, whereas hygiene areas harbored higher levels of bacteria related to human waste. This means that astronaut exercise considerably influences microbial distribution, simply because it does in properties and hospitals on Earth.
One stunning discovering was that ISS microbial variety is decrease than almost any constructed atmosphere on Earth, together with hospitals and industrial buildings. That is doubtless because of rigorous cleansing protocols and the station’s isolation from pure microbial sources.
Nonetheless, this excessive sterility won’t be preferrred. On Earth, publicity to a various vary of microbes helps preserve immune system stability. With out it, astronauts could also be at higher threat for inflammatory conditions, allergy symptoms, and immune dysfunction.
The Function of Microbes in Astronaut Well being
Whereas decreasing dangerous micro organism is essential in house, the whole absence of useful microbes may very well be counterproductive. Research have linked lowered microbial publicity to persistent inflammatory illnesses in extremely sanitized environments on Earth. In house, astronauts steadily expertise rashes, allergy symptoms, and immune dysfunction, together with the reactivation of latent viruses and an elevated threat of infections.
“Really sterile environments—fully devoid of microbial life—are exceptionally uncommon on Earth,” stated Rodolfo Salido Benítez, the examine’s co-first creator and Director of Laboratory Automation on the Knight Lab, UC San Diego. “In house, extreme chemical decontamination could also be counterproductive to sustaining a wholesome ecosystem.”
Past particular person well being, microbial life in house might additionally pose dangers to spacecraft integrity. Some bacterial species discovered on the ISS have demonstrated elevated resistance to antibiotics, heightened virulence, and biofilm formation.
These diversifications might result in corrosion of spacecraft materials, gear malfunctions, or heightened astronaut well being dangers. Though present proof means that house doesn’t essentially promote the evolution of extra harmful microbes, ongoing monitoring is vital.
Rethinking Microbial Administration in House
The examine underscores the necessity for a brand new method to microbial administration in house. As an alternative of aiming for excessive sterility, researchers counsel fostering a managed however numerous microbial atmosphere that mimics Earth’s pure exposures. Introducing beneficial microbes might assist preserve astronaut well being whereas mitigating the dangers related to antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation.
“Future constructed environments, together with house stations, may benefit from deliberately fostering numerous microbial communities that higher mimic the pure microbial exposures skilled on Earth, relatively than counting on extremely sanitized areas,” Salido Benítez famous.
The findings have implications past house journey. Insights gained from the ISS might assist enhance microbial threat administration in hospitals and different extremely sanitized environments on Earth. By understanding which microbes are needed for well being and the way to preserve a balanced microbial atmosphere, researchers hope to design more healthy residing areas each in house and on the bottom.
NASA and different house businesses are already exploring new strategies for microbial monitoring. Whereas conventional culture-based strategies have been used to evaluate microbial security thresholds, these approaches fail to seize the total variety of microbes current.

Advances in metagenomics and in-flight DNA sequencing now enable astronauts to investigate microbial samples in real-time, paving the way in which for extra adaptive and exact microbial administration methods.
As human house exploration extends past the ISS to the Moon and Mars, sustaining a secure and wholesome microbial ecosystem will likely be important. Future habitats should stability sanitation with the necessity for useful microbial variety, making certain that astronauts can thrive in house with out pointless well being dangers.
