Introduction
Drug-induced liver damage (DILI) is a situation during which the liver is broken as a consequence of publicity to prescription prescribed drugs, over-the-counter medicines, and natural and dietary dietary supplements (HDS) (Real et al., 2019). It’s characterised by a spread of liver abnormalities, various from gentle elevations in liver enzyme ranges (transaminases) to extreme liver injury or failure, which will be life-threatening (Real et al., 2019; Nunes et al., 2022). The incidence of DILI is rising worldwide due to the prevalence and widespread use of wholesome purposeful meals and self-medication, accessible from a wide range of sources.
Latest research have highlighted the rising DILI danger posed by HDS, alongside conventional danger components akin to antibiotics and anti inflammatory medication (Real et al., 2019; Nunes et al., 2022). In South Korea, stories have introduced conflicting findings concerning the first causative brokers of DILI, significantly regarding natural medicines prescribed by conventional Korean drugs (TKM) medical doctors (Kim et al., 2003; Yoo et al., 2007; Suk et al., 2012). Preliminary stories in 2003 recommended a big affiliation between natural medicines and DILI, accounting for 57.9% of instances (Kim et al., 2003); subsequent research in 2007 and 2012 additionally discovered they accounted for roughly 30% of instances (Yoo et al., 2007; Suk et al., 2012). Nonetheless, stories from multi-pharmacovigilance facilities in South Korea have revealed that antibiotics, anti-epileptics, anti-inflammatory medication, and statins are the foremost brokers related to DILI (>80%), whereas natural medicines accounted for under 0.5% of instances (Shin et al., 2009; Kwon et al., 2012). Retrospective research amongst sufferers taking natural medicines prescribed by TKM medical doctors additionally indicated a low DILI prevalence (∼0.5%), with subclinical or gentle signs (Lee A. R. et al., 2012; Lee et al., 2015). Moreover, a nationwide potential examine carried out between April 2013 and January 2016 estimated the incidence of DILI from natural medicines to be 0.6% (Cho et al., 2017).
Taken collectively, the protection profiles of natural medicines in South Korea exhibit discrepancies (Lee et al., 2019). It’s crucial to conduct a nationwide population-based examine encompassing all DILI instances to handle the constraints inherent in relying solely on research carried out in Western or TKM establishments. Given the great healthcare protection supplied by South Korea’s common healthcare system, strong knowledge from nationwide medical insurance claims are readily accessible by way of the Well being Insurance coverage and Assessment Evaluation (HIRA) course of.
Right here, we adopted the self-controlled case sequence (SCCS) as a consequence of a number of compelling causes. In the beginning, SCCS successfully controls for all confounders that don’t range over time inside a person, akin to genetic components, way of life decisions, and long-term well being situations (Petersen et al., 2016). That is essential in our examine the place such confounders might considerably influence the outcomes. By utilizing SCCS, we reduce bias arising from these time-invariant confounders, guaranteeing extra correct and dependable findings. Furthermore, SCCS is very environment friendly because it solely contains people who’ve skilled the occasion of curiosity—on this case, DILI (Lee C. H. et al., 2012; Brauer et al., 2016). This permits for a targeted and environment friendly evaluation, which is especially invaluable given the potential rarity of DILI occasions. One other key purpose for the need of SCCS in our examine is its skill to attenuate choice bias (Mostofsky et al., 2018). In conventional cohort or case-control research, there’s a danger of choice bias as a consequence of variations between uncovered and non-exposed teams. SCCS mitigates this danger through the use of every particular person as their very own management, thereby enhancing the validity of our findings. By SCCS, we investigated the relative incidence of DILI related to publicity to TKM hospitals/clinics and natural medicines prescribed by TKM medical doctors 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 days earlier than the onset of DILI signs.
Supplies and strategies
Information supply
The nationwide well being claims database supplied by the HIRA in South Korea between January 2011 and December 2019 was used, which was chosen to make sure the provision and completeness of the newest, high-quality knowledge. The info comprised three components: common info on people, all electronically submitted diagnoses (primarily based on the Worldwide Classification of Ailments tenth Revision; ICD-10), and medicine prescriptions (together with natural medicines). The examine protocol was reviewed by the Institutional Assessment Board of Dankook College (Approval Quantity: DKU 2020-09-001). Entry to and use of the HIRA database have been licensed by HIRA by way of a remote-controlled desktop (Approval Quantity: HIRA M20200924766), guaranteeing compliance with moral tips and knowledge safety rules all through the examine interval.
Examine inhabitants
Information on 707,365 people who developed DILI from January 2011 to December 2019 was obtained. DILI was outlined as poisonous liver illness (ICD-10 code: K71). Recurrent episodes have been excluded from the evaluation to make sure adherence to the SCCS assumptions, and 34,954 instances from 2011 have been excluded as a result of DILI episodes earlier than 2011 weren’t thought of, leading to a ultimate dataset of 672,411 people.
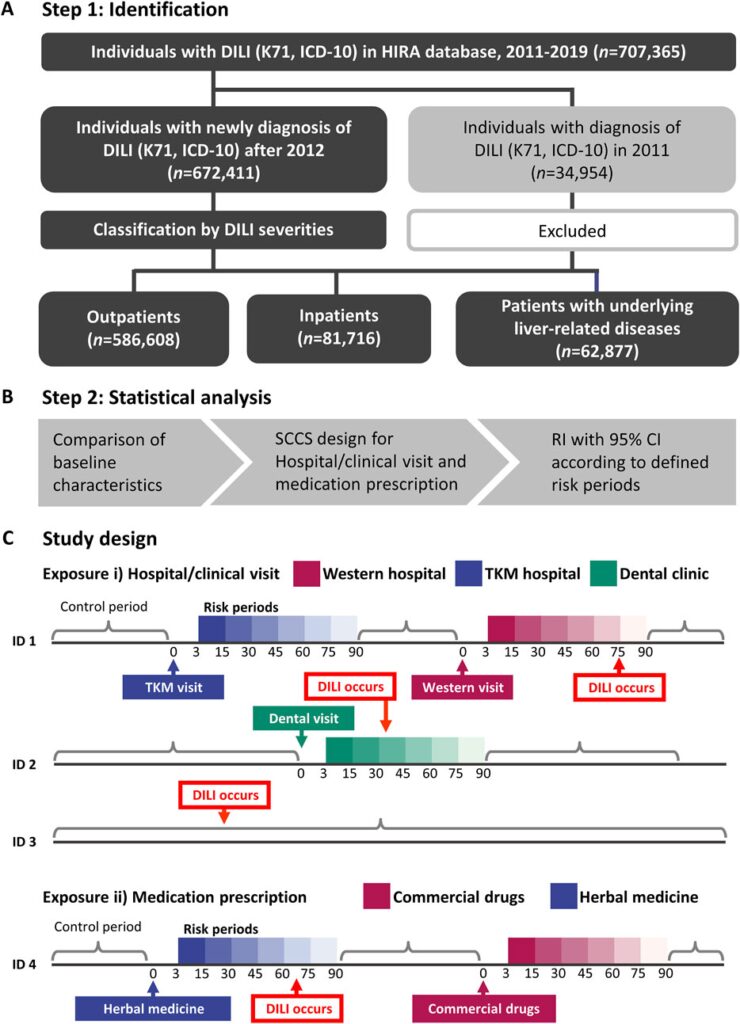
To categorize DILI severity, the examine inhabitants was divided into three teams: outpatients (people who obtained a DILI prognosis and weren’t admitted to hospital), inpatients (people admitted to hospital on the time of DILI prognosis), and sufferers with liver illness (a high-risk DILI group comprising people with pre-existing liver situations akin to hepatitis, malignant neoplasm of liver and intrahepatic bile ducts, alcoholic liver illness, hepatic failure, fibrosis and cirrhosis of liver, and different inflammatory liver illnesses; detailed in Supplementary Table S1). The investigation workflow is illustrated in Figure 1A.
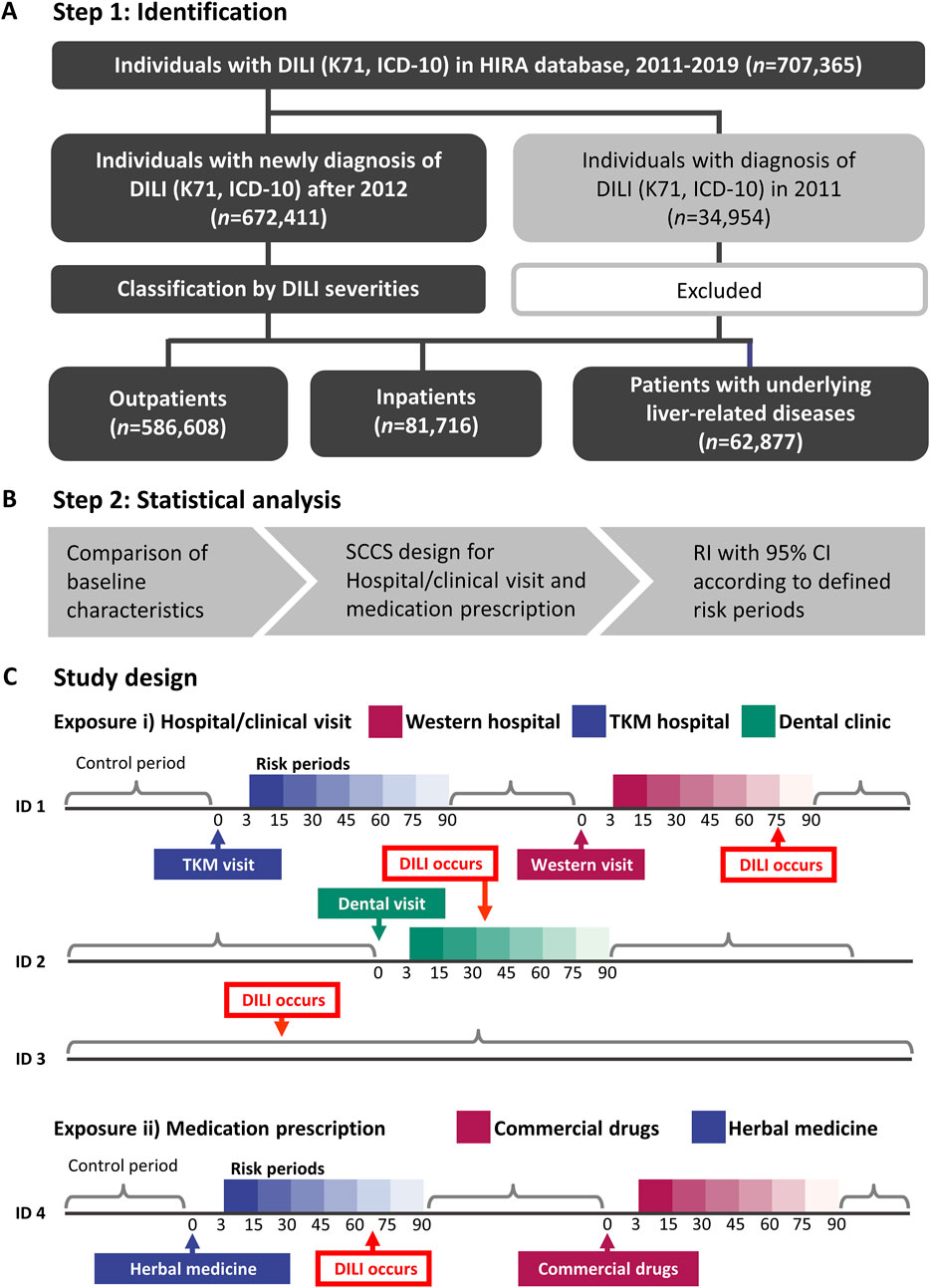
Determine 1. The flowchart for the examine inhabitants inclusion/exclusion and the ultimate three teams (A), evaluation move for self-controlled case sequence (B), and the detailed examine design (C). Threat of hospital go to or prescription and the management interval of sufferers have been outlined. DILI, drug-induced liver damage; HIRA, Well being Insurance coverage and Assessment Evaluation; ICD-10, Worldwide Statistical Classification of Ailments, tenth Revision; RI, relative incidence; TKM, conventional Korean drugs; SCCS, self-controlled case sequence.
Examine design
A SCCS design was used to mitigate the influence of time-invariant confounding variables (Figures 1B, C). Age and publicity have been handled as time-variant variables. Exposures have been outlined as i) hospital/clinic visits or ii) prescriptions, respectively. Particularly, hospital/scientific go to refers to any go to, whether or not or not drugs have been prescribed. Though knowledge on most drugs prescribed in Western medical establishments have been accessible within the nationwide well being claims database, 56 natural extracts prescribed in TKM establishments have been collected. Subsequently, a go to to both a Western or TKM establishments could possibly be conservatively thought of as exposures to industrial medication or natural medicines.
For each publicity varieties, danger durations have been outlined inside 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 days following every publicity to watch the temporal sample of DILI incidence. This enabled an analysis of the consistency and time of DILI relative to preliminary publicity. The first end result was the primary incidence of DILI, coded as K71. To cut back the potential for the reverse causation between publicity and end result, K71 occasions occurring inside 0–2 days after publicity have been excluded. Circumstances the place sufferers had concurrent exposures to each natural and traditional medicines inside the similar danger interval have been excluded from the evaluation to keep away from potential confounding results.
Statistical evaluation
Demographic and scientific traits are reported as imply ± commonplace deviation for steady variables and as frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. The important thing assumptions of the SCCS mannequin included the independence of recurrent end result occasions, the place the incidence of 1 occasion doesn’t affect the likelihood of subsequent occasions or the independence of end result occasions from subsequent publicity (Petersen et al., 2016). The primary incidence of DILI was targeted on, for which the estimated relative incidence (RIs) could also be conservative. RIs with 95% CIs as compared with the management interval have been individually estimated in response to outlined danger durations (Figure 1C). Statistical analyses have been carried out utilizing R (model 4.3.1) with the SCCS bundle of the R Basis for Statistical Computing and SAS Enterprise Information (model 7.13; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, United States) (Farrington et al., 2018).
Outcomes
Examine inhabitants and traits
A complete of 586,608 outpatients (Group A), 85,803 inpatients (Group B), and 62,877 sufferers with liver illness (Group C) have been included; demographic and scientific traits can be found in Table 1. Throughout all teams, the common age was roughly 50 years, with the next proportion of males than females; Group C had the very best variety of male sufferers (61.38%). Nearly all of Group A obtained their prognosis at major care establishments (58.96%), whereas most inpatients have been recognized at secondary or tertiary care hospitals (73.32% and 23.24%, respectively). Mortality charges have been highest in Group B, indicating extra extreme DILI. Group C had the next prevalence of comorbidities, with dyslipidemia being the commonest. The predominant subtype of DILI in Group C was poisonous liver illness with cholestasis (45.27%), whereas unspecified DILI was extra prevalent in Teams A and B (>55%).
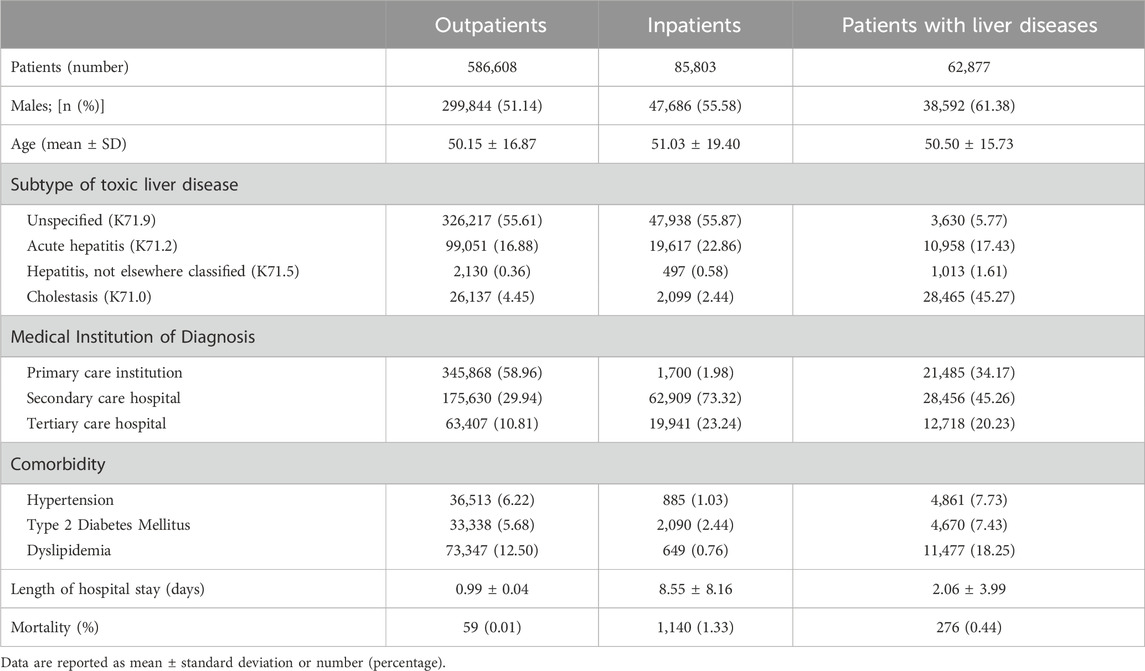
Desk 1. Affected person demographics and scientific options at prognosis of drug-induced liver damage (DILI) for outpatients, inpatients, and sufferers with liver illnesses.
DILI incidence danger evaluation after totally different medical establishment visits
The dangers of DILI related to every medical establishment are proven in Figures 2A–C. The dangers inside 3–15 days following visits to Western hospitals/clinics have been persistently greater than these for visits to different medical establishments throughout Group A, B, and C (RI = 1.55 [95% CI: 1.55–1.56]; RI = 1.67 [95% CI: 1.65–1.70]; RI = 1.76 [95% CI: 1.71–1.81], respectively). The elevated RIs converged to 1.0 after 3–15 days, indicating a lower within the danger of DILI over time.
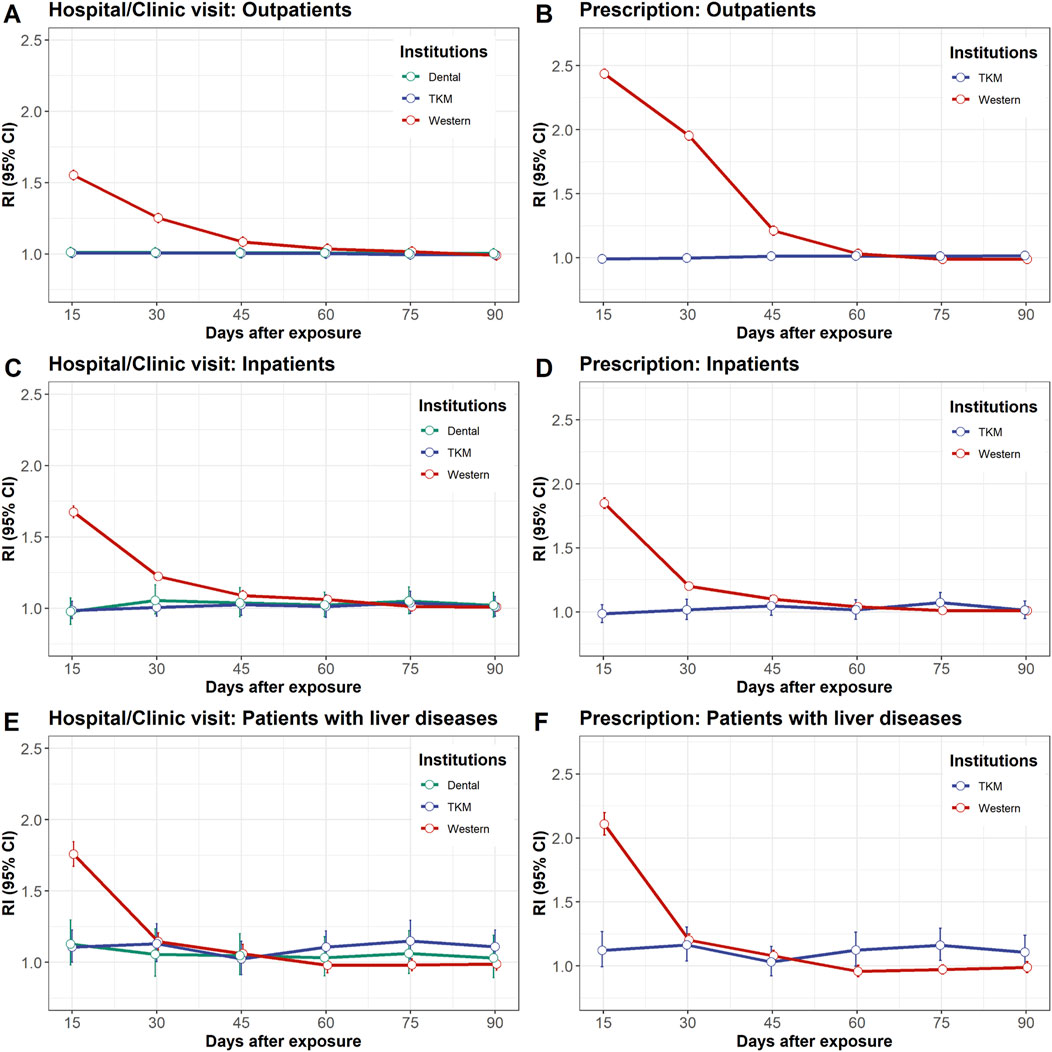
Determine 2. Relative incidence of drug-induced liver damage after publicity to hospital/scientific visits left panel: (A, C, E) or prescriptions proper panel: (B, D, F). The examine inhabitants was divided into three teams: outpatients higher panel: (A, B), inpatients center panel: (C, D), and sufferers with liver illness decrease panel: (E, F). Publicity to hospital/scientific go to refers to any go to, with or with out prescriptions for industrial medication or natural medicines. CI, confidence interval; RI, relative incidence.
In distinction, no elevated danger of DILI was noticed in Group A and Group B inside 3–15 days following visits to TKM hospitals/clinics (RI = 1.01 [95% CI: 1.00–1.01] and RI = 0.98 [95% CI: 0.93–1.05], respectively) (Figures 2A, B). This development persevered throughout the opposite danger durations for as much as 90 days. Equally, the RIs of DILI for all danger durations related to visits to dental hospitals/clinics have been near 1.0, indicating minimal danger. In Group C, the danger of DILI was mildly elevated 61–75 days after visits to TKM hospitals/clinics (RI = 1.15 [95% CI: 1.05–1.25]) (Figure 2C).
DILI incidence danger evaluation after prescription (industrial drug or natural drugs)
The chance of DILI from prescription is proven in Figures 2D–F. The dangers inside 3–15 days following prescription of business medication have been persistently greater in comparison with natural drugs prescribed by TKM medical doctors throughout Teams A, B, and C (RI = 2.44 [95% CI: 2.43–2.44]; RI = 1.85 [95% CI: 1.83–1.87]; RI = 2.11 [95% CI: 2.07–2.15], respectively). The elevated RIs progressively converged to 1.0 after 16 days, indicating a lower within the danger of DILI over time.
Conversely, there was no elevated danger of DILI inside 3-15 days following natural drugs prescription in Group A or B (RI = 0.99 [95% CI: 0.99–1.00] and RI = 0.98 [95% CI: 0.92–1.06], respectively) (Figures 2D, E). In Group C, the danger of DILI was mildly elevated at 16–30 and 61–75 days following natural drugs prescription (RI = 1.16 [95% CI: 1.05–1.28] and RI = 1.16 [95% CI: 1.05–1.27], respectively) (Figure 2F).
Dialogue
This examine established that visits to TKM establishments or prescriptions of natural medicines, each for outpatients and inpatients populations, have been related to a negligible danger of DILI in a large-scale, population-based cohort. In distinction, a prominently elevated RI of DILI was noticed following visits to Western establishments or prescriptions of business medication. Moreover, sufferers with pre-existing liver illness skilled a modest improve in DILI danger inside 90 days of publicity to both hospital/clinic go to or prescriptions.
The chance components for DILI stay poorly understood as a result of most idiosyncratic instances are unpredictable and happen inside the therapeutic doses of prescribed remedy, indicating the absence of a dose-response relationship (Hoofnagle and Bjornsson, 2019). The pathophysiology of DILI is profoundly influenced by a number of variables together with particular person traits and environmental components (Hussaini and Farrington, 2007; Chalasani and Bjornsson, 2010). Conventional epidemiological examine designs, akin to cohort and case-control research, usually battle to adequately account for the myriad confounding variables inherent in DILI instances, significantly as a result of figuring out appropriate management teams is difficult (Lee C. H. et al., 2012; Petersen et al., 2016). Figuring out the publicity timing to a candidate substance in DILI instances poses a pivotal problem (Mostofsky et al., 2018). The SCCS design is especially effectively fitted to analyzing the influence of natural medicines on DILI, addressing these complexities (Petersen et al., 2016; Nunes et al., 2022) Nonetheless, the SCCS methodology additionally has some weaknesses (Mostofsky et al., 2018; Takeuchi et al., 2018) It requires correct timing of each the publicity (akin to natural drugs utilization) and the occasion (DILI), as misclassification can result in biased outcomes. Moreover, whereas SCCS controls for time-invariant confounders, it doesn’t mechanically management for time-varying confounders, which may introduce bias if not correctly accounted for. There can be points with reverse causality, the place the end result would possibly affect the publicity timing, which must be fastidiously thought of and addressed within the examine design. Lastly, if there are underlying temporal tendencies within the incidence of the occasion or publicity, these must be accounted for to keep away from biased estimates.
On this examine, each visitation and prescription of medication in Western establishments resulted in a considerably greater danger of DILI throughout all teams. The sequentially reducing danger from 3 to fifteen days following publicity means that each these components affect DILI improvement. In distinction, inpatients and outpatients visiting and/or prescribed drugs at TKM establishments confirmed a minimal danger of DILI, although elevated danger was noticed inside 75 days of publicity in sufferers with liver illnesses. This means that getting affected person histories is important earlier than prescription by TKM physicians.
Earlier research in East Asian international locations have additionally had controversial outcomes concerning the consequences of natural medicines on DILI. In Taiwan, a population-based cohort examine highlighted acetaminophen (35.0%) and anti-tuberculous medication (34.7%) are main causes of DILI, whereas natural medicines weren’t (Sobhonslidsuk et al., 2016). One other potential examine in Taiwan from 2011 to 2019 recommended 78.0% of DILI instances have been attributable to standard medication, with 22.0% attributable to HDS, however included numerous dietary dietary supplements with out prescriptions (Huang et al., 2021). In mainland China, a retrospective examine recognized Conventional Chinese language Medication (TCM) or HDS because the main reason for DILI, accounting for 26.81% of instances (Shen et al., 2019). Nonetheless, a big methodological concern has been raised concerning the examine by Shen et al. (Shen et al., 2019), significantly the choice to categorise TCM and HDS as a single class (Cong et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2019). TCM, like TKM, is a extremely regulated observe, prescribed by licensed practitioners, which is in stark distinction to HDS, a class encompassing a wide selection of merchandise with various levels of regulation and high quality. By combining these distinct entities into one class, the examine oversimplifies the information, probably exaggerating the danger related to TCM whereas obscuring the particular risks posed by much less regulated HDS merchandise. This flawed classification leads to an unequal comparability with standard medication, probably resulting in deceptive conclusions about the primary contributors to DILI. For a extra correct evaluation, TCM and HDS must be categorized individually, with additional subcategories to account for his or her variety and regulatory variations. Total, the clear hepatotoxicity dangers related to unregulated natural medicines emphasizes the necessity for these merchandise to prescribed inside medical establishments, as advocated by our examine.
This examine had a number of limitations. First, the K71 code used to establish instances of DILI encompasses each idiosyncratic and intrinsic types of liver damage, and we have been unable to carry out additional distinctions or stratified analyses because of the absence of related info, akin to laboratory knowledge, within the HIRA database (Kim et al., 2017). The reliance on ICD-10 codes, which lack detailed scientific info, might have led to the potential misclassification of DILI instances in comparison with diagnoses established by way of scientific analysis. Because of this, we have been unable to use the Roussel Uclaf Causality Evaluation Technique (RUCAM) causality grading (Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) in Drug Induced Liver Injury (2012)) to substantiate the affiliation between publicity and DILI occasions. Second, the HIRA database doesn’t embrace particulars on particular drugs indicating the exact causes of liver damage. Info on natural medicines within the HIRA database was restricted to insurance-covered extracts, excluding decoctions and non-insured natural formulations, that are generally utilized in observe. The restricted scope of knowledge on non-insured natural medicines introduces potential bias and restricts the generalizability of our findings. Consequently, we couldn’t clearly distinguish herb-induced liver damage from different types of DILI inside the K71-coded occasions. Third, the noticed IRs inside 3–15 days of publicity in Western establishments might have been overestimated because of the case-only design, which targeted on the primary episode of DILI. Nonetheless, the elevated danger noticed in the course of the subsequent 16–30 days, adopted by a decline, helps the temporal affiliation. As a reference level, visits to dental clinics confirmed no related danger for any group all through the examine interval, reinforcing the reliability of the findings. Lastly, pre-existing liver illness has been reported to lead to extra extreme outcomes upon the incidence of DILI slightly than influencing its incidence (Chalasani and Bjornsson, 2010). Nonetheless, the danger related to particular natural elements in sufferers with liver illness couldn’t be evaluated.
Future analysis on natural drugs security ought to undertake a multifaceted strategy by integrating digital medical information with medical insurance claims knowledge to establish particular herbs or formulations that will pose greater dangers for DILI. This integration would supply a extra complete understanding by combining scientific observations with prescription knowledge. Moreover, community pharmacology approaches must be employed to foretell hepatotoxicity dangers of particular person herbs or compounds (Hong et al., 2017), uncovering potential interactions and aiding in proactive danger administration methods. Regulatory and legislative assist is important to ascertain strong pharmacovigilance methods for natural prescriptions, together with real-time monitoring, reporting, and danger mitigation mechanisms. Moreover, future research ought to deal with the protection profiles of particular herbs, significantly their results on weak populations, akin to people with pre-existing liver situations or these utilizing concurrent drugs, to handle current data gaps and improve the protected use of natural medicines in scientific observe.
In conclusion, this examine highlights a big affiliation between industrial medication and DILI incidence, whereas confirming that natural medicines prescribed by TKM medical doctors have minimal influence on DILI danger. These findings contribute to our understanding of the DILI dangers related to natural drugs, significantly by emphasizing the heightened vulnerability of sufferers with liver illnesses. Furthermore, they underscore the need for additional analysis into the danger components underlying DILI improvement. Moreover, there’s an pressing demand to evaluate the hepatotoxicity danger posed by unregulated natural merchandise compared to natural medicines prescribed inside medical establishments.
Information availability assertion
Publicly accessible datasets have been analyzed on this examine. This knowledge will be discovered right here: HIRA database. Entry to and use of the HIRA database have been licensed by HIRA by way of a remote-controlled desktop (Approval Quantity: HIRA M20200924766).
Ethics assertion
The research involving people have been accredited by Institutional Assessment Board of Dankook College (Approval Quantity: DKU 2020-09-001). The research have been carried out in accordance with the native laws and institutional necessities. Written knowledgeable consent for participation was not required from the contributors or the contributors’ authorized guardians/subsequent of kin in accordance with the nationwide laws and institutional necessities.
Writer contributions
TY: Writing–unique draft, Formal Evaluation, Methodology. JA: Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing–evaluate and enhancing. SW: Supervision, Writing–evaluate and enhancing. SL: Conceptualization, Information curation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–unique draft.
Funding
The creator(s) declare that monetary assist was obtained for the analysis, authorship, and/or publication of this text. This analysis was supported by a grant of the Korea Well being Expertise R&D Challenge by way of the Korea Well being Trade Improvement Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Well being and Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant quantity: HF20C0172 and RS-2023-KH139182).
Battle of curiosity
Writer SW was employed by RexSoft Inc.
The remaining authors declare that the analysis was carried out within the absence of any industrial or monetary relationships that could possibly be construed as a possible battle of curiosity.
Writer’s word
All claims expressed on this article are solely these of the authors and don’t essentially signify these of their affiliated organizations, or these of the writer, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that could be evaluated on this article, or declare that could be made by its producer, just isn’t assured or endorsed by the writer.
Supplementary materials
The Supplementary Materials for this text will be discovered on-line at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1498124/full#supplementary-material
References
Brauer, R., Ruigomez, A., Klungel, O., Reynolds, R., Feudjo Tepie, M., Smeeth, L., et al. (2016). The chance of acute liver damage amongst customers of antibiotic drugs: a comparability of case-only research. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 25 (Suppl. 1), 39–46. doi:10.1002/pds.3846
Cho, J. H., Oh, D. S., Hong, S. H., Ko, H., Lee, N. H., Park, S. E., et al. (2017). A nationwide examine of the incidence fee of herb-induced liver damage in Korea. Arch. Toxicol. 91, 4009–4015. doi:10.1007/s00204-017-2007-9
Farrington, P., Whitaker, H., and Ghebremichael-Weldeselassie, Y. (2018). Self-controlled case sequence research: a modelling Information with R.
Hong, M., Li, S., Tan, H. Y., Cheung, F., Wang, N., Huang, J., et al. (2017). A network-based pharmacology examine of the herb-induced liver damage potential of conventional hepatoprotective Chinese language natural medicines. Molecules 22, 632. doi:10.3390/molecules22040632
Huang, Y. S., Chang, T. T., Peng, C. Y., Lo, G. H., Hsu, C. W., Hu, C. T., et al. (2021). Natural and dietary supplement-induced liver damage in Taiwan: comparability with standard drug-induced liver damage. Hepatol. Int. 15, 1456–1465. doi:10.1007/s12072-021-10241-3
Kim, D. J., Ahn, B. M., Choe, S. G., Son, J. H., Website positioning, J. I., and Park, S. H. (2003). A preliminary multicenter examine for the detection of poisonous hepatitis induced by varied plant preparations and wholesome meals and the event of nationwide reporting system of poisonous hepatitis. Seoul: Nationwide Institute of Toxicological Analysis.
Kim, J.-A., Yoon, S., Kim, L.-Y., and Kim, D.-S. (2017). In the direction of actualizing the worth potential of Korea medical insurance evaluate and evaluation (HIRA) knowledge as a useful resource for well being analysis: strengths, limitations, functions, and techniques for optimum use of HIRA knowledge. J. Korean Med. Sci. 32, 718–728. doi:10.3346/jkms.2017.32.5.718
Kwon, H., Lee, S. H., Kim, S. E., Lee, J. H., Jee, Y. Okay., Kang, H. R., et al. (2012). Spontaneously reported hepatic adversarial drug occasions in Korea: multicenter examine. J. Korean Med. Sci. 27, 268–273. doi:10.3346/jkms.2012.27.3.268
Lee, A. R., Yim, J. M., and Kim, W. I. (2012a). Affect of prescribed natural and Western drugs on sufferers with irregular liver perform checks: a retrospective quasi-experimental examine. J. Pharmacopuncture 15, 34–39. doi:10.3831/KPI.2012.15.1.034
Lee, C. H., Wang, J. D., and Chen, P. C.Well being Information Evaluation in Taiwan Analysis Group (2012b). Case-crossover design: another technique for detecting drug-induced liver damage. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 65, 560–567. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.11.002
Lee, J., Shin, J. S., Kim, M. R., Byun, J. H., Lee, S. Y., Shin, Y. S., et al. (2015). Liver enzyme abnormalities in taking conventional natural drugs in Korea: a retrospective massive pattern cohort examine of musculoskeletal dysfunction sufferers. J. Ethnopharmacol. 169, 407–412. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.04.048
Lee, J., Shin, J. S., Lee, Y. J., Kim, M. R., Shin, B. C., Lee, J. H., et al. (2019). Battle over herb-induced liver damage: low prevalence confirmed by way of secondary analysis and analysis crew’s clarifying rebuttal to unwarranted public claims. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 25, 260–264. doi:10.1089/acm.2018.0253
Mostofsky, E., Coull, B. A., and Mittleman, M. A. (2018). Evaluation of observational self-matched knowledge to look at acute triggers of end result occasions with abrupt onset. Epidemiology 29, 804–816. doi:10.1097/EDE.0000000000000904
Petersen, I., Douglas, I., and Whitaker, H. (2016). Self managed case sequence strategies: a substitute for commonplace epidemiological examine designs. BMJ 354, i4515. doi:10.1136/bmj.i4515
Actual, M., Barnhill, M. S., Higley, C., Rosenberg, J., and Lewis, J. H. (2019). Drug-induced liver damage: highlights of the latest literature. Drug Saf. 42, 365–387. doi:10.1007/s40264-018-0743-2
Roussel Uclaf Causality Evaluation Technique (RUCAM) in Drug Induced Liver Harm (2012). in LiverTox: scientific and analysis info on drug-induced liver damage (Bethesda (MD)).
Shen, T., Liu, Y., Shang, J., Xie, Q., Li, J., Yan, M., et al. (2019). Incidence and etiology of drug-induced liver damage in mainland China. Gastroenterology 156, 2230–2241.e11. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.002
Shin, Y. S., Lee, Y. W., Choi, Y. H., Park, B., Jee, Y. Okay., Choi, S. Okay., et al. (2009). Spontaneous reporting of adversarial drug occasions by Korean regional pharmacovigilance facilities. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 18, 910–915. doi:10.1002/pds.1796
Sobhonslidsuk, A., Poovorawan, Okay., Soonthornworasiri, N., Pan-Ngum, W., and Phaosawasdi, Okay. (2016). The incidence, presentation, outcomes, danger of mortality and financial knowledge of drug-induced liver damage from a nationwide database in Thailand: a population-base examine. BMC Gastroenterol. 16, 135. doi:10.1186/s12876-016-0550-0
Suk, Okay. T., Kim, D. J., Kim, C. H., Park, S. H., Yoon, J. H., Kim, Y. S., et al. (2012). A potential nationwide examine of drug-induced liver damage in Korea. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 107, 1380–1387. doi:10.1038/ajg.2012.138
Takeuchi, Y., Shinozaki, T., and Matsuyama, Y. (2018). A comparability of estimators from self-controlled case sequence, case-crossover design, and sequence symmetry evaluation for pharmacoepidemiological research. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 18, 4. doi:10.1186/s12874-017-0457-7
Yoo, T. W., Kim, B.Ik, Kim, J. B., Kim, D. J., Kim, J. W., Baik, S. Okay., et al. (2007). The survey for the precise situation of drug remedy and improvement of well being care value related to poisonous liver damage in Korean: a multicenter examine for the detection and the event of nationwide reporting system of poisonous liver damage. Clin. Mol. Hepatology 13, 34–43.