Conny Waters – AncientPages.com – Researchers have performed an evaluation of human stays from the Oakhurst rock shelter in southernmost Africa, efficiently reconstructing the genomes of 13 people who lived between 1,300 and 10,000 years in the past.
Rock artwork at Oakhurst rock shelter, Oakhurst farm, close to Hoekwil, South Africa. Credit score: V. Gibbon
This examine consists of the oldest human genome from South Africa recognized so far.
A workforce included researchers from the College of Cape City (South Africa) and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig (Germany)
“Oakhurst rock shelter is a perfect web site to review human historical past, because it contained greater than 40 human graves and preserved layers of human artefacts, reminiscent of stone instruments, going again 12,000 years,” says Victoria Gibbon, Professor of Organic Anthropology on the College of Cape City and co-senior writer of the examine.
“Websites like this are uncommon in South Africa, and Oakhurst has allowed a greater understanding of native inhabitants actions and relationships throughout the panorama over almost 9,000 years.”
Lengthy historical past of genetic stability in southernmost Africa
The profitable genetic sequencing of 13 people from the positioning was not with out its challenges, as Stephan Schiffels, co-senior writer of the examine, explains:
“Such historic and poorly preserved DNA is sort of tough to sequence, and it took a number of makes an attempt utilizing totally different applied sciences and laboratory protocols to extract and course of the DNA.”
The traditional genomes symbolize a time sequence from 10,000 to 1,300 years in the past, offering a singular alternative to review human migrations by means of time and the connection to the various teams of individuals residing within the area at present.
A key discovering was that the oldest genomes from the Oakhurst rock shelter are genetically fairly just like San and Khoekhoe teams residing in the identical area at present.
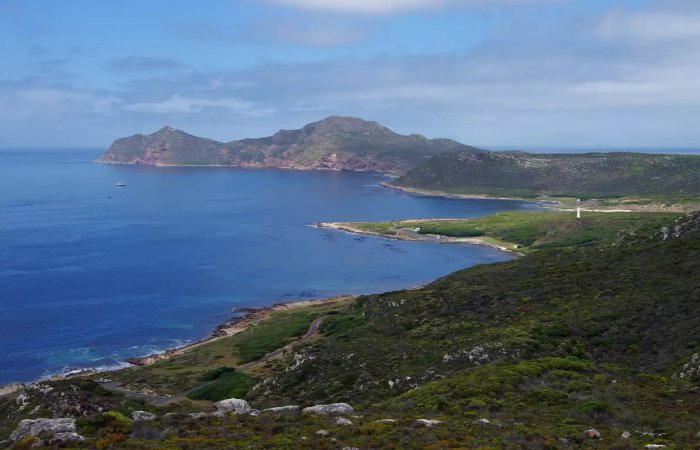
Cape Level promontory, Cape Level Nature reserve, South Africa. Picture credit score: © R. Gibbon
Joscha Gretzinger, lead writer of the examine, mentioned “comparable research from Europe have revealed a historical past of large-scale genetic adjustments attributable to human actions over the past 10,000 years. These new outcomes from southernmost Africa are fairly totally different, and recommend an extended historical past of relative genetic stability.”
This solely modified round 1,200 years in the past, when newcomers arrived and launched pastoralism, agriculture and new languages to the area and commenced interacting with native hunter-gatherer teams.
In one of the vital culturally, linguistically and genetically numerous areas of the world, the brand new examine reveals that South Africa’s wealthy archaeological report is turning into more and more accessible to archaeogenetics, offering new insights into human historical past and previous demography.
Paper
Joscha Gretzinger et al, 9,000 years of genetic continuity in southernmost Africa demonstrated at Oakhurst rockshelter, Nature Ecology & Evolution (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41559-024-02532-3
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Employees Author